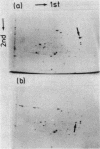
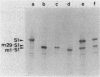
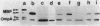Abstract
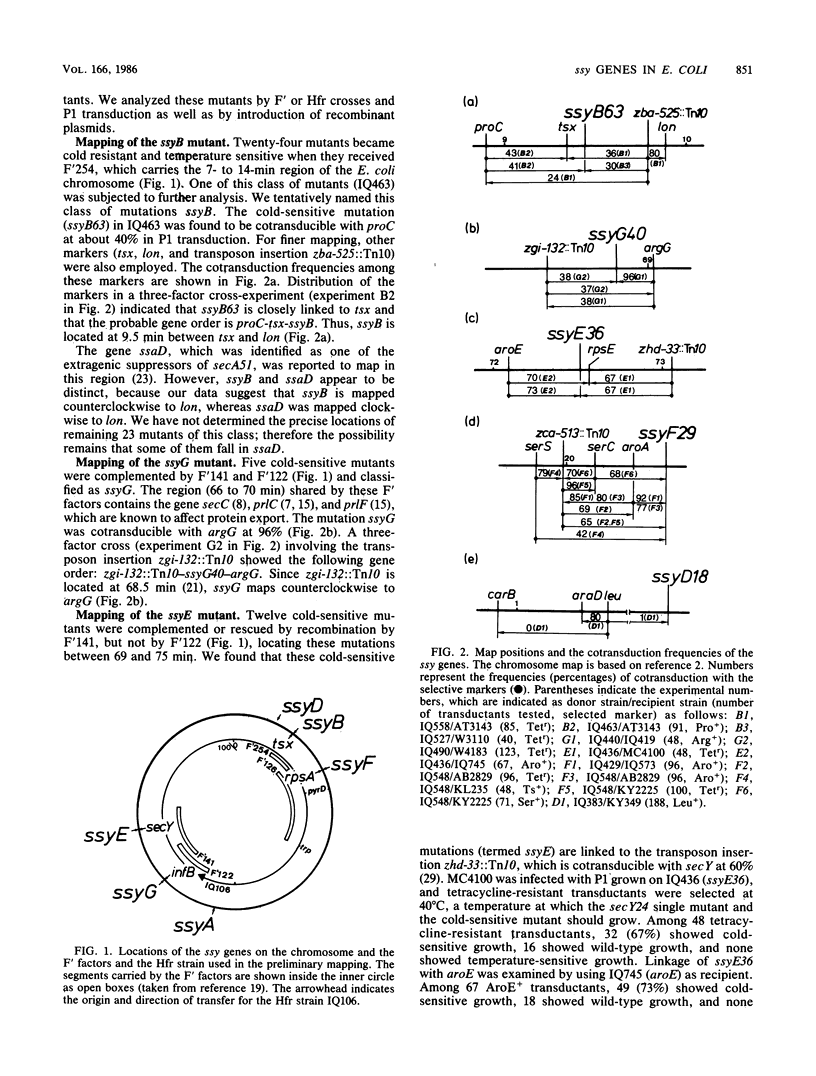
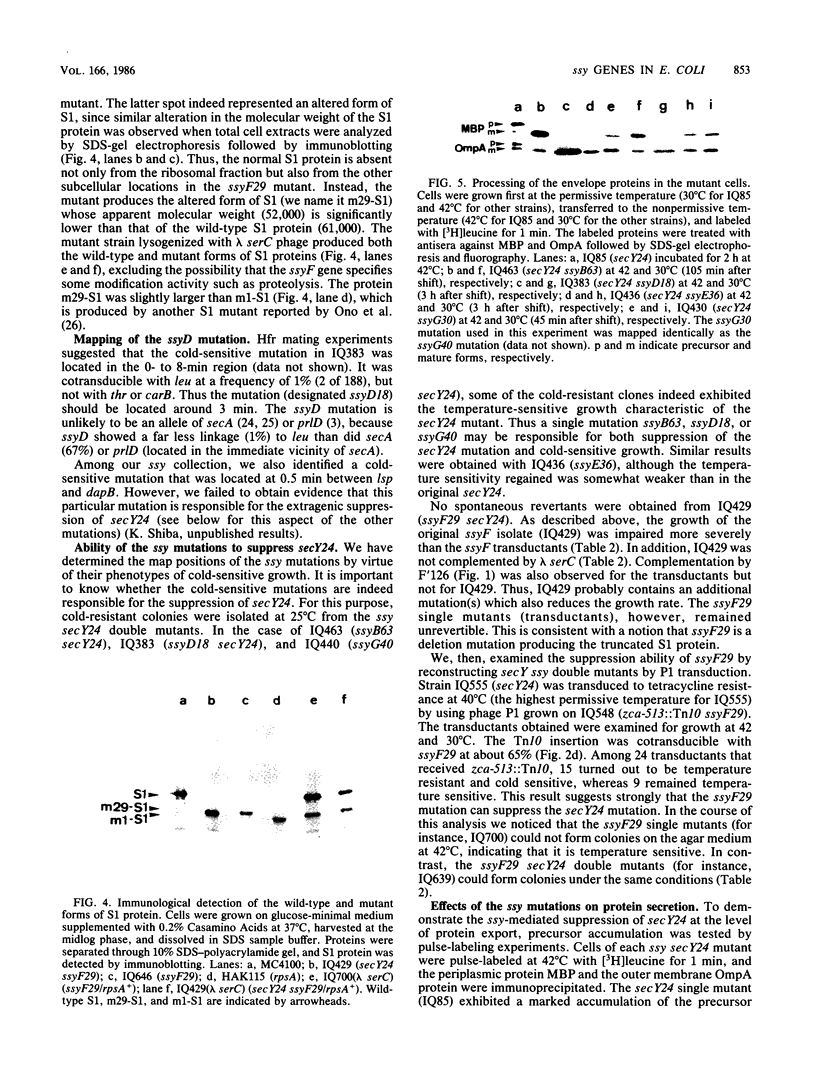
We previously reported (Shiba et al., J. Bacteriol. 160:696-701, 1984) the isolation and characterization of the mutation (ssy) that suppresses the protein export defect due to the secY24(Ts) mutation and causes cold-sensitive growth of Escherichia coli. This report describes more systematic isolation of ssy mutations. Among temperature-resistant revertants of the secY24 mutant, 65 mutants were found to be cold sensitive. These cold-sensitive mutations have been classified by genetic mapping. Twenty-two mutations fell into the ssyA class previously described. The remaining mutations were located at five new loci: ssyB at 9.5 min between tsx and lon; ssyD around 3 min; ssyE at 72.5 min near secY; ssyF at 20.5 min within rpsA; and ssyG at 69.0 min near argG. Two predominant classes, ssyA and ssyB, are probably affected in protein synthesis at the elongation step, whereas the ssyF mutant contained an altered form of ribosomal protein S1 (the gene product of rpsA). These cold-sensitive ssy mutations which suppress secY24 may define genes whose function is somehow involved in the secY-dependent protein secretion mechanism. However, the existence of multiple suppressor loci makes it unlikely that all of these genes specify additional components of the export machinery. A delicate balance may exist between the systems for synthesizing and exporting proteins.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama Y., Ito K. The SecY membrane component of the bacterial protein export machinery: analysis by new electrophoretic methods for integral membrane proteins. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3351–3356. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04088.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 7. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Jun;47(2):180–230. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.2.180-230.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brickman E. R., Oliver D. B., Garwin J. L., Kumamoto C., Beckwith J. The use of extragenic suppressors to define genes involved in protein export in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(1):24–27. doi: 10.1007/BF00334087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Carbon J. A colony bank containing synthetic Col El hybrid plasmids representative of the entire E. coli genome. Cell. 1976 Sep;9(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferro-Novick S., Honma M., Beckwith J. The product of gene secC is involved in the synthesis of exported proteins in E. coli. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90542-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geyl D., Böck A., Isono K. An improved method for two-dimensional gel-electrophoresis: analysis of mutationally altered ribosomal proteins of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;181(3):309–312. doi: 10.1007/BF00425603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Cerretti D. P., Nashimoto H., Nomura M. Characterization of an amber mutation in the structural gene for ribosomal protein L15, which impairs the expression of the protein export gene, secY, in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2319–2324. