Abstract
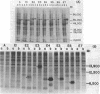
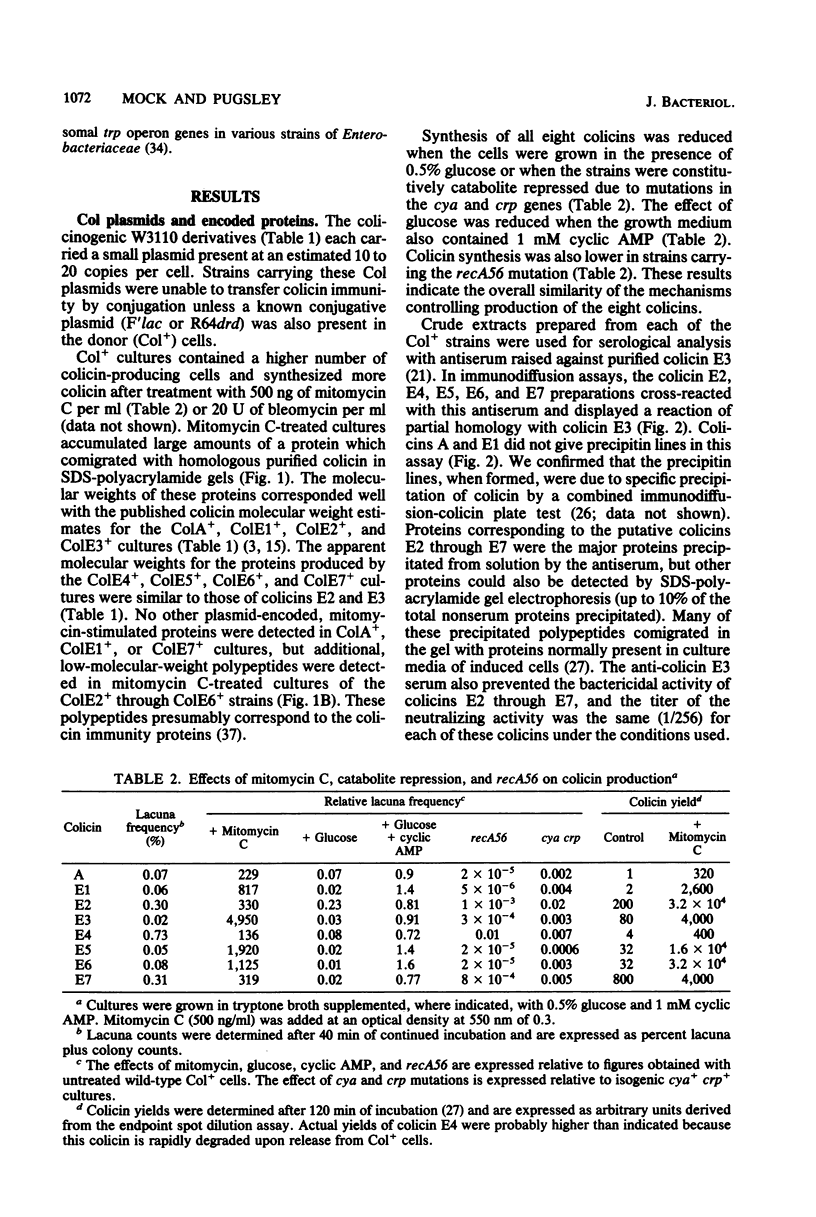
