Abstract
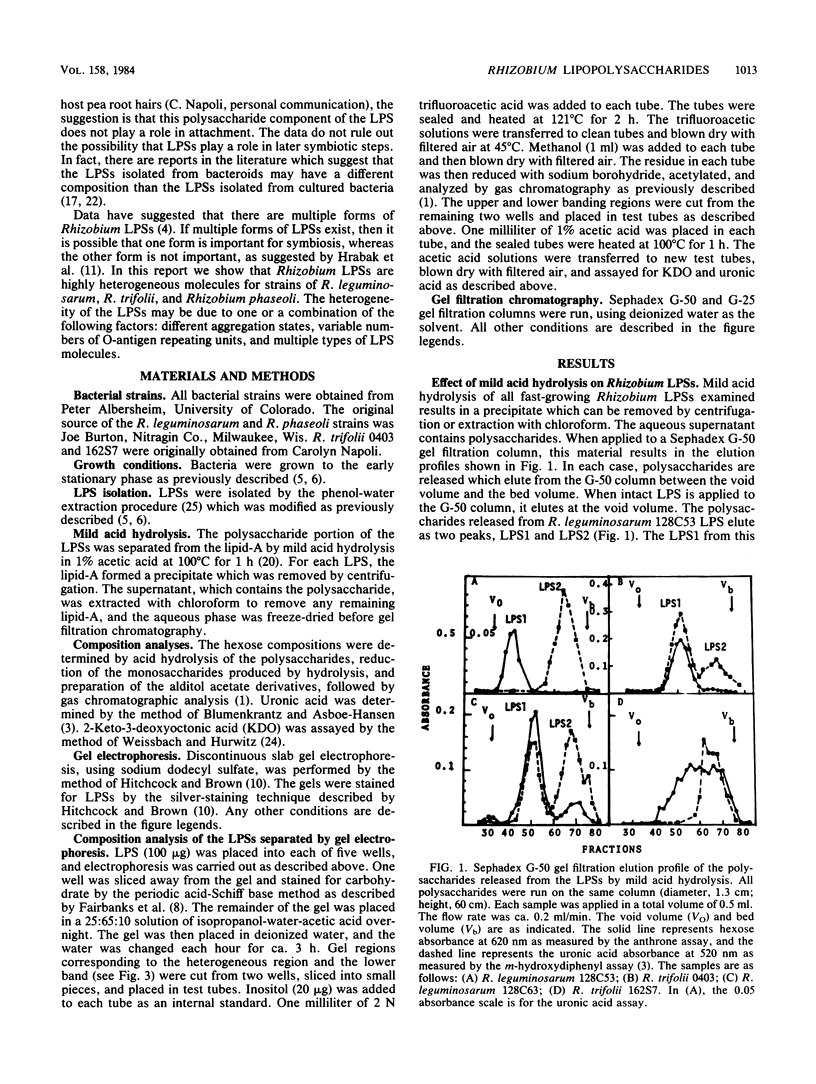
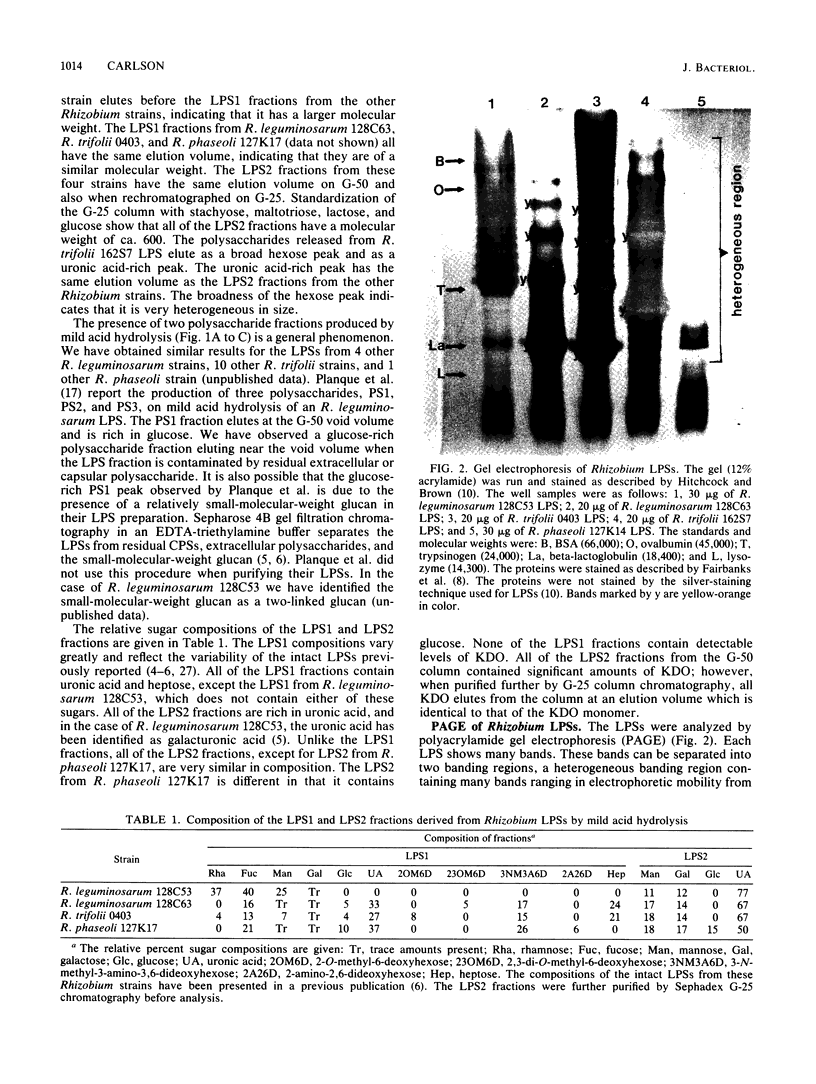
The lipopolysaccharides ( LPSs ) from strains of Rhizobium leguminosarum, Rhizobium trifolii, and Rhizobium phaseoli were isolated and partially characterized by mild acid hydrolysis and by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Mild acid hydrolysis results in a precipitate which can be removed by centrifugation or extraction with chloroform. The supernatant contains polysaccharides which, in general, are separated into two fractions ( LPS1 and LPS2 ) by Sephadex G-50 gel filtration chromatography. The higher-molecular-weight LPS1 fractions among the various Rhizobium strains are highly variable in composition and reflect the variability reported in the intact LPSs (R. W. Carlson and R. Lee, Plant Physiol. 71:223-228, 1983; Carlson et al., Plant Physiol. 62:912-917, 1978; Zevenhuizen et al., Arch. Microbiol. 125:1-8, 1980). The LPS1 fraction of R. leguminosarum 128C53 has a higher molecular weight than all other LPS1 fractions examined. All LPS2 fractions examined are oligosaccharides with a molecular weight of ca. 600. The major sugar component of all LPS2 oligosaccharides is uronic acid. The LPS2 compositions are similar for strains of R. leguminosarum and R. trifolii, but the LPS2 from R. phaseoli was different in that it contained glucose, a sugar not found in the other LPS2 fractions or found only in trace amounts. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoretic analysis shows that each LPS contains two banding regions, a higher-molecular-weight heterogeneous region often containing many bands and a lower-molecular-weight band. The lower-molecular-weight bands of all LPSs have the same electrophoretic mobility, which is greater than that of lysozyme. The banding pattern of the heterogeneous regions varies among the different Rhizobium strains. In the case of R. leguminosarum 128C53 LPS, the heterogeneous region of a higher molecular weight than is this region from all other Rhizobium strains examined and consists of many bands separated from one another by a small and apparently constant molecular weight interval. When the heterogeneous region of R. Leguminosarum 128C53 LPS was cut from the gel and analyzed, its composition was found to be that of the intact LPS, whereas the lower-molecular-weight band contains only sugars found in the LPS2 oligosaccharide. In the case of R. leguminosarum 128C63 and R. trifolii 0403 LPSs, the heterogeneous regions are similar and consist of several band s separated by a large-molecular-weight interval with a the major band of these heterogeneous regions having the lowest molecular weight with an electrophoretic mobility near that of beta-lactoglobulin. The heterogeneous region from R. phaseoli 127K14 consists of several bands with electrophoretic mobilities near that of beta-lactoglobulin, whereas this region from R. trifolii 162S7 shows a continuous staining region, indicating a great deal of heterogeneity. The results described in this paper are discussed with regard to the reported properties of Escherichia coli and Salmonella LPSs.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blumenkrantz N., Asboe-Hansen G. New method for quantitative determination of uronic acids. Anal Biochem. 