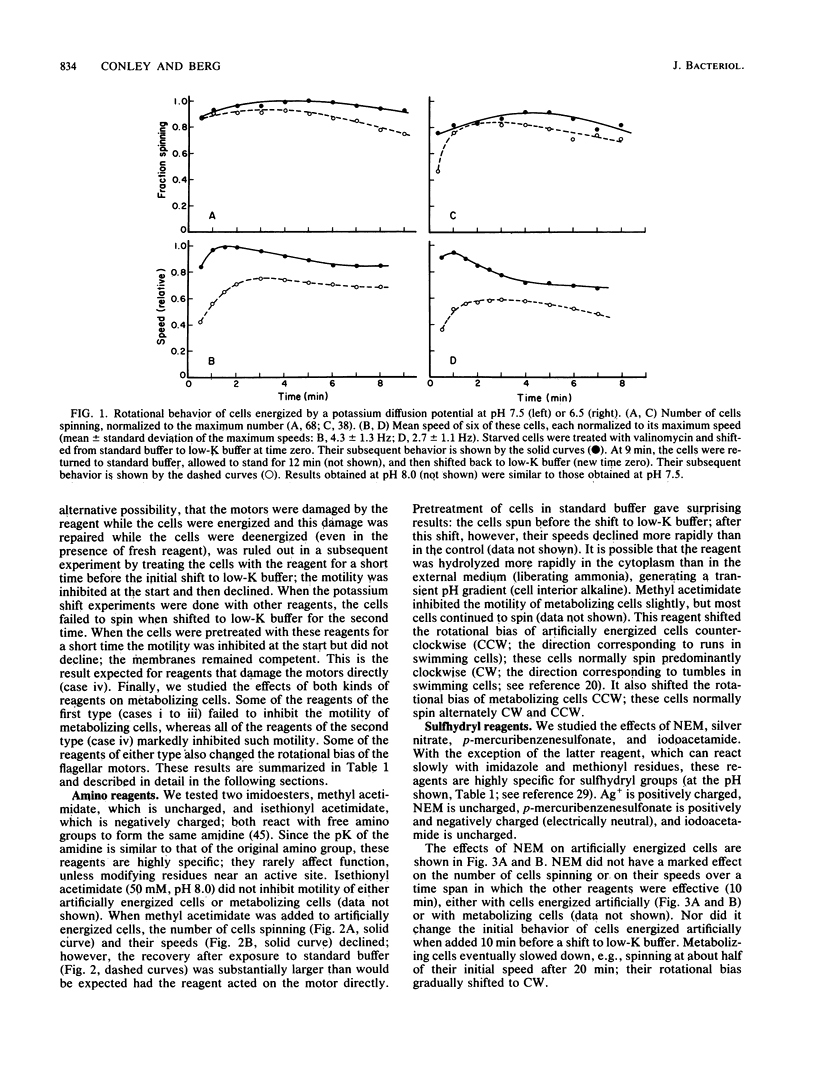
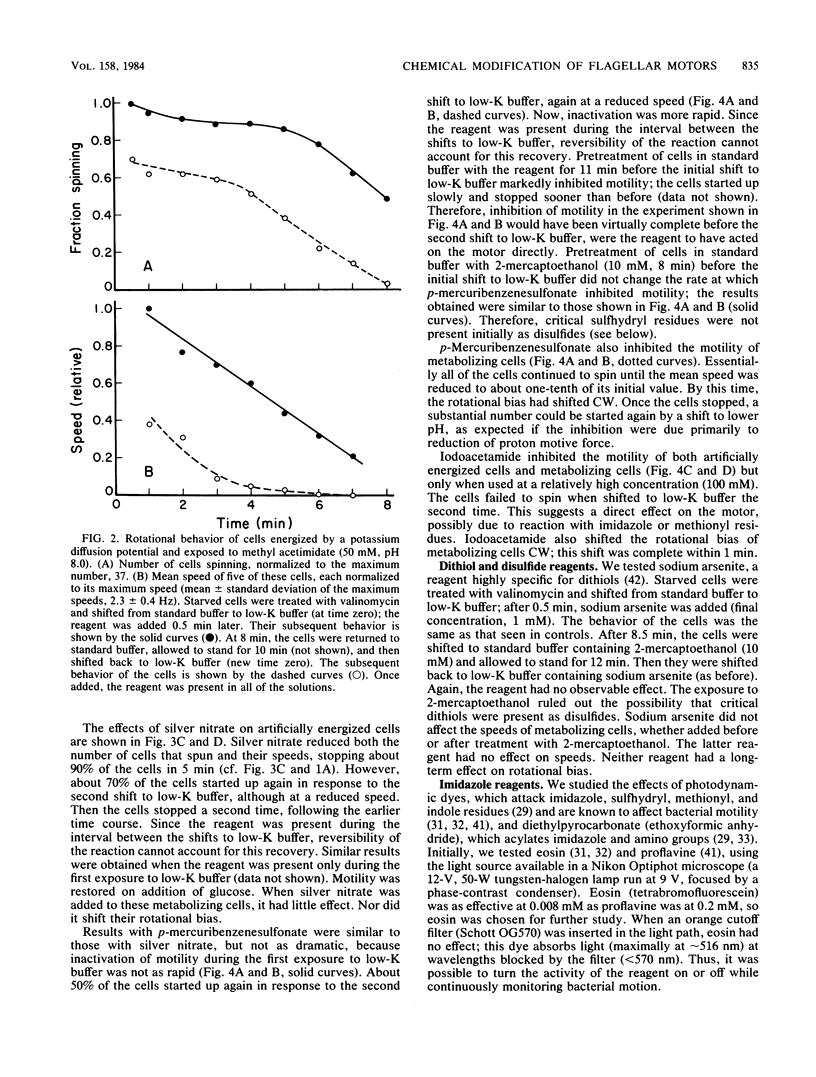
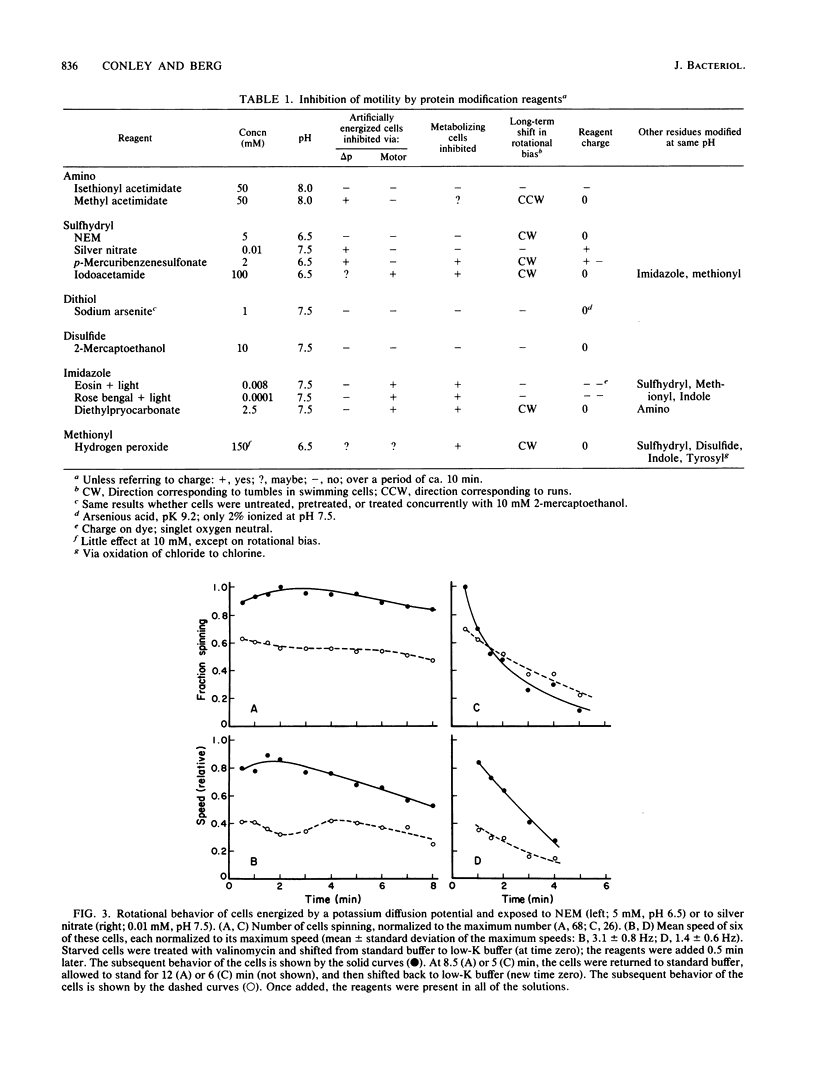
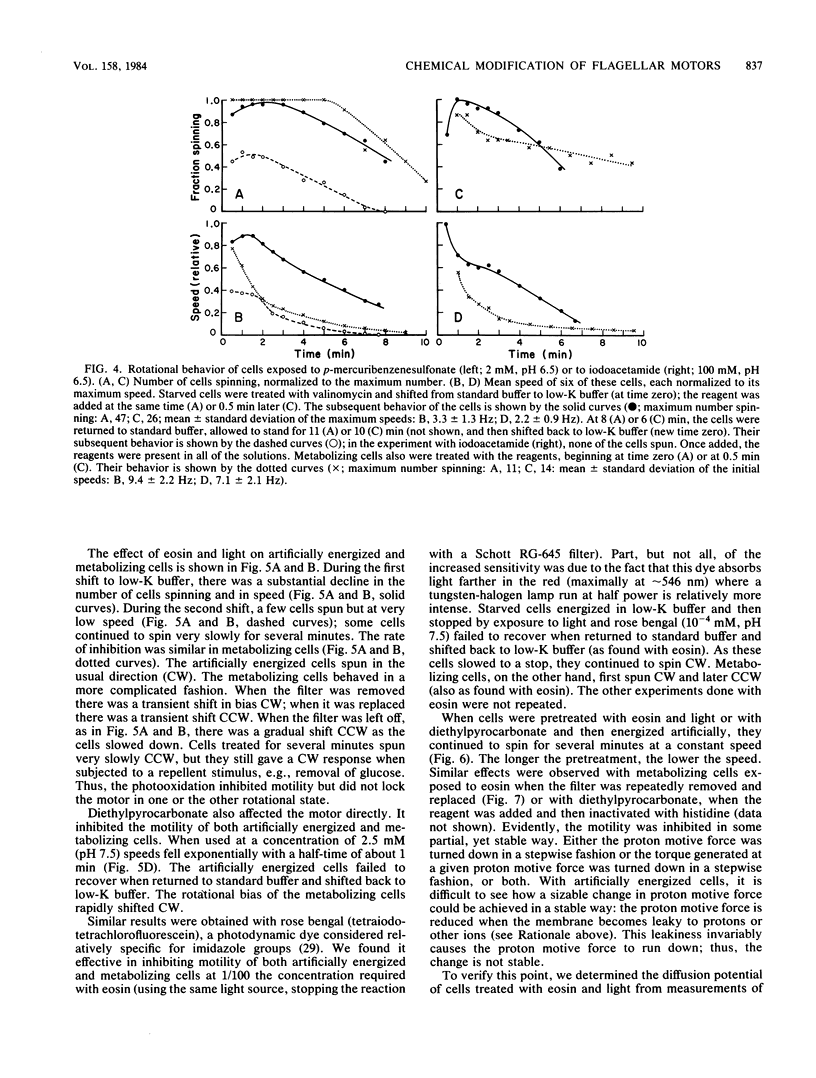
Abstract
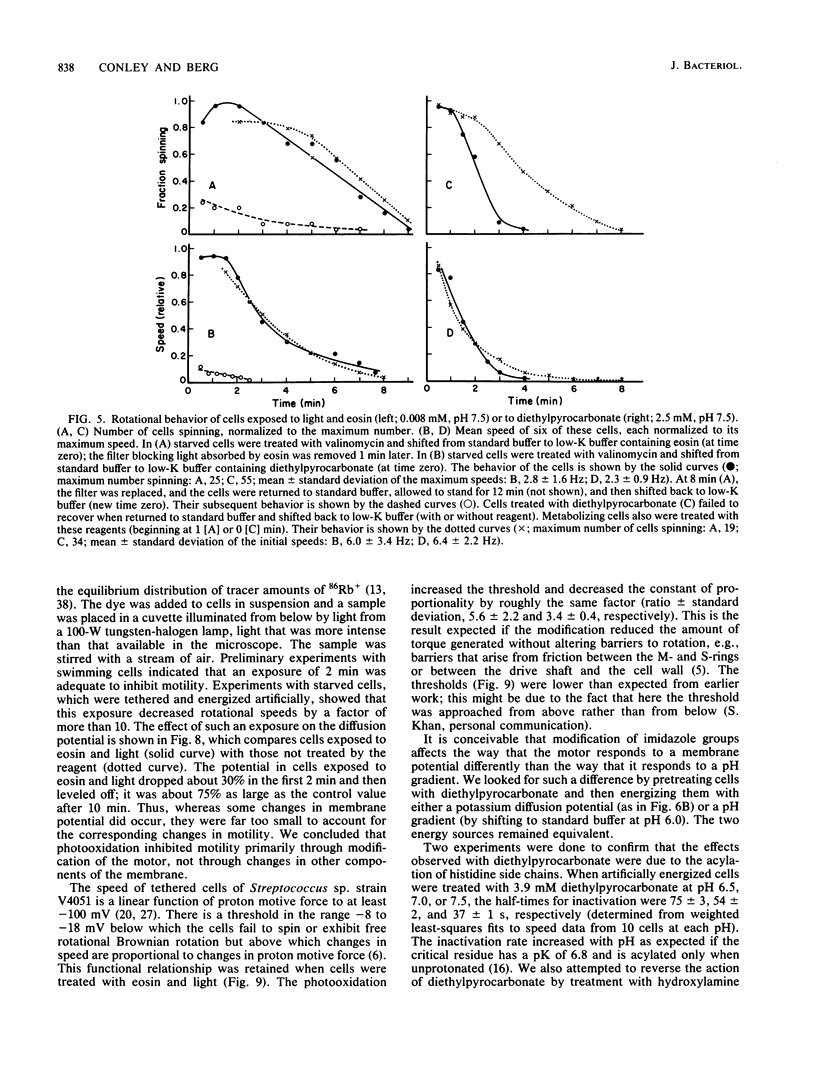
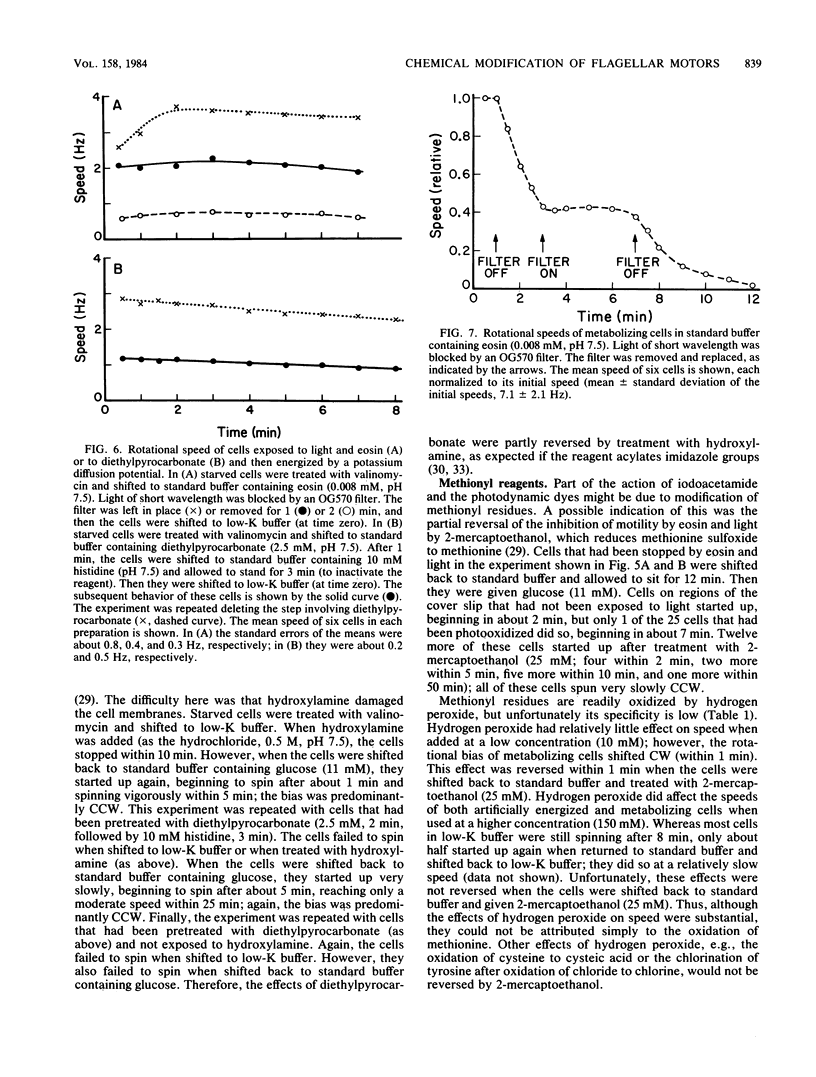
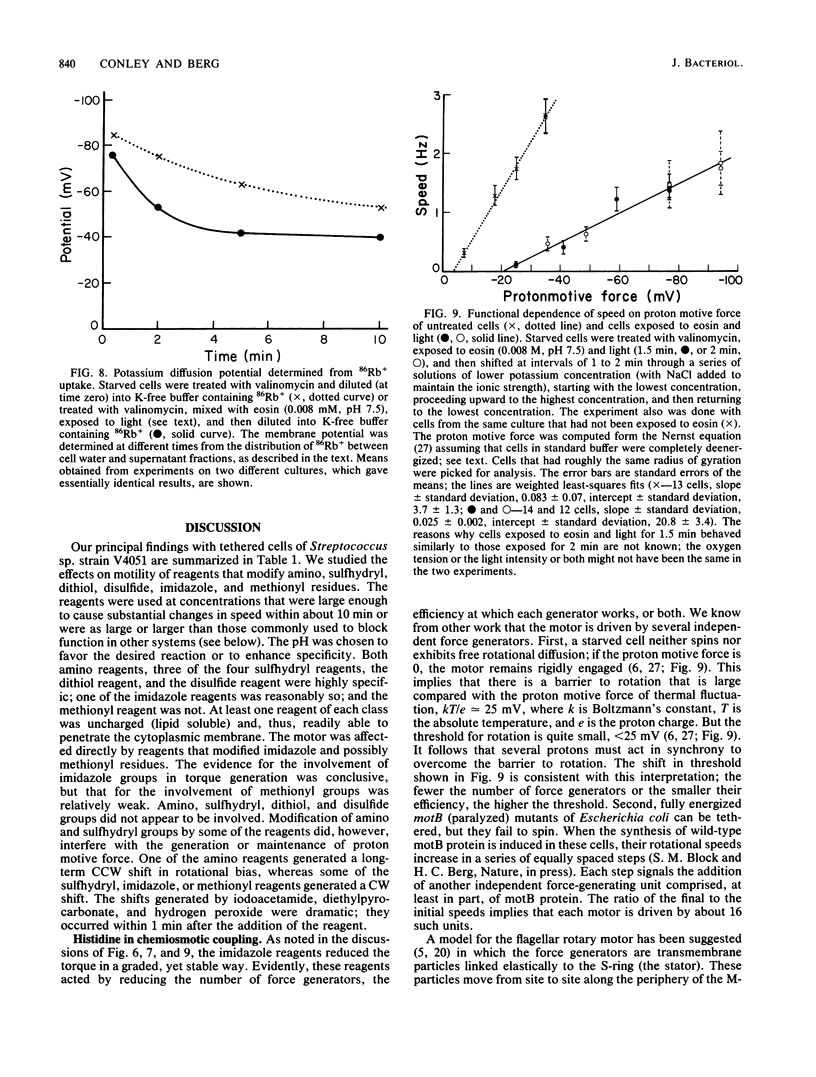
Video techniques were used to record changes in motility of cells of Streptococcus sp. strain V4051 exposed to a variety of protein modification reagents. Starved cells were tethered to glass by a single flagellum, energized metabolically with glucose, or treated with valinomycin and energized artificially via shifts to media containing low concentrations of potassium ion. Experiments were devised that distinguished reagents that lowered the proton motive force from those that blocked the generation of torque (damaged the flagellar motors). Imidazole reagents blocked the generation of torque. Amino, sulfhydryl, dithiol, and disulfide reagents did not. Some of the imidazole, amino, and sulfhydryl reagents had long-term effects on the direction of flagellar rotation.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler J., Templeton B. The effect of environmental conditions on the motility of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Feb;46(2):175–184. doi: 10.1099/00221287-46-2-175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker E. P., Harold F. M. Energy coupling to potassium transport in Streptococcus faecalis. Interplay of ATP and the protonmotive force. