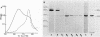Abstract
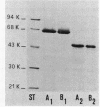
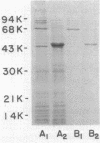
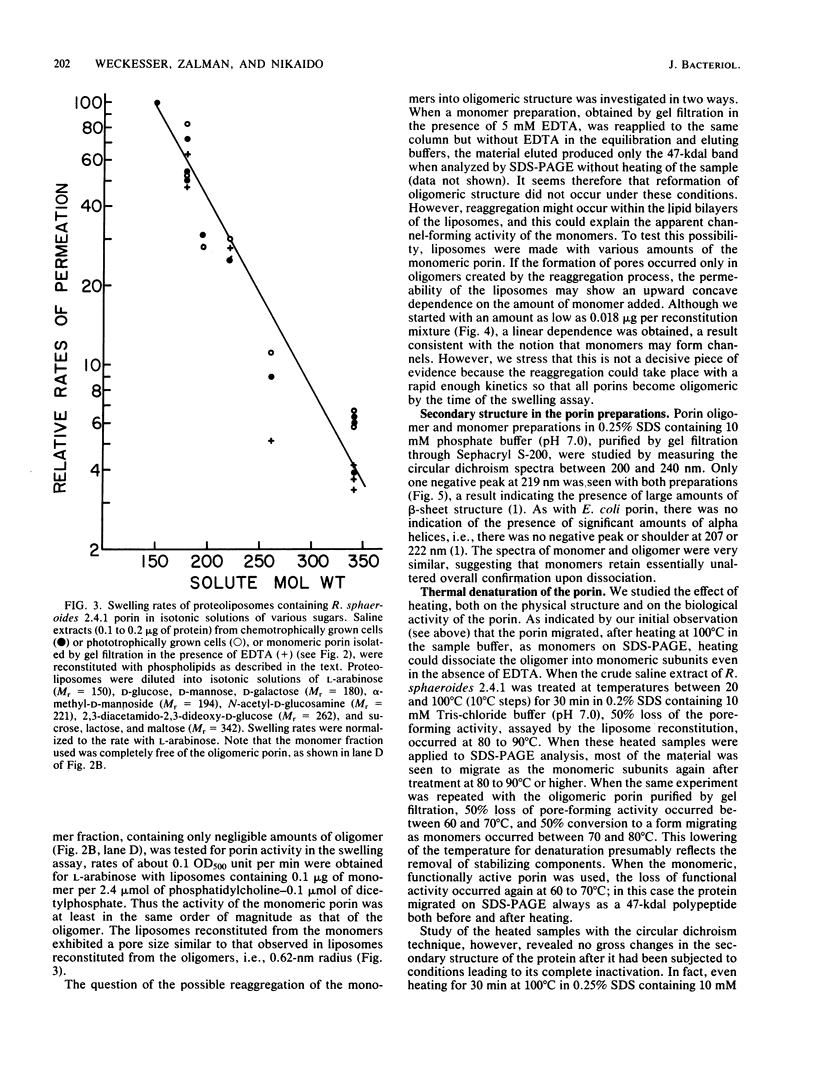
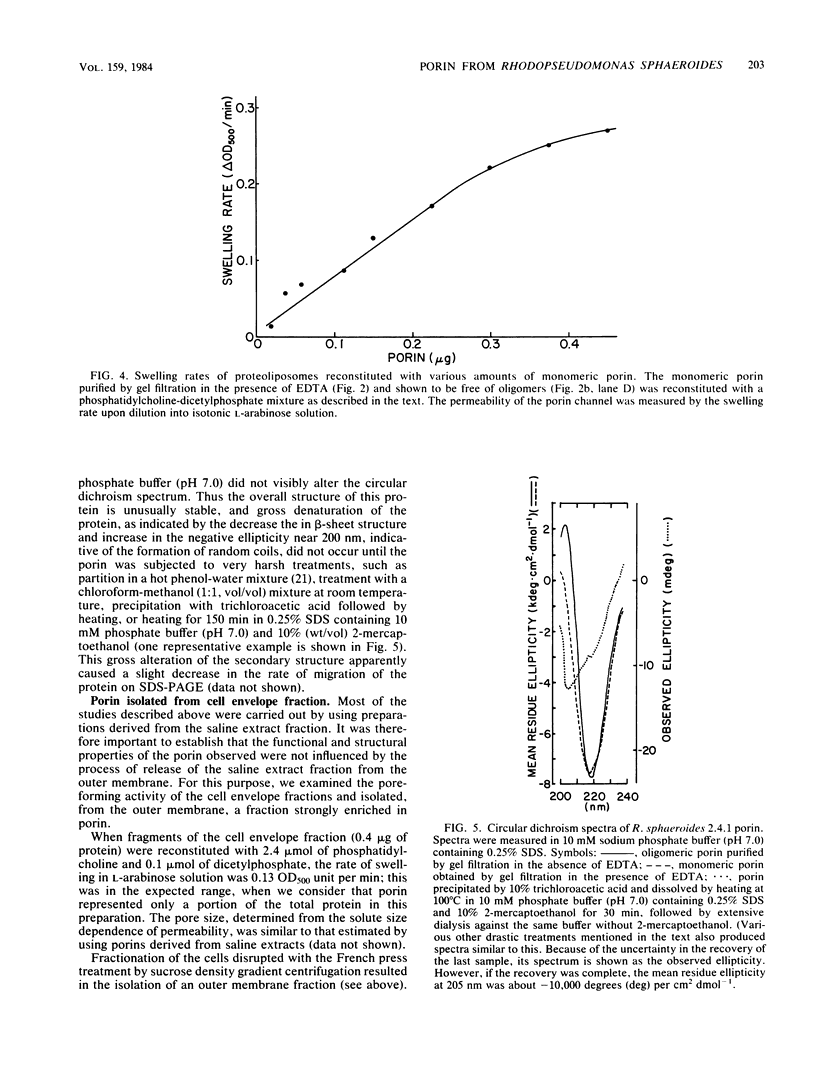
A protein homooligomer was purified from both the cell envelope fractions and the saline extracts of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides cells. This oligomer exhibited strong porin activity when reconstituted into proteoliposomes with egg phosphatidylcholine. In the saline extracts of both chemotrophically and phototrophically grown cells, the porin oligomer was the most predominant polypeptide, which produced pores whose behavior toward various sugars could be approximated by hollow cylinders of 0.62 nm in radius. The oligomer was dissociated, in the presence of EDTA, into monomers that migrated on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis as though their molecular weight was about 47,000. The monomer was active in the reconstitution assay and produced pores with sizes comparable to those produced by the oligomer. Circular dichroism spectra indicated the predominance of beta-sheet structure in both the oligomeric and EDTA-dissociated monomeric forms. Drastic conditions, for example, precipitation with 10% trichloroacetic acid or heating for a few hours at 100 degrees C in sodium dodecyl sulfate, were necessary to denature the protein into a form with a reduced content of beta-sheet structure.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES B. N., DUBIN D. T. The role of polyamines in the neutralization of bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:769–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler A. J., Greenfield N. J., Fasman G. D. Circular dichroism and optical rotatory dispersion of proteins and polypeptides. Methods Enzymol. 1973;27:675–735. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(73)27030-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumgardner D., Deal C., Kaplan S. Protein composition of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides outer membrane. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):265–273. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.265-273.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deal C. D., Kaplan S. Physical and chemical characterization of the major outer membrane protein of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6530–6536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deal C. D., Kaplan S. Solubilization, isolation, and immunochemical characterization of the major outer membrane protein from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6524–6529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding D. H., Kaplan S. Separation of inner and outer membranes of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. Prep Biochem. 1976;6(1):61–79. doi: 10.1080/00327487608061599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flammann H. T., Weckesser J. Characterization of the cell wall and outer membrane of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):191–198. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.191-198.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flammann H. T., Weckesser J. Porin isolated from the cell envelope of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):410–412. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.410-412.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Decad G. M., Nikaido H. Identification of the protein producing transmembrane diffusion pores in the outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA01. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jul 5;554(2):323–331. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90373-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Nikaido H. Outer membranes of gram-negative bacteria. XIX. Isolation from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 and use in reconstitution and definition of the permeability barrier. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):381–390. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.381-390.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane B. C., Hurlbert R. E. Isolation and partial characterization of the major outer membrane protein of Chromatium vinosum. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):349–354. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.349-354.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckey M., Nikaido H. Specificity of diffusion channels produced by lambda phage receptor protein of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):167–171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakae T., Ishii J., Tokunaga M. Subunit structure of functional porin oligomers that form permeability channels in the other membrane of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 10;254(5):1457–1461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Nakae T. The outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. Adv Microb Physiol. 1979;20:163–250. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60208-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Rosenberg E. Y. Effect on solute size on diffusion rates through the transmembrane pores of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Feb;77(2):121–135. doi: 10.1085/jgp.77.2.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RENKIN E. M. Filtration, diffusion, and molecular sieving through porous cellulose membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1954 Nov 20;38(2):225–243. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salimath P. V., Weckesser J., Strittmatter W., Mayer H. Structural studies on the non-toxic lipid A from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides ATCC 17023. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Oct 17;136(1):195–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07726.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokunaga M., Tokunaga H., Okajima Y., Nakae T. Characterization of porins from the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. 2. Physical properties of the functional oligomeric aggregates. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Apr;95(3):441–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12983.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weckesser J., Drews G., Fromme I. Chemical analysis of and degradation studies on the cell wall lipopolysaccharide of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. J Bacteriol. 1972 Mar;109(3):1106–1113. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.3.1106-1113.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weckesser J., Drews G., Ladwig R. Localization and biological and physicochemical properties of the cell wall lipopolysaccharide of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):346–353. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.346-353.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F., Zalman L. S., Nikaido H. Purification and properties of Pseudomonas aeruginosa porin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2308–2314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]