Abstract
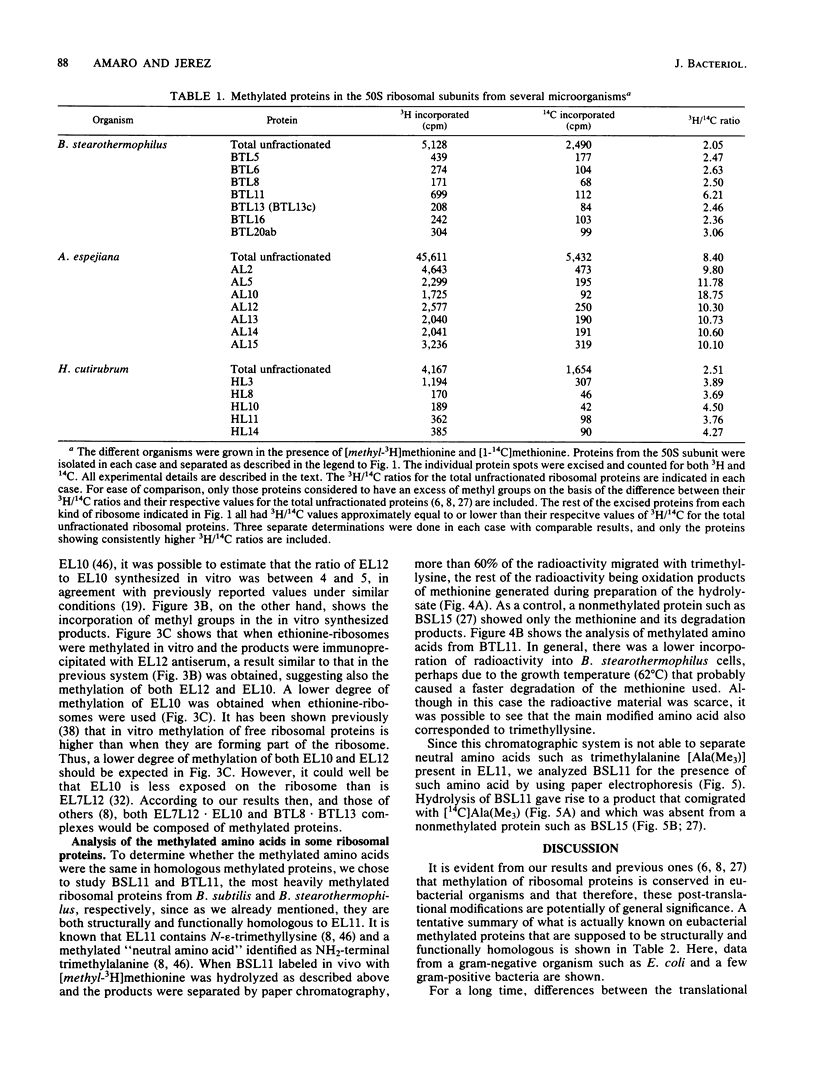
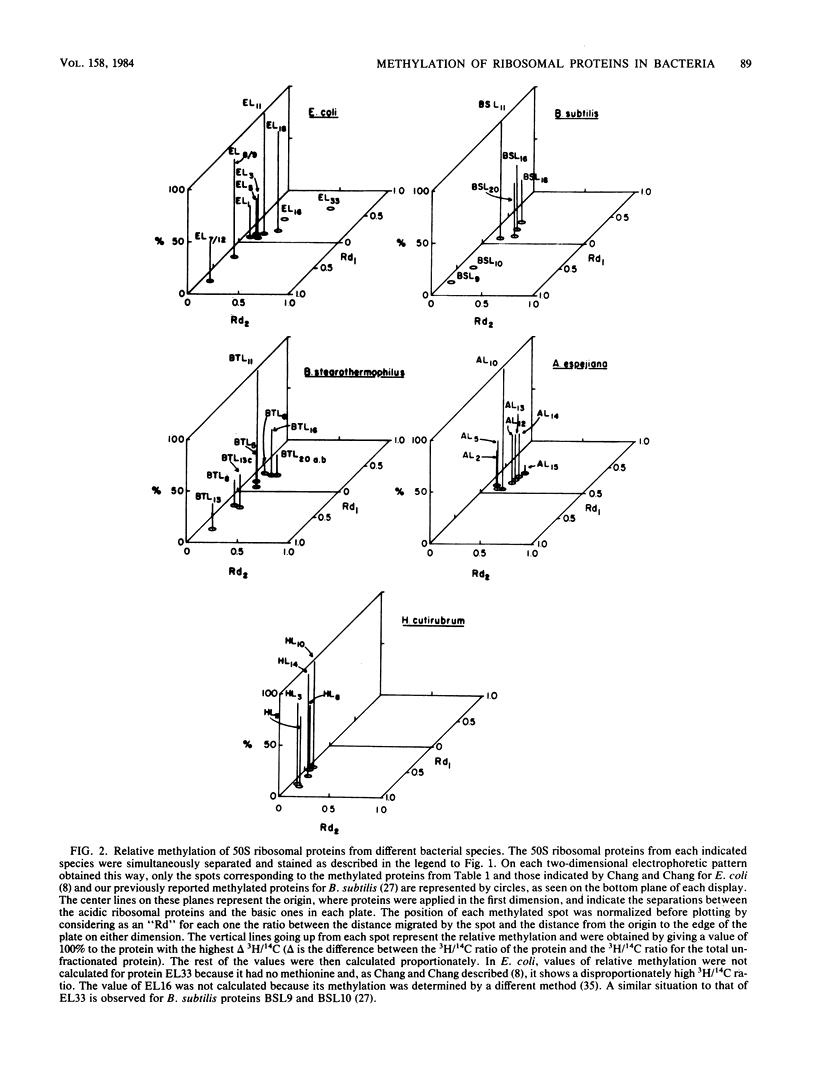
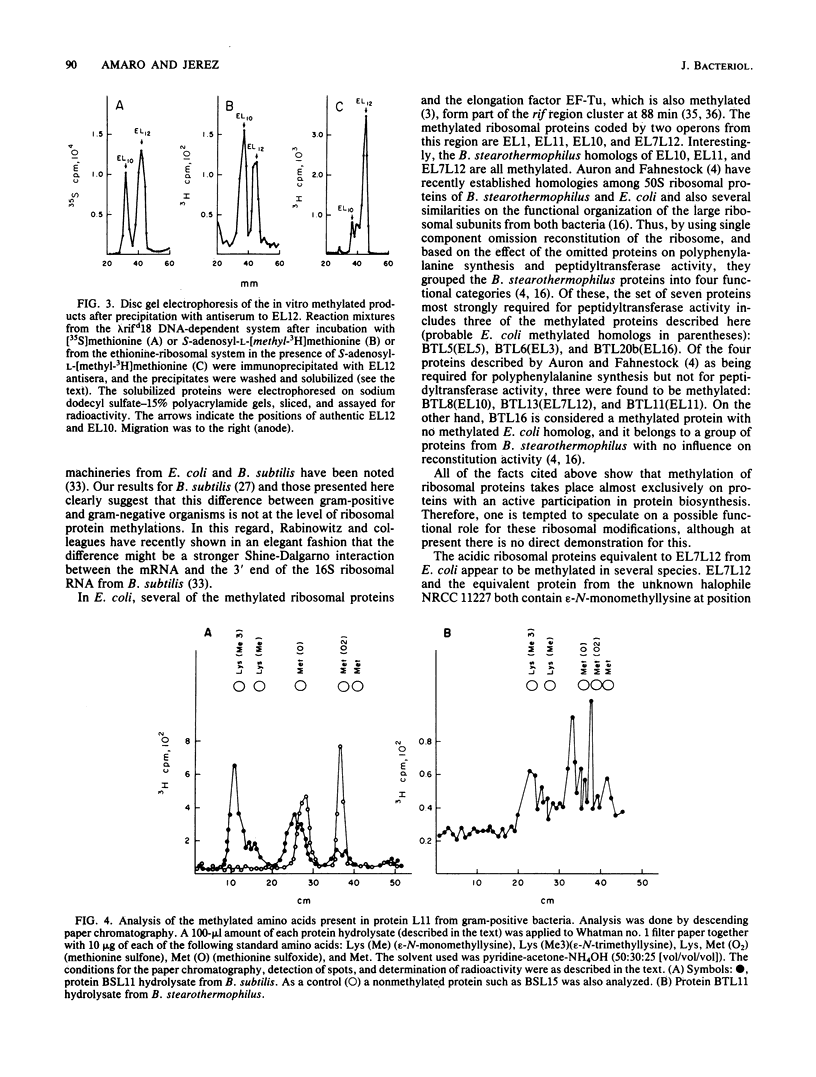
Methylation of the 50S ribosomal proteins from Bacillus stearothermophilus, Bacillus subtilis, Alteromonas espejiana, and Halobacterium cutirubrum was measured after the cells were grown in the presence of [1-14C]methionine or [methyl-3H]methionine or both. Two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoretic analysis revealed, in general, similar relative electrophoretic mobilities of the methylated proteins from each eubacterium studied. Proteins known to be structurally and functionally homologous in several microorganisms were all methylated. Thus, the following group of proteins, which appear to be involved in peptidyltransferase or in polyphenylalanine-synthesizing activity in B. stearothermophilus (P.E. Auron and S. R. Fahnestock, J. Biol. Chem. 256:10105-10110, 1981), were methylated (possible Escherichia coli methylated homologs are indicated in parentheses): BTL5(EL5), BTL6(EL3), BTL8(EL10), BTL11(EL11), BTL13(EL7L12) and BTL20b(EL16). In addition, the pentameric ribosomal complex BTL13 X BTL8, analogous to the complex EL7L12 X EL10 of E. coli, contained methylated proteins. Analysis of the methylated amino acids in the most heavily methylated proteins, BSL11 from B. subtilis and BTL11 from B. stearothermophilus, showed the presence of epsilon-N-trimethyllysine as the major methylated amino acid in both proteins, in agreement with known data for E. coli. In addition, BSL11 appeared to contain trimethylalanine, a characteristic, modified amino acid previously described only in EL11 from E. coli. These results and those previously obtained from other bacteria indicate a high degree of conservation for ribosomal protein methylation and suggest an important, albeit unknown, role for the modification of these components in eubacterial ribosomes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alix J. H., Hayes D., Nierhaus K. H. Properties of ribosomes and RNA synthesized by Escherichia coli grown in the presence of ethionine. V. Methylation dependence on the assembly of E. coli 50 S ribosomal subunits. J Mol Biol. 1979 Feb 5;127(4):375–395. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90228-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alix J. H. Molecular aspects of the in vivo and in vitro effects of ethionine, an analog of methionine. Microbiol Rev. 1982 Sep;46(3):281–295. doi: 10.1128/mr.46.3.281-295.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F., Niakido K. In vivo methylation of prokaryotic elongation factor Tu. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):9947–9950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auron P. E., Fahnestock S. R. Functional organization of the large ribosomal subunit of Bacillus stearothermophilus. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 10;256(19):10105–10110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartsch M., Kimura M., Subramanian A. R. Purification, primary structure, and homology relationships of a chloroplast ribosomal protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6871–6875. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon M., Cundliffe E. Methylation of basic proteins in ribosomes from wild-type and thiostrepton-resistant strains of Bacillus megaterium and their electrophoretic analysis. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jul;97(2):541–545. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13142.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. N., Chang F. N. Methylation of ribosomal proteins in vitro. Nature. 1974 Oct 25;251(5477):731–733. doi: 10.1038/251731a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. N., Chang N. Methylation of the ribosomal proteins in Escherichia coli. Nature and stoichiometry of the methylated amino acids in 50S ribosomal proteins. Biochemistry. 1975 Feb 11;14(3):468–477. doi: 10.1021/bi00674a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F. N. Temperature-dependent variation in the extent of methylation of ribosomal proteins L7 and L12 in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):1165–1166. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.1165-1166.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu F., Caldwell P., Samuels M., Weissbach H., Brot N. DNA-dependent in vitro synthesis of Escherichia coli ribosomal protein L10 and the formation of an L10L12 complex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 May 23;76(2):593–601. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90765-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohlberg J. A., Nomura M. Reconstitution of Bacillus stearothermophilus 50 S ribosomal subunits from purified molecular components. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 10;251(1):209–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colson C., Lhoest J., Urlings C. Genetics of ribosomal protein methylation in Escherichia coli. III. Map position of two genes, prmA and prmB, governing methylation of proteins L11 and L3. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Feb 1;169(3):245–250. doi: 10.1007/BF00382270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cundliffe E., Dixon P., Stark M., Stöffler G., Ehrlich R., Stöffler-Meilicke M., Cannon M. Ribosomes in thiostrepton-resistant mutants of Bacillus megaterium lacking a single 50 S subunit protein. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 5;132(2):235–252. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90393-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espejo R. T., Canelo E. S. Properties of bacteriophage PM2: a lipid-containing bacterial virus. Virology. 1968 Apr;34(4):738–747. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90094-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahnestock S. R., Strycharz W. A., Marquis D. M. Immunochemical evidence of homologies among 50 S ribosomal proteins of Bacillus stearothermophilus and Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 10;256(19):10111–10116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahnestock S., Erdmann V., Nomura M. Reconstitution of 50 S ribosomal subunits from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Methods Enzymol. 1974;30:554–562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin R. M., Salditt M., Silbert J. A. Structure and synthesis of a lipid-containing bacteriophage. I. Growth of bacteriophage PM2 and alterations in nucleic acid metabolism in the infected cell. Virology. 1969 Aug;38(4):627–640. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90182-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisser M., Tischendorf G. W., Stöffler G. Comparative immunological and electrophoretic studies on ribosomal proteins of bacillaceae. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Dec 20;127(2):129–145. doi: 10.1007/BF00333661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg G., Caldwell P., Weissbach H., Brot N. In vitro regulation of DNA-dependent synthesis of Escherichia coli ribosomal protein L12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1716–1720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guha S., Szulmajster J. Isolation of 30S and 50S active ribosomal subunits of Bacillus subtilis, Marburg strain. J Bacteriol. 1975 Dec;124(3):1062–1066. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.3.1062-1066.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy S. J., Kurland C. G., Voynow P., Mora G. The ribosomal proteins of Escherichia coli. I. Purification of the 30S ribosomal proteins. Biochemistry. 1969 Jul;8(7):2897–2905. doi: 10.1021/bi00835a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higo K., Held W., Kahan L., Nomura M. Functional correspondence between 30S ribosomal proteins of Escherichia coli and Bacillus stearothermophilus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):944–948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerez C. A., Mardones E., Amaro A. M. Alteration of the acidic ribosomal proteins from dormant spores of Bacillus subtilis. FEBS Lett. 1976 Sep 1;67(3):276–280. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80546-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerez C., Weissbach H. Methylation of newly synthesized ribosomal protein L11 in a DNA-directed in vitro system. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8706–8710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltschmidt E., Wittmann H. G. Ribosomal proteins. XII. Number of proteins in small and large ribosomal subunits of Escherichia coli as determined by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1276–1282. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legault-Demare L., Chambliss G. H. Natural messenger ribonucleic acid-directed cell-free protein-synthesizing system of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1300–1307. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1300-1307.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mardones E., Amaro A. M., Jerez C. A. Methylation of ribosomal proteins in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1980 Apr;142(1):355–358. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.1.355-358.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquis D., Fahnestock S. R. A complex of acidic ribosomal proteins. Evidence of a four-to-one complex of proteins in the Bacillus stearothermophilus ribosome. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 15;119(4):557–567. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90202-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray C. L., Rabinowitz J. C. Nucleotide sequences of transcription and translation initiation regions in Bacillus phage phi 29 early genes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):1053–1062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möller W., Schrier P. I., Maassen J. A., Zantema A., Schop E., Reinalda H., Cremers A. F., Mellema J. E. Ribosomal proteins L7/L12 of Escherichia coli. Localization and possible molecular mechanism in translation. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 5;163(4):553–573. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90112-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nierhaus K. H. Structure, assembly, and function of ribosomes. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1982;97:81–155. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68318-3_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ONISHI H., MCCANCE E., GIBBONS N. E. A SYNTHETIC MEDIUM FOR EXTREMELY HALOPHILIC BACTERIA. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Apr;11:365–373. doi: 10.1139/m65-044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson I., Hardy S. J., Liljas A. The ribosomal protein L8 is a complex L7/L12 and L10. FEBS Lett. 1976 Apr 15;64(1):135–138. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80267-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe J. J., Goldberg I. D., Amelunxen R. E. Development of defined and minimal media for the growth of Bacillus stearothermophilus. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):279–284. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.279-284.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEHGAL S. N., GIBBONS N. E. Effect of some metal ions on the growth of Halobacterium cutirubrum. Can J Microbiol. 1960 Apr;6:165–169. doi: 10.1139/m60-018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith N., Matheson A. T., Yaguchi M., Willick G. E., Nazar R. N. The 5-S RNA . protein complex from an extreme halophile, Halobacterium cutirubrum. Purification and characterization. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Sep 1;89(2):501–509. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12554.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strom A. R., Visentin L. P. Acidic ribosomal proteins from the extreme halophile, Halobacterium cutirubrum. The simultaneous separation, identification and molecular weight determination. FEBS Lett. 1973 Dec 1;37(2):274–280. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80477-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöffler G., Cundliffe E., Stöffler-Meilicke M., Dabbs E. R. Mutants of Escherichia coli lacking ribosomal protein L11. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10517–10522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visentin L. P., Chow C., Matheson A. T., Yaguchi M., Rollin F. Halobacterium cutirubrum ribosomes. Properties of the ribosomal proteins and ribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1972 Nov;130(1):103–110. doi: 10.1042/bj1300103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wienen B., Ehrlich R., Stöffler-Meilicke M., Stöffler G., Smith I., Weiss D., Vince R., Pestka S. Ribosomal protein alterations in thiostrepton- and Micrococcin-resistant mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):8031–8041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittmann H. G. Components of bacterial ribosomes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:155–183. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.001103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Fox G. E. Phylogenetic structure of the prokaryotic domain: the primary kingdoms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5088–5090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]