Abstract
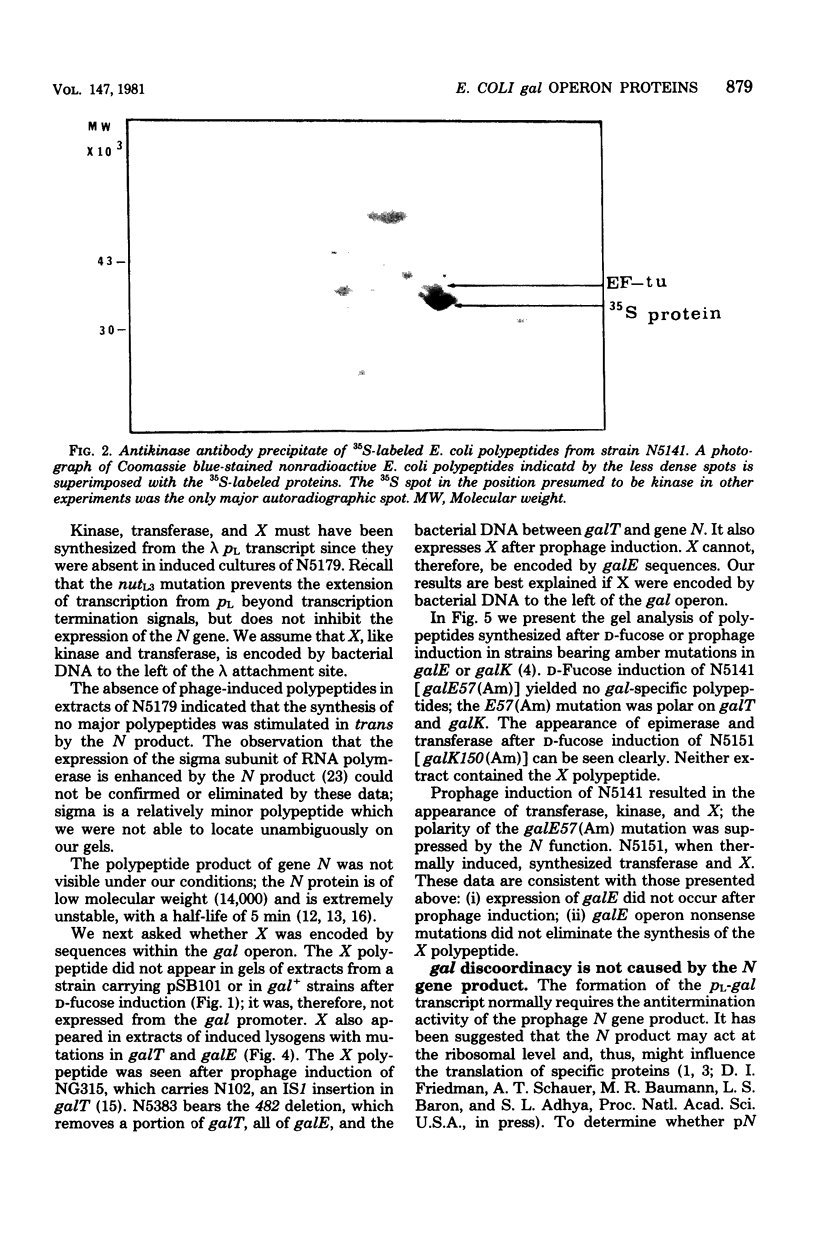
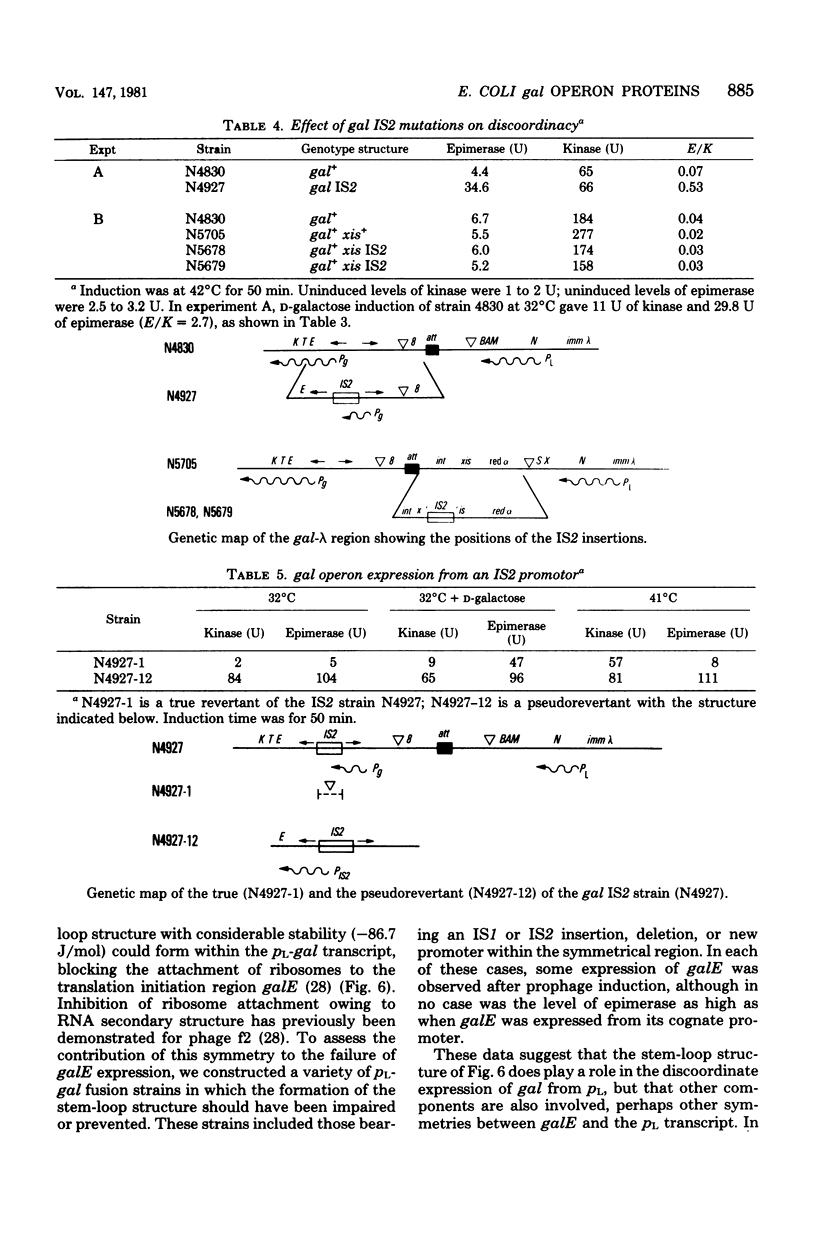
Expression of the EScherichia coli gal operon under the control of the prophage lambda promoter pL leads to gross discoordinacy of gal expression. Expression of the most promoter-distal cistron galK is much greater than expression of the promoter-proximal cistron galE. We had previously shown that transcription of the gal operon is coordinate after prophage induction. A survey of protein synthesized after prophage induction indicated that lack of expression of galE is due to a failure of translation of the galE sequence in the pL-gal transcript. This failure of translation of the galE sequence may be due to extensive dyad symmetry present in the vicinity of the gal promoter region of the pL-gal transcript. This symmetry could result in a ribonucleic acid stem-loop structure, blocking the attachment of ribosomes at the Shine-Dalgarno sequence of galE. To test this model, strains bearing the IS1 or IS2 insertion, deletion, or new promoter mutation within the symmetrical region were constructed. The restoration of some galE expression after such disruptions of the symmetrical region indicated that the ribonucleic acid stem-loop structure did play a role in the discoordinate expression of gal from pL. However, failure to obtain galE expression coordinated with high levels of galK expression suggested that other components were involved, perhaps other symmetries between galE and the pL transcript.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S. L., Shapiro J. A. The galactose operon of E. coli K-12. I. Structural and pleiotropic mutations of the operon. Genetics. 1969 Jun;62(2):231–247. doi: 10.1093/genetics/62.2.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adhya S., Gottesman M. Control of transcription termination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:967–996. