Abstract
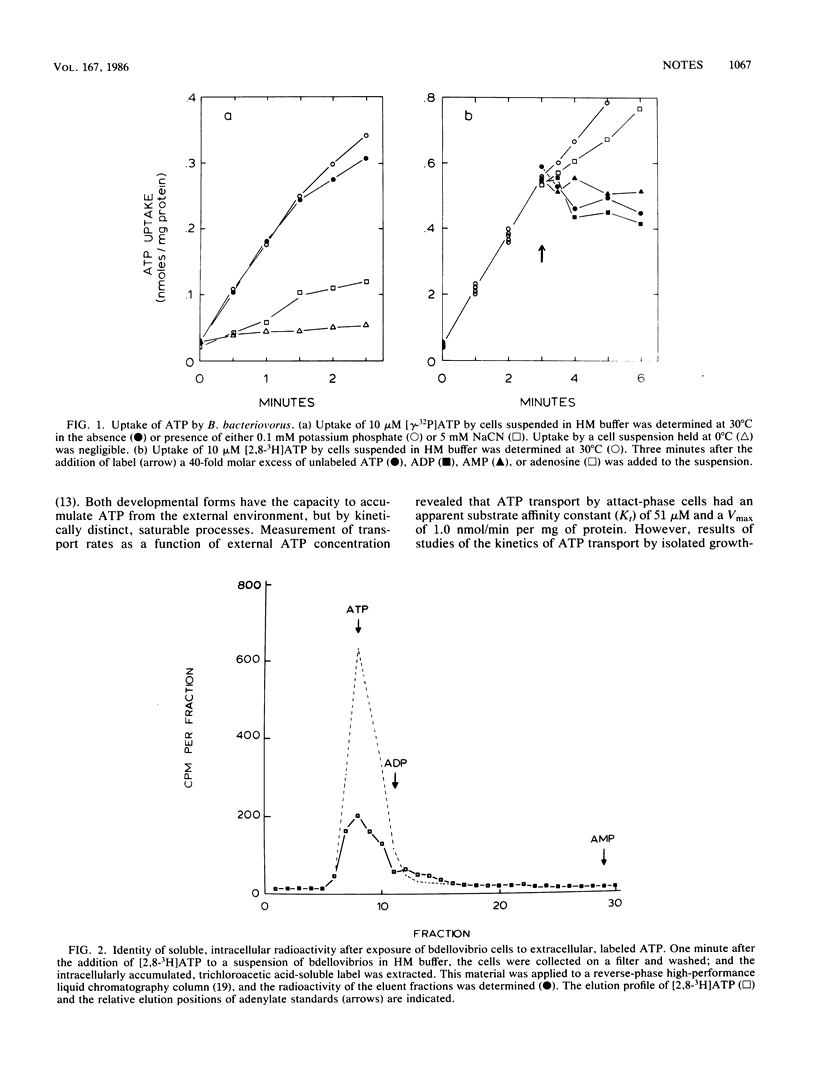
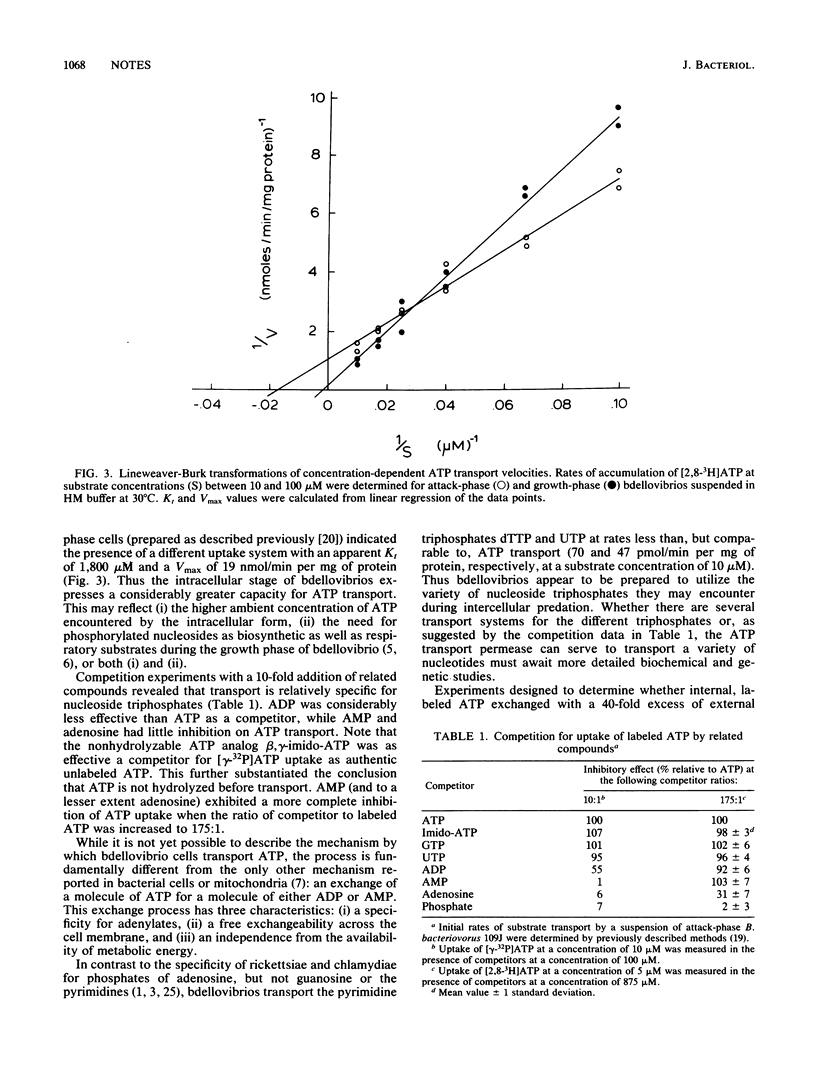
The intracellularly growing bacterium Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus 109J transports intact ATP by a specific, energy-requiring process. ATP transport does not involve either an ADP-ATP or an AMP-ATP exchange mechanism but, instead, has characteristics of an active transport permease. Kinetically distinct systems for ATP transport are expressed by the two developmental stages of the bdellovibrio life cycle.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson W. H., Winkler H. H. Transport of AMP by Rickettsia prowazekii. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):32–38. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.32-38.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch T. P., Al-Hossainy E., Silverman J. A. Adenine nucleotide and lysine transport in Chlamydia psittaci. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):662–670. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.662-670.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengge R., Larson T. J., Boos W. sn-Glycerol-3-phosphate transport in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):186–195. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.186-195.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hespell R. B., Miozzari G. F., Rittenberg S. C. Ribonucleic acid destruction and synthesis during intraperiplasmic growth of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1975 Aug;123(2):481–491. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.2.481-491.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hespell R. B., Odelson D. A. Metabolism of RNA-ribose by Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus during intraperiplasmic growth on Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1978 Dec;136(3):936–946. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.3.936-946.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klingenberg M. The ADP-ATP translocation in mitochondria, a membrane potential controlled transport. J Membr Biol. 1980 Sep 30;56(2):97–105. doi: 10.1007/BF01875961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALAMY M., HORECKER B. L. The localization of alkaline phosphatase in E. coli K12. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1961 Jun 2;5:104–108. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(61)90020-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W. Intracellular parasitism: life in an extreme environment. J Infect Dis. 1974 Sep;130(3):300–306. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.3.300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neale G. A., Mitchell A., Finch L. R. Uptake and utilization of deoxynucleoside 5'-monophosphates by Mycoplasma mycoides subsp. mycoides. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):943–947. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.943-947.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick A., Weiner M. ENZYME INDUCTION AS AN ALL-OR-NONE PHENOMENON. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1957 Jul 15;43(7):553–566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.43.7.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odelson D. A., Patterson M. A., Hespell R. B. Periplasmic enzymes in Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus and Bdellovibrio stolpii. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):756–763. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.756-763.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenberg S. C., Hespell R. B. Energy efficiency of intraperiplasmic growth of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):1158–1165. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.1158-1165.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenberg S. C., Langley D. Utilization of nucleoside monophosphates per Se for intraperiplasmic growth of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):1137–1144. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.1137-1144.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg H., Medveczky N., La Nauze J. M. Phosphate transport in Bacillus cereus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Oct 14;193(1):159–167. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90069-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruby E. G., McCabe J. B., Barke J. I. Uptake of intact nucleoside monophosphates by Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus 109J. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1087–1094. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1087-1094.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruby E. G., Rittenberg S. C. Differentiation after premature release of intraperiplasmically growing Bdellovibrio bacteriovorous. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):32–40. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.32-40.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Wentzel D. L., Feucht B. U., Judice J. J. A transport system for phosphoenolpyruvate, 2-phosphoglycerate, and 3-phosphoglycerate in Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 10;250(13):5089–5096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TORRIANI A. Influence of inorganic phosphate in the formation of phosphatases by Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Mar 11;38:460–469. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91281-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H. A hexose-phosphate transport system in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Mar 28;117(1):231–240. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90170-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H., Daugherty R. M. Regulatory role of phosphate and other anions in transport of ADP and ATP by Rickettsia prowazekii. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):76–79. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.76-79.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H. Rickettsial permeability. An ADP-ATP transport system. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 25;251(2):389–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H., Wilson T. H. The role of energy coupling in the transport of beta-galactosides by Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 25;241(10):2200–2211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagil E., Beacham I. R. Uptake of adenosine 5'-monophosphate by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1975 Feb;121(2):401–405. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.2.401-405.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