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):433–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Brown D. A. Chemotaxis in Escherichia coli analysed by three-dimensional tracking. Nature. 1972 Oct 27;239(5374):500–504. doi: 10.1038/239500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Manson M. D., Conley M. P. Dynamics and energetics of flagellar rotation in bacteria. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1982;35:1–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAYTON R. K. On the interplay of environmental factors affecting taxis and motility in Rhodospirillum rubrum. Arch Mikrobiol. 1958;29(2):189–212. doi: 10.1007/BF00409860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke S., Koshland D. E., Jr The effect of protein modification reagents on the chemotactic response in Salmonella typhimurium. Can J Biochem. 1979 Dec;57(12):1331–1336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn D. E., Kaczorowski G. J., Kaback H. R. Effect of the proton electrochemical gradient on maleimide inactivation of active transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Biochemistry. 1981 May 26;20(11):3308–3313. doi: 10.1021/bi00514a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE ROBERTIS E., PELUFFO C. A. Chemical stimulation and inhibition of bacterial motility studied with a new method. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1951 Nov;78(2):584–589. doi: 10.3181/00379727-78-19148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox C. F., Kennedy E. P. Specific labeling and partial purification of the M protein, a component of the beta-galactoside transport system of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):891–899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia M. L., Patel L., Padan E., Kaback H. R. Mechanism of lactose transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles: evidence for the involvement of histidine residue(s) in the response of the lac carrier to the proton electrochemical gradient. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 9;21(23):5800–5805. doi: 10.1021/bi00266a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghazi A., Schechter E., Letellier L., Labedan B. Probes of membrane potential in Escherichia coli cells. FEBS Lett. 1981 Mar 23;125(2):197–200. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80717-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glagolev A. N., Skulachev V. P. The proton pump is a molecular engine of motile bacteria. Nature. 1978 Mar 16;272(5650):280–282. doi: 10.1038/272280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M., Papineau D. Cation transport and electrogenesis by Streptococcus faecalis. I. The membrane potential. J Membr Biol. 1972;8(1):27–44. doi: 10.1007/BF01868093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook J. J., Ingram V. A. Ionic properties of an essential histidine residue in pig heart lactate dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1973 Apr;131(4):729–738. doi: 10.1042/bj1310729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino T. Genetics of structure and function of bacterial flagella. Annu Rev Genet. 