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.004535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adhya S., Gottesman M., De Crombrugghe B. Release of polarity in Escherichia coli by gene N of phage lambda: termination and antitermination of transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2534–2538. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTTIN G. M'ECANISMES R'EGULATEURS DANS LA BIOSYNTH'ESE DES ENZYMES DU M'ETABOLISME DU GALACTOSE CHEZ ESCHERICHIA COLI K12. I. LA BIOSYNTH'ESE INDUITE DE LA GALACTOKINASE ET L'INDUCTION SIMULTAN'EE DE LA S'EQUENCE ENZYMATIQUE. J Mol Biol. 1963 Aug;7:164–182. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80044-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannistraro V. J., Kennell D. Escherichia coli lac operator mRNA affects translation initiation of beta-galactosidase mRNA. Nature. 1979 Feb 1;277(5695):407–409. doi: 10.1038/277407a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das A., Court D., Adhya S. Isolation and characterization of conditional lethal mutants of Escherichia coli defective in transcription termination factor rho. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1959–1963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I., Wilgus G. S., Mural R. J. Gene N regulator function of phage lambda immun21: evidence that a site of N action differs from a site of N recognition. J Mol Biol. 1973 Dec 25;81(4):505–516. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90519-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukasawa T., Hirai K., Segawa T., Obonai K. Regional replication of the bacterial chromosome induced by derepression of prophage lambda. IV. Escape synthesis of gal operon in phage 82. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Nov 16;167(1):83–93. doi: 10.1007/BF00270324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman M. E., Adhya S., Das A. Transcription antitermination by bacteriophage lambda N gene product. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jun 15;140(1):57–75. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90356-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman S., Gottesman M., Shaw J. E., Pearson M. L. Protein degradation in E. coli: the lon mutation and bacteriophage lambda N and cII protein stability. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90518-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J., Malnoe P., Li J. Purification of the gene N transcription anti-termination protein of bacteriophage lambda. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1465–1470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilliker S., Gottesman M., Adhya S. The activity of Salmonella phage P22 gene 24 product in Escherichia coli. Virology. 1978 May 1;86(1):37–47. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch H. J., Starlinger P., Brachet P. Two kinds of insertions in bacterial genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;119(3):191–206. doi: 10.1007/BF00333858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii S., Kuroki K., Sugino Y., Imamoto F. Purification and characterization of the N gene product of bacteriophage lambda. Gene. 1980 Sep;10(4):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90149-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn S., Fritz H. J., Starlinger P. Close vicinity of IS1 integration sites in the leader sequence of the gal operon of E. coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 2;167(3):235–241. doi: 10.1007/BF00267414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Leavitt J., Van Keuren M. L., Ebert M. H., Caine E. D. Hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRT) in Gilles de la Tourette syndrome. Neurology. 1979 Jan;29(1):131–134. doi: 10.1212/wnl.29.1.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
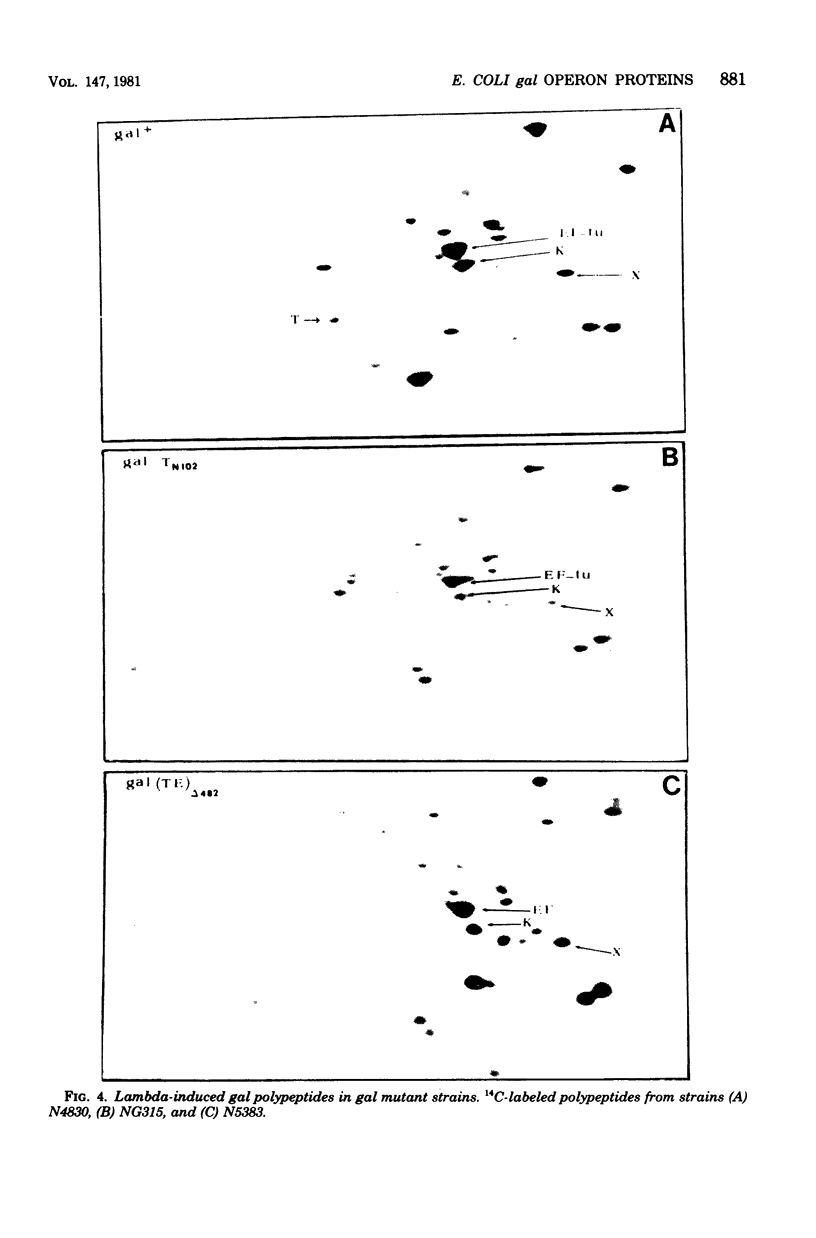
- Merril C., Gottesman M., Court D., Adhya S. Disco-ordinate expression of the Escherichia coli gal operon after prophage lambda induction. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jan 15;118(2):241–245. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90415-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse D. E., Baker R. F., Yanofsky C. Translation of the tryptophan messenger RNA of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1428–1435. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musso R. E., de Crombrugghe B., Pastan I., Sklar J., Yot P., Weissman S. The 5'-terminal nucleotide sequence of galactose messenger ribonucleic acid of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4940–4944. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Yura T. Induction of sigma factor synthesis in Escherichia coli by the N gene product of bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4405–4409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts T. M., Kacich R., Ptashne M. A general method for maximizing the expression of a cloned gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):760–764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salstrom J. S., Szybalski W. Coliphage lambdanutL-: a unique class of mutants defective in the site of gene N product utilization for antitermination of leftward transcription. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 5;124(1):195–221. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90156-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklar J., Weissman S., Musso R. E., DiLauro R., de Crombrugghe B. Determination of the nucleotide sequence of part of the regulatory region for the galactose operon from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 25;252(10):3538–3547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B., Hogness D. S. The enzymes of the galactose operon in Escherichia coli. IV. The frequencies of translation of the terminal cistrons in the operon. J Biol Chem. 1969 Apr 25;244(8):2143–2148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Crombrugghe B., Mudryj M., DiLauro R., Gottesman M. Specificity of the bacteriophage lambda N gene product (pN): nut sequences are necessary and sufficient for antitermination by pN. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1145–1151. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90227-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