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02133.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K. Identification of the secY (prlA) gene product involved in protein export in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):204–208. doi: 10.1007/BF00330964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Wittekind M., Nomura M., Shiba K., Yura T., Miura A., Nashimoto H. A temperature-sensitive mutant of E. coli exhibiting slow processing of exported proteins. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):789–797. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90065-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvik J., Botstein D. Conditional-lethal mutations that suppress genetic defects in morphogenesis by altering structural proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2738–2742. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaskunas S. R., Lindahl L., Nomura M. Specialized transducing phages for ribosomal protein genes of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):6–10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiino D. R., Silhavy T. J. Mutation prlF1 relieves the lethality associated with export of beta-galactosidase hybrid proteins in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):878–883. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.878-883.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitakawa M., Blumenthal L., Isono K. Isolation and characterization of specialized transducing lambda phages carrying ribosomal protein genes of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;180(2):343–349. doi: 10.1007/BF00425846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N., Barker D. F., Ross D. G., Botstein D. Properties of the translocatable tetracycline-resistance element Tn10 in Escherichia coli and bacteriophage lambda. Genetics. 1978 Nov;90(3):427–461. doi: 10.1093/genetics/90.3.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumamoto C. A., Beckwith J. Mutations in a new gene, secB, cause defective protein localization in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):253–260. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.253-260.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low K. B. Escherichia coli K-12 F-prime factors, old and new. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):587–607. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.587-607.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Uchida H. Isolation of conditionally lethal amber mutations affecting synthesis of the nusA protein of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;190(2):196–203. doi: 10.1007/BF00330640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. B., Beckwith J. E. coli mutant pleiotropically defective in the export of secreted proteins. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):765–772. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90184-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. B., Beckwith J. Identification of a new gene (secA) and gene product involved in the secretion of envelope proteins in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):686–691. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.686-691.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. B. Identification of five new essential genes involved in the synthesis of a secreted protein in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):285–291. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.285-291.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono M., Kuwano M., Mizushima S. Genetic analysis of a mutation affecting ribosomal protein S1 in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jul 2;174(1):11–15. doi: 10.1007/BF00433299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnier J., Isono K. The DNA sequence of the gene rpsA of Escherichia coli coding for ribosomal protein S1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 25;10(6):1857–1865. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.6.1857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiba K., Ito K., Yura T., Cerretti D. P. A defined mutation in the protein export gene within the spc ribosomal protein operon of Escherichia coli: isolation and characterization of a new temperature-sensitive secY mutant. EMBO J. 1984 Mar;3(3):631–635. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01859.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiba K., Ito K., Yura T. Mutation that suppresses the protein export defect of the secY mutation and causes cold-sensitive growth of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):696–701. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.696-701.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shultz J., Silhavy T. J., Berman M. L., Fiil N., Emr S. D. A previously unidentified gene in the spc operon of Escherichia coli K12 specifies a component of the protein export machinery. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):227–235. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90422-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian A. R. Structure and functions of ribosomal protein S1. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1983;28:101–142. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60085-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe P. B., Rice M., Wickner W. Effects of two sec genes on protein assembly into the plasma membrane of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1836–1841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagata H., Dombou M., Sato T., Mizushima S., Uchida H. Deletion mapping and heterogenote analysis of a mutation responsible for osmosis-sensitive growth, spectinomycin resistance, and alteration of cytoplasmic membrane in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):661–667. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.661-667.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]