Abstract
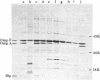
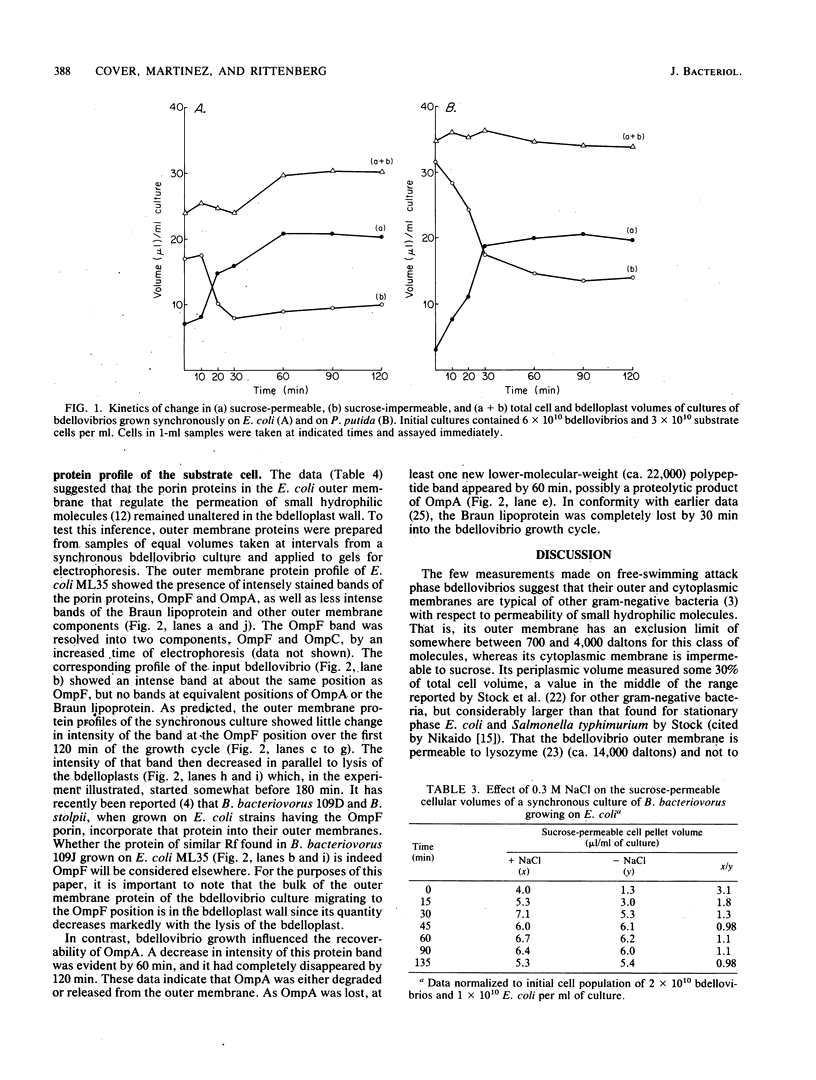
Measurements of the sucrose-permeable and -impermeable volumes during Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus attack on Escherichia coli or Pseudomonas putida showed that the volume of the bdelloplast increased over that of the substrate cell. Although the pattern of the increase differed with the two organisms, the volumes reached maximum at about 60 min into the bdellovibrio growth cycle. By this time, the cytoplasmic membranes of the attacked cells were completely permeable to sucrose. The kinetics of increase in sucrosepermeable volumes were similar to the kinetics of attachment and penetration (Varon and Shilo, J. Bacteriol. 95:744-753, 1968). These data show that the original cytoplasmic and periplasmic compartmentalization of the substrate cell ceases to exist with respect to small hydrophilic molecules during bdellovibrio attack. In contrast, the effective pore size of the outer membrane of the substrate cell to small oligosaccharides remains unaltered during bdelloplast formation as was shown by direct measurements of its exclusion limits. The major porin protein of E. coli, OmpF, was recoverable from the bdelloplast outer membrane fraction until the onset of lysis. The Braun lipoprotein was removed from the bdelloplast wall early, and OmpA was lost in the terminal part of the bdellovibrio growth cycle.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braun V., Rehn K. Chemical characterization, spatial distribution and function of a lipoprotein (murein-lipoprotein) of the E. coli cell wall. The specific effect of trypsin on the membrane structure. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Oct;10(3):426–438. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00707.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cover W. H., Rittenberg S. C. Change in the surface hydrophobicity of substrate cells during bdelloplast formation by Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus 109J. J Bacteriol. 1984 Feb;157(2):391–397. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.2.391-397.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decad G. M., Nikaido H. Outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria. XII. Molecular-sieving function of cell wall. J Bacteriol. 1976 Oct;128(1):325–336. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.1.325-336.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diedrich D. L., Summers A. O., Schnaitman C. A. Outer membrane proteins of Escherichia coli. V. Evidence that protein 1 and bacteriophage-directed protein 2 are different polypeptides. J Bacteriol. 1977 Aug;131(2):598–607. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.2.598-607.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galdiero F. Membrane damage and incorporation of Escherichia coli components into Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1975;230(2):203–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Nikaido H. Outer membranes of gram-negative bacteria. XIX. Isolation from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 and use in reconstitution and definition of the permeability barrier. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):381–390. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.381-390.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hespell R. B., Miozzari G. F., Rittenberg S. C. Ribonucleic acid destruction and synthesis during intraperiplasmic growth of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1975 Aug;123(2):481–491. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.2.481-491.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakae T., Nikaido H. Outer membrane as a diffusion barrier in Salmonella typhimurium. Penetration of oligo- and polysaccharides into isolated outer membrane vesicles and cells with degraded peptidoglycan layer. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 25;250(18):7359–7365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakae T. Outer membrane of Salmonella. Isolation of protein complex that produces transmembrane channels. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):2176–2178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. R., Rittenberg S. C. Incorporation of substrate cell lipid A components into the lipopolysaccharide of intraperiplasmically grown Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):860–868. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.860-868.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Wu H. C. Proteins of the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:369–422. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.002101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenberg S. C., Hespell R. B. Energy efficiency of intraperiplasmic growth of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):1158–1165. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.1158-1165.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenberg S. C., Langley D. Utilization of nucleoside monophosphates per Se for intraperiplasmic growth of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):1137–1144. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.1137-1144.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenberg S. C., Shilo M. Early host damage in the infection cycle of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1970 Apr;102(1):149–160. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.1.149-160.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruby E. G., Rittenberg S. C. Differentiation after premature release of intraperiplasmically growing Bdellovibrio bacteriovorous. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):32–40. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.32-40.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Rauch B., Roseman S. Periplasmic space in Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7850–7861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomashow M. F., Rittenberg S. C. Intraperiplasmic growth of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus 109J: N-deacetylation of Escherichia coli peptidoglycan amino sugars. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):1008–1014. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.1008-1014.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomashow M. F., Rittenberg S. C. Intraperiplasmic growth of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus 109J: attachment of long-chain fatty acids to escherichia coli peptidoglycan. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):1015–1023. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.1015-1023.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomashow M. F., Rittenberg S. C. Intraperiplasmic growth of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus 109J: solubilization of Escherichia coli peptidoglycan. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):998–1007. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.998-1007.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomashow M. F., Rittenberg S. C. Penicillin-induced formation of osmotically stable spheroplasts in nongrowing Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1484–1491. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1484-1491.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varon M., Shil M. Interacton of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus and host bacteria. I. Kinetic studies of attachment and invasion of Escherichia coli B by Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):744–753. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.744-753.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]