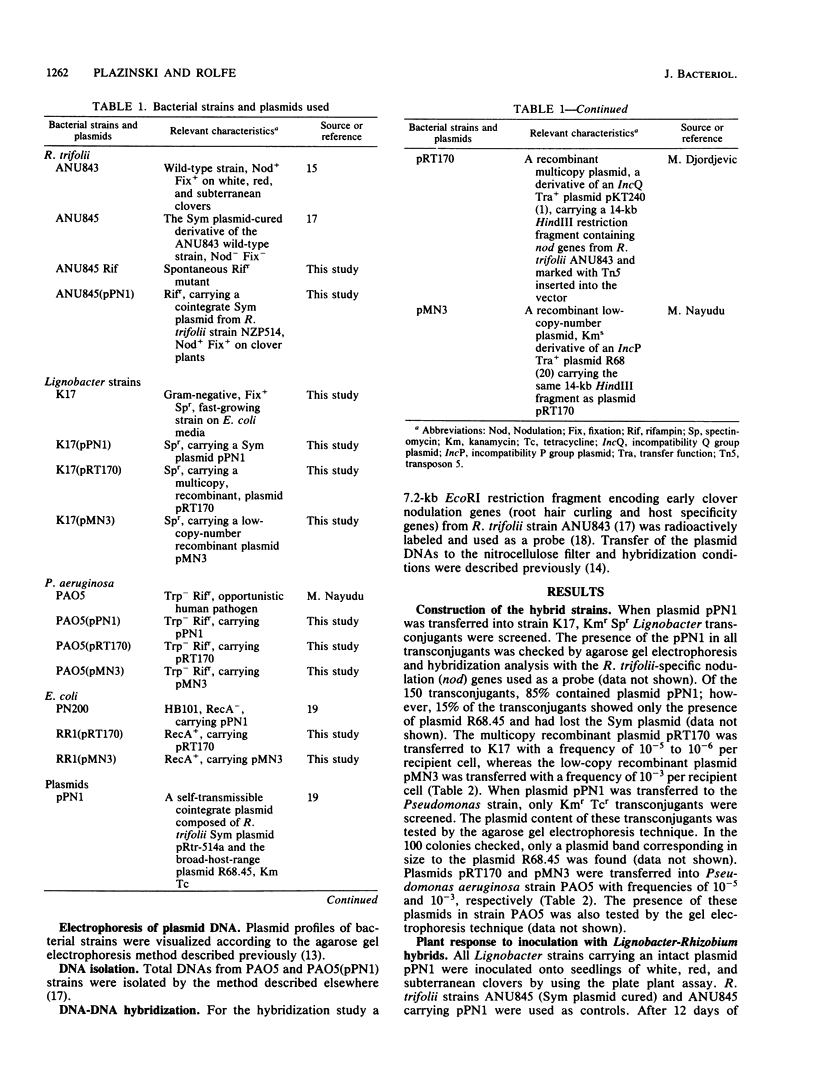
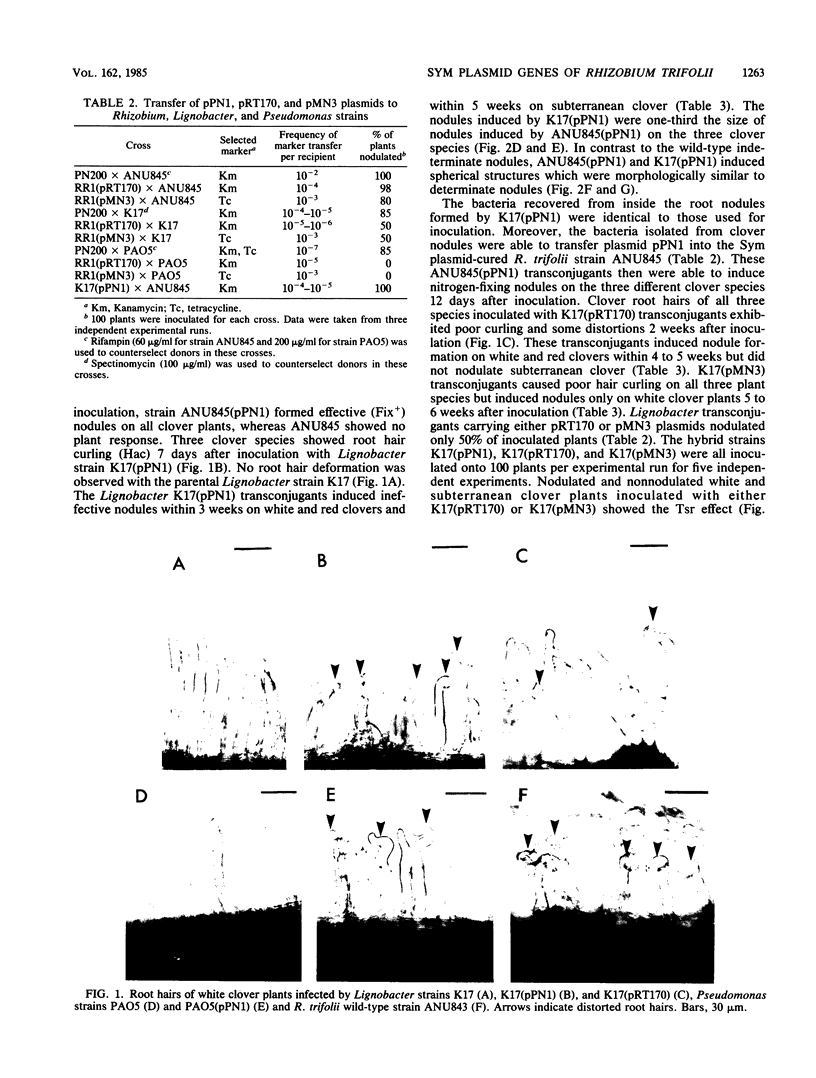
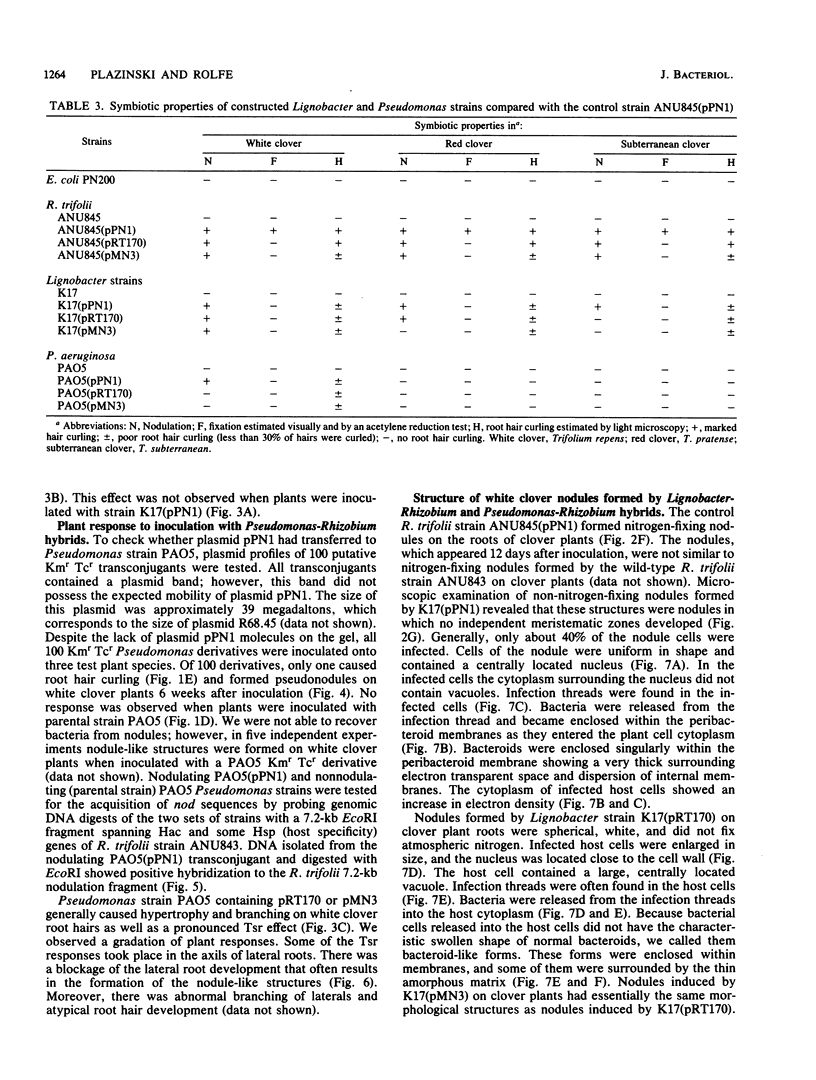
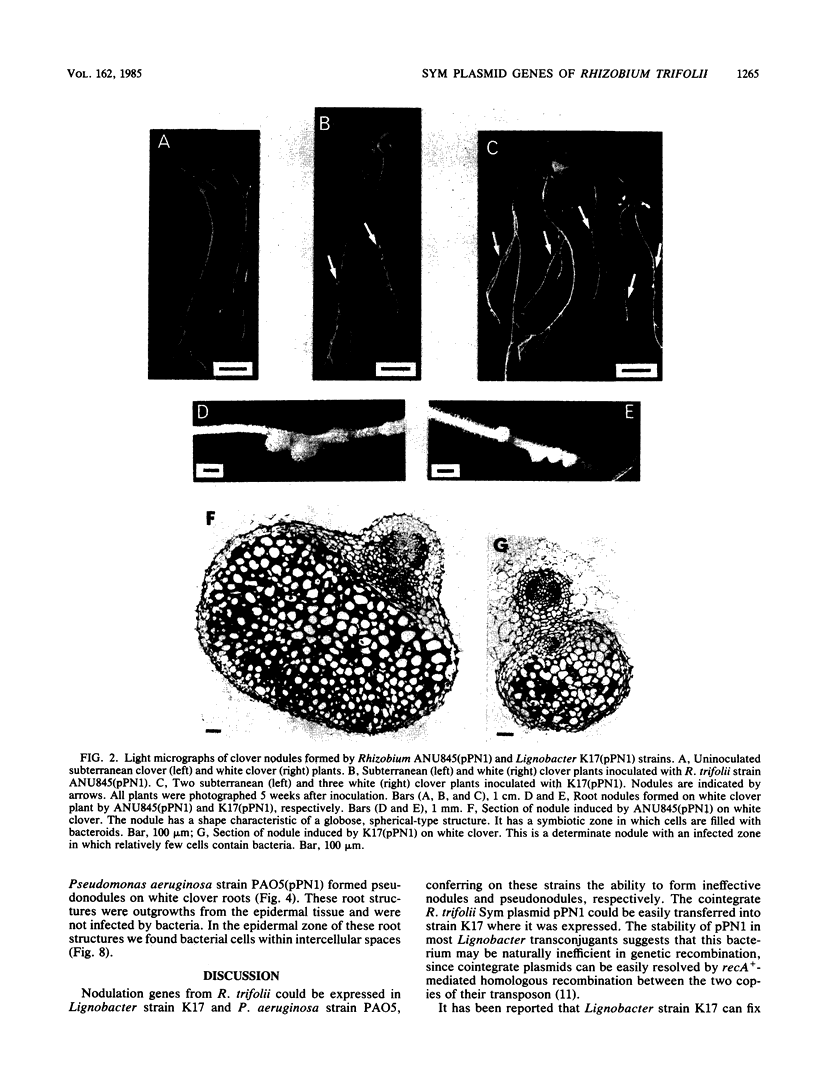
Abstract
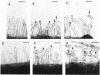
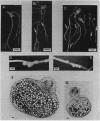
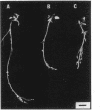
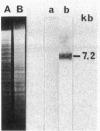
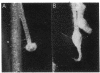
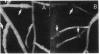
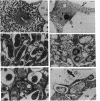
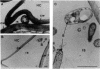
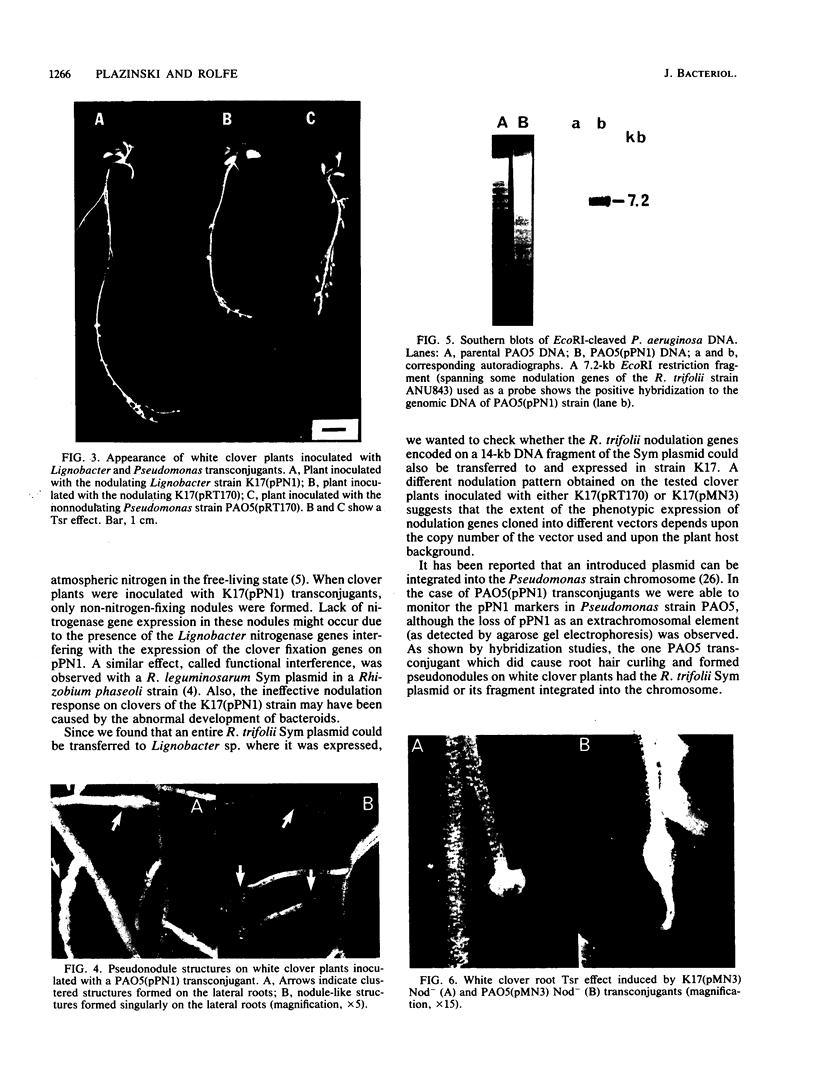
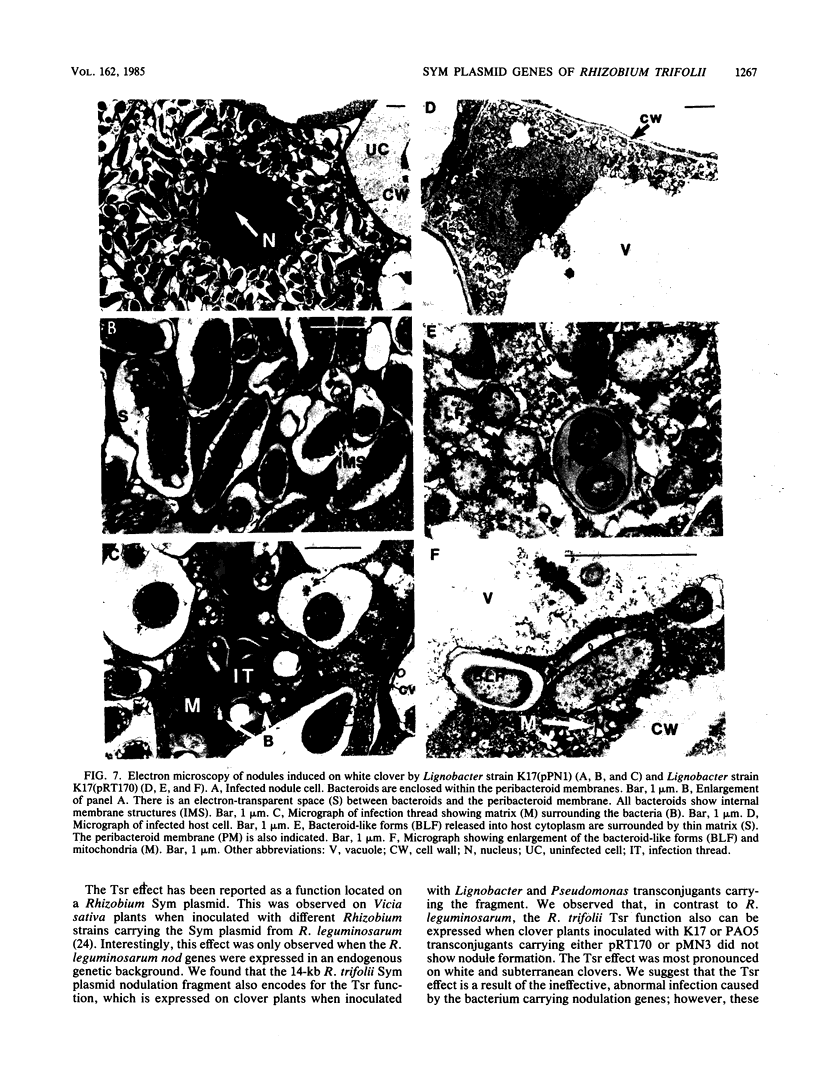
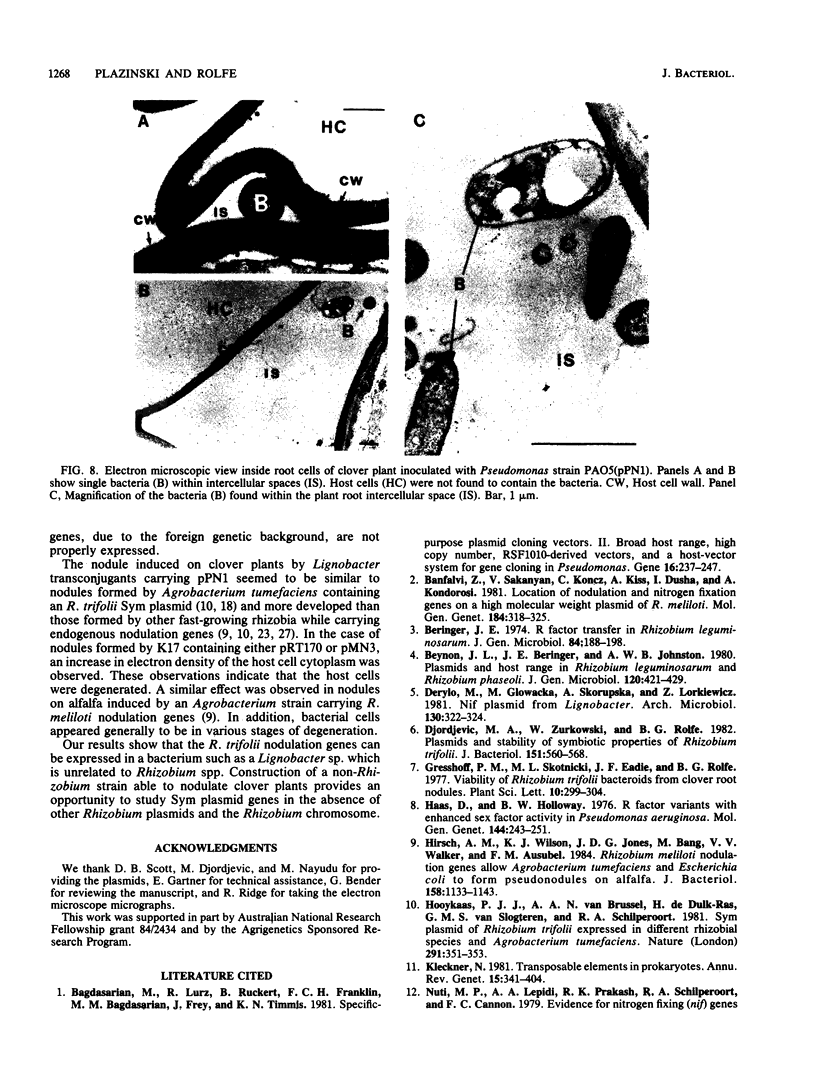
A 14-kilobase (kb) fragment of Rhizobium trifolii Sym plasmid containing nodulation (nod) genes or the pSym plasmid of R. trifolii cointegrated with a broad-host-range vector R68.45 (pPN1) were transferred to Lignobacter strain K17 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO5 by conjugation. Lignobacter transconjugants carrying Sym plasmid pPN1 formed nodules on white, red, and subterranean clover plants. Lignobacter