1973 Aug;54(2):484–489. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90377-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson R. W., Lee R. P. A Comparison of the Surface Polysaccharides from Rhizobium leguminosarum 128C53 smrif with the Surface Polysaccharides from Its Exo Mutant. Plant Physiol. 1983 Feb;71(2):223–228. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.2.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson R. W., Sanders R. E., Napoli C., Albersheim P. Host-Symbiont Interactions: III. Purification and Partial Characterization of Rhizobium Lipopolysaccharides. Plant Physiol. 1978 Dec;62(6):912–917. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.6.912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. C., Leive L. Heterogeneity of antigenic-side-chain length in lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli 0111 and Salmonella typhimurium LT2. Eur J Biochem. 1980;107(1):145–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04635.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hrabak E. M., Urbano M. R., Dazzo F. B. Growth-phase-dependent immunodeterminants of Rhizobium trifolii lipopolysaccharide which bind trifoliin A, a white clover lectin. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):697–711. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.697-711.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jann B., Reske K., Jann K. Heterogeneity of lipopolysaccharides. Analysis of polysaccharide chain lengths by sodium dodecylsulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Dec 1;60(1):239–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb20996.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palva E. T., Mäkelä P. H. Lipopolysaccharide heterogeneity in Salmonella typhimurium analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Eur J Biochem. 1980;107(1):137–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04634.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J. M., Conrad H. E. Structural heterogeneity in the lipopolysaccharide of Salmonella newington. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Jun;162(2):530–535. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90213-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarcsay L., Wang C. S., Li S. C., Alaupovic P. Composition and structure of the O-specific side chain of endotoxin from Serratia marcescens 08. Biochemistry. 1973 May 8;12(10):1948–1955. doi: 10.1021/bi00734a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISSBACH A., HURWITZ J. The formation of 2-keto-3-deoxyheptonic acid in extracts of Escherichia coli B. I. Identification. J Biol Chem. 1959 Apr;234(4):705–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. S., Alaupovic P. Composition and structure of the O-specific side chain of endotoxin from Serratia marcescens Bizio. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 16;12(2):309–315. doi: 10.1021/bi00726a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson T. The problems and the values of objective nursing observations in psychiatric nursing care. J Adv Nurs. 1979 Mar;4(2):151–159. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2648.1979.tb02996.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]