1977;11:161–182. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.11.120177.001113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEPES A. [Kinetic studies on galactoside permease of Escherichia coli]. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 May 6;40:70–84. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91316-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R., Patel L. The role of functional sulfhydryl groups in active transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Biochemistry. 1978 May 2;17(9):1640–1646. doi: 10.1021/bi00602a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S., Berg H. C. Isotope and thermal effects in chemiosmotic coupling to the flagellar motor of Streptococcus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):913–919. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90076-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S., Macnab R. M. The steady-state counterclockwise/clockwise ratio of bacterial flagellar motors is regulated by protonmotive force. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr 15;138(3):563–597. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(80)80018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konings W. N., Robillard G. T. Physical mechanism for regulation of proton solute symport in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5480–5484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen S. H., Reader R. W., Kort E. N., Tso W. W., Adler J. Change in direction of flagellar rotation is the basis of the chemotactic response in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):74–77. doi: 10.1038/249074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M. Bacterial motility and chemotaxis: the molecular biology of a behavioral system. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1978;5(4):291–341. doi: 10.3109/10409237809177145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M., Koshland D. E., Jr The gradient-sensing mechanism in bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2509–2512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloney P. C. Energy coupling to ATP synthesis by the proton-translocating ATPase. J Membr Biol. 1982;67(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF01868643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manson M. D., Tedesco P. M., Berg H. C. Energetics of flagellar rotation in bacteria. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr 15;138(3):541–561. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(80)80017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manson M. D., Tedesco P., Berg H. C., Harold F. M., Van der Drift C. A protonmotive force drives bacterial flagella. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):3060–3064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.3060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchior W. B., Jr, Fahrney D. Ethoxyformylation of proteins. Reaction of ethoxyformic anhydride with alpha-chymotrypsin, pepsin, and pancreatic ribonuclease at pH 4. Biochemistry. 