transconjugants containing a 14-kb fragment of nod genes cloned into a multicopy plasmid nodulated only white and subterranean clover plants, whereas transconjugants carrying the same fragment cloned into a low-copy plasmid vector nodulated only white clover plants. All nodules formed by Lignobacter transconjugants showed bacterial release from the infection threads into the host cytoplasm. Pseudomonas transconjugants with plasmid pPN1 formed nodule-like structures on white clover plants. These structures were not invaded by bacteria; however, a few bacteria were found within the intercellular spaces of the outermost cells of the structures. Pseudomonas transconjugants carrying the 14-kb fragment of R. trifolii nod genes did not form nodules on tested clover plants. All clover plants inoculated with either Pseudomonas or Lignobacter transconjugants containing a 14-kb fragment of nod genes (but not entire Sym plasmid) showed the "thick-and-short-root" response when compared to the control plants inoculated with the R. trifolii wild-type strain.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagdasarian M., Lurz R., Rückert B., Franklin F. C., Bagdasarian M. M., Frey J., Timmis K. N. Specific-purpose plasmid cloning vectors. II. Broad host range, high copy number, RSF1010-derived vectors, and a host-vector system for gene cloning in Pseudomonas. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):237–247. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beringer J. E. R factor transfer in Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Sep;84(1):188–198. doi: 10.1099/00221287-84-1-188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bánfalvi Z., Sakanyan V., Koncz C., Kiss A., Dusha I., Kondorosi A. Location of nodulation and nitrogen fixation genes on a high molecular weight plasmid of R. meliloti. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(2):318–325. doi: 10.1007/BF00272925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djordjevic M. A., Zurkowski W., Rolfe B. G. Plasmids and stability of symbiotic properties of Rhizobium trifolii. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):560–568. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.560-568.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas D., Holloway B. W. R factor variants with enhanced sex factor activity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Mar 30;144(3):243–251. doi: 10.1007/BF00341722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch A. M., Wilson K. J., Jones J. D., Bang M., Walker V. V., Ausubel F. M. Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes allow Agrobacterium tumefaciens and Escherichia coli to form pseudonodules on alfalfa. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1133–1143. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1133-1143.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N. Transposable elements in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:341–404. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plazinski J., Cen Y. H., Rolfe B. G. General method for the identification of plasmid species in fast-growing soil microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Apr;49(4):1001–1003. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.4.1001-1003.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plazinski J., Dart P. J., Rolfe B. G. Plasmid visualization and nif gene location in nitrogen-fixing Azospirillum strains. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1429–1433. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1429-1433.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUNDMAN V. THE ABILITY OF ALPHA-CONIDENDRIN-DECOMPOSING AGROBACTERIUM STRAINS TO UTILIZE OTHER LIGNANS AND LIGNIN-RELATED COMPOUNDS. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Aug;36:185–201. doi: 10.1099/00221287-36-2-185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanisich V. A., Holloway B. W. Chromosome transfer in Pseudomonas aeruginosa mediated by R factors. Genet Res. 1971 Apr;17(2):169–172. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300012179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truchet G., Rosenberg C., Vasse J., Julliot J. S., Camut S., Denarie J. Transfer of Rhizobium meliloti pSym genes into Agrobacterium tumefaciens: host-specific nodulation by atypical infection. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):134–142. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.134-142.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent J. R., Fulbright D. W. Transfer of pRD1 to Pseudomonas syringae and evidence for its integration into the chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1349–1351. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1349-1351.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong C. H., Pankhurst C. E., Kondorosi A., Broughton W. J. Morphology of root nodules and nodule-like structures formed by Rhizobium and Agrobacterium strains containing a Rhizobium meliloti megaplasmid. J Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;97(3):787–794. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.3.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]