Abstract
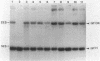
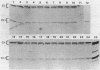
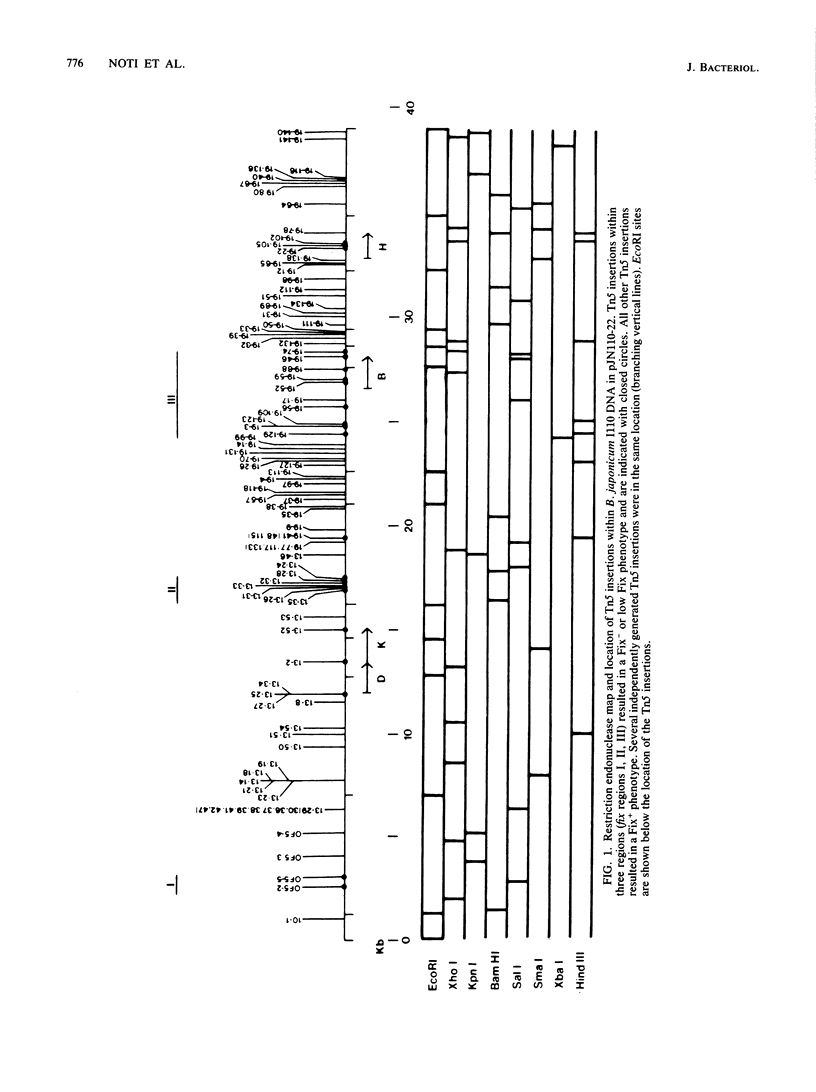
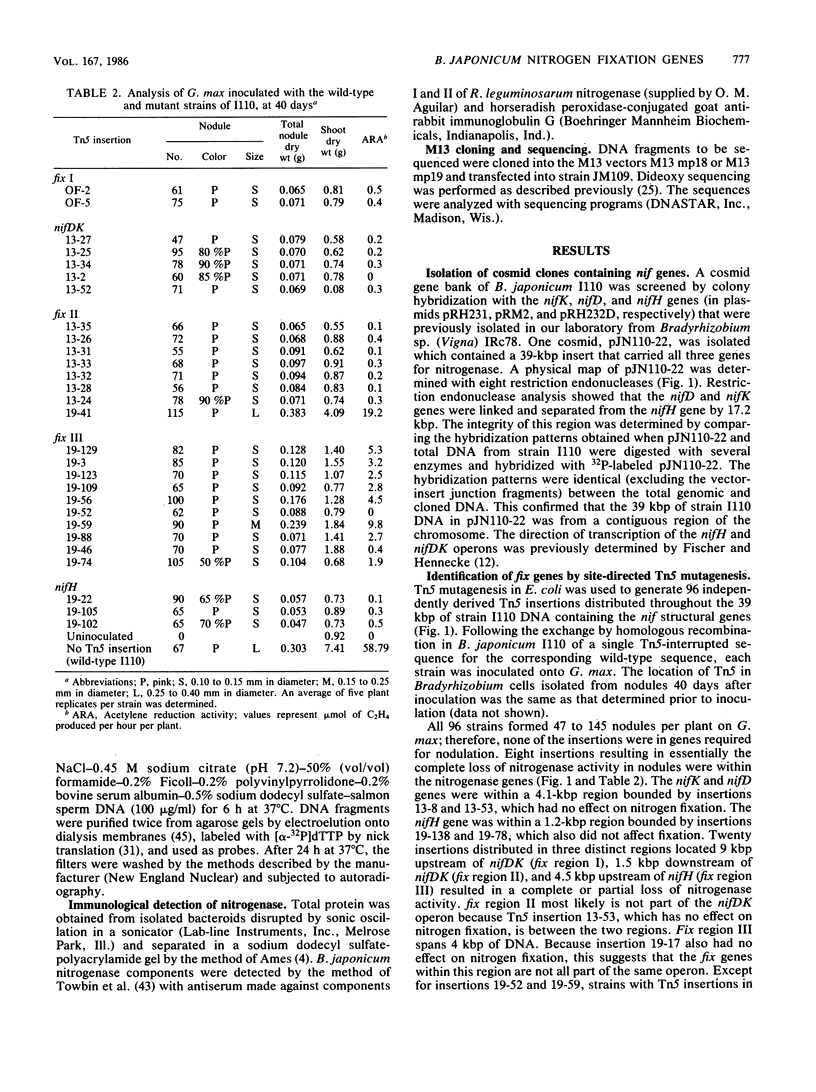
A total of 96 independent Tn5 insertions within a 39-kilobase-pair (kbp) segment of chromosomal DNA containing the three structural genes for nitrogenase (nifH, nifD, and nifK) from Bradyhizobium japonicum I110 were obtained in Escherichia coli and transferred to the wild-type strain by marker exchange. Individual transconjugants containing a Tn5 insertion were inoculated onto Glycine max cv. Wilkin (soybeans) and analyzed for their effect on symbiotic nitrogen fixation. In addition to the three structural genes, genes essential for nitrogen fixation (fix genes) were located in three separate regions: 9 kbp upstream of the nifDK operon; 1.5 kbp downstream of the nifDK operon; 4.5 kbp upstream of nifH. All of the fix::Tn5 insertion strains formed nodules which contained low or undetectable levels of nitrogenase activity. Bacteroids isolated from these nodules had approximately the same levels of the nifDK and nifH transcripts as those detectable from nodules formed by the wild-type strain. Western blot analysis of bacteroid proteins from nodules formed by the fix::Tn5 mutants or the wild-type strain showed the presence of similar levels of the nitrogenase protein subunits. The region upstream of nifH was characterized further by DNA sequence analysis and was shown to contain the nifB gene. The coding sequence of the nifB gene consisted of 1,494 nucleotides and was preceded by putative promoter (5' GTGG-10 base pairs [bp] TTGCA 3') and upstream activator (5' TGT-4 bp-T-5 bp-ACA 3') sequences.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams T. H., Chelm B. K. The nifH and nifDK promoter regions from Rhizobium japonicum share structural homologies with each other and with nitrogen-regulated promoters from other organisms. J Mol Appl Genet. 1984;2(4):392–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams T. H., McClung C. R., Chelm B. K. Physical organization of the Bradyrhizobium japonicum nitrogenase gene region. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):857–862. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.857-862.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aguilar O. M., Kapp D., Pühler A. Characterization of a Rhizobium meliloti fixation gene (fixF) located near the common nodulation region. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):245–254. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.245-254.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F. Resolution of bacterial proteins by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis on slabs. Membrane, soluble, and periplasmic fractions. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):634–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. III. Derivatives of plasmid pBR322 carrying unique Eco RI sites for selection of Eco RI generated recombinant DNA molecules. Gene. 1978 Oct;4(2):121–136. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinault A. C., Carbon J. Overlap hybridization screening: isolation and characterization of overlapping DNA fragments surrounding the leu2 gene on yeast chromosome III. Gene. 1979 Feb;5(2):111–126. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin D., Barran L., Ditta G. Organization and expression of Rhizobium meliloti nitrogen fixation genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3005–3009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D., Meselson M. Plasmid screening at high colony density. Gene. 1980 Jun;10(1):63–67. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard K. S., McLean P. A., Hansen F. B., Lemley P. V., Koblan K. S., Orme-Johnson W. H. Klebsiella pneumoniae nifM gene product is required for stabilization and activation of nitrogenase iron protein in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):772–778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krol A. J., Hontelez J. G., Roozendaal B., van Kammen A. On the operon structure of the nitrogenase genes of Rhizobium leguminosarum and Azotobacter vinelandii. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jul 24;10(14):4147–4157. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.14.4147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacNeil T., MacNeil D., Roberts G. P., Supiano M. A., Brill W. J. Fine-structure mapping and complementation analysis of nif (nitrogen fixation) genes in Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):253–266. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.253-266.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris D. W., Noti J. D., Osborne F. A., Szalay A. A. Plasmid vectors capable of transferring large DNA fragments to yeast. DNA. 1981;1(1):27–36. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1981.1.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reibach P. H., Mask P. L., Streeter J. G. A rapid one-step method for the isolation of bacteroids from root nodules of soybean plants, utilizing self-generating Percoll gradients. Can J Microbiol. 1981 May;27(5):491–495. doi: 10.1139/m81-072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. P., Brill W. J. Genetics and regulation of nitrogen fixation. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:207–235. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.001231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. P., MacNeil T., MacNeil D., Brill W. J. Regulation and characterization of protein products coded by the nif (nitrogen fixation) genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):267–279. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.267-279.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg C., Boistard P., Dénarié J., Casse-Delbart F. Genes controlling early and late functions in symbiosis are located on a megaplasmid in Rhizobium meliloti. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(2):326–333. doi: 10.1007/BF00272926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg C., Casse-Delbart F., Dusha I., David M., Boucher C. Megaplasmids in the plant-associated bacteria Rhizobium meliloti and Pseudomonas solanacearum. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):402–406. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.402-406.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruvkun G. B., Sundaresan V., Ausubel F. M. Directed transposon Tn5 mutagenesis and complementation analysis of Rhizobium meliloti symbiotic nitrogen fixation genes. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):551–559. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90171-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott K. F., Rolfe B. G., Shine J. Nitrogenase structural genes are unlinked in the nonlegume symbiont Parasponia rhizobium. DNA. 1983;2(2):141–148. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Summers M. D. The bidirectional transfer of DNA and RNA to nitrocellulose or diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg N., Tiemeier D., Enquist L. In vitro packaging of a lambda Dam vector containing EcoRI DNA fragments of Escherichia coli and phage P1. Gene. 1977 May;1(3-4):255–280. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(77)90049-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szeto W. W., Zimmerman J. L., Sundaresan V., Ausubel F. M. A Rhizobium meliloti symbiotic regulatory gene. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1035–1043. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90053-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang R., Lis J., Wu R. Elution of DNA from agarose gels after electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:176–182. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yun A. C., Szalay A. A. Structural genes of dinitrogenase and dinitrogenase reductase are transcribed from two separate promoters in the broad host range cowpea Rhizobium strain IRc78. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7358–7362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]