1970 Jan 20;9(2):251–258. doi: 10.1021/bi00804a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles E. W. Modification of histidyl residues in proteins by diethylpyrocarbonate. Methods Enzymol. 1977;47:431–442. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(77)47043-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padan E., Patel L., Kaback H. R. Effect of diethylpyrocarbonate on lactose/proton symport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6221–6225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel L., Garcia M. L., Kaback H. R. Direct measurement of lactose/proton symport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles: further evidence for the involvement of histidine residue(s). Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 9;21(23):5805–5810. doi: 10.1021/bi00266a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robillard G. T., Konings W. N. A hypothesis for the role of dithiol-disulfide interchange in solute transport and energy-transducing processes. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Oct;127(3):597–604. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06914.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottenberg H. The measurement of membrane potential and deltapH in cells, organelles, and vesicles. Methods Enzymol. 1979;55:547–569. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)55066-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Simon M. I. Bacterial flagella. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:397–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slonczewski J. L., Rosen B. P., Alger J. R., Macnab R. M. pH homeostasis in Escherichia coli: measurement by 31P nuclear magnetic resonance of methylphosphonate and phosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6271–6275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor B. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Intrinsic and extrinsic light responses of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1975 Aug;123(2):557–569. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.2.557-569.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang N., Macnab R., Koshland D. E., Jr Common mechanism for repellents and attractants in bacterial chemotaxis. Science. 1973 Jul 6;181(4094):60–63. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4094.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteley N. M., Berg H. C. Amidination of the outer and inner surfaces of the human erythrocyte membrane. J Mol Biol. 1974 Aug 15;87(3):541–561. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90103-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Drift C., Duiverman J., Bexkens H., Krijnen A. Chemotaxis of a motile Streptococcus toward sugars and amino acids. J Bacteriol. 1975 Dec;124(3):1142–1147. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.3.1142-1147.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


