Abstract
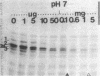
Methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus has been associated with alterations in the penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs). An intriguing property of all methicillin-resistant staphylococci is the dependence of resistance on the pH value of the growth medium. Growth of such bacteria at pH 5.2 completely suppressed the expression of methicillin resistance. We have examined the PBP patterns of methicillin-resistant staphylococci grown at pH 7.0. We detected a high-molecular-weight PBP (PBP-2a; approximate size, 78,000 daltons) that was only present in the resistant bacteria but not in the isogenic sensitive strain. In cultures grown at pH 5.2, the extra PBP was not detectable.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. F., Reynolds P. E. Intrinsic resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics in Staphylococcus aureus. FEBS Lett. 1980 Dec 29;122(2):275–278. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80455-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan C. E., Strominger J. L. Altered penicillin-binding components in penicillin-resistant mutants of Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1816–1820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty T. J., Koller A. E., Tomasz A. Penicillin-binding proteins of penicillin-susceptible and intrinsically resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):730–737. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana R., Cerini R., Longoni P., Grossato A., Canepari P. Identification of a streptococcal penicillin-binding protein that reacts very slowly with penicillin. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1343–1350. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1343-1350.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopapadakou N. H., Smith S. A., Bonner D. P. Penicillin-binding proteins in a Staphylococcus aureus strain resistant to specific beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jul;22(1):172–175. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.1.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman B., Tomasz A. Altered penicillin-binding proteins in methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 May;19(5):726–735. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.5.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D., Nuchamowitz Y., Rubinstein E. Insensitivity of peptidoglycan biosynthetic reactions to beta-lactam antibiotics in a clinical isolate of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 May;19(5):687–695. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.5.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D. Chemical and physical factors influencing methicillin resistance of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1977 Nov;3 (Suppl 100):47–51. doi: 10.1093/jac/3.suppl_c.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D., Wallace S. J., Gerstein D. A. Suppression of intrinsic resistance to methicillin and other penicillins in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Nov;2(5):350–355. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.5.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saravolatz L. D., Pohlod D. J., Arking L. M. Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections: a new source for nosocomial outbreaks. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Sep;97(3):325–329. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-3-325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Escherichia coli resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics through a decrease in the affinity of a target for lethality. Nature. 1978 Aug 17;274(5672):713–715. doi: 10.1038/274713a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. L., Cabezudo I., Wenzel R. P. Epidemiology of nosocomial infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Sep;97(3):309–317. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-3-309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zighelboim S., Tomasz A. Penicillin-binding proteins of multiply antibiotic-resistant South African strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Mar;17(3):434–442. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.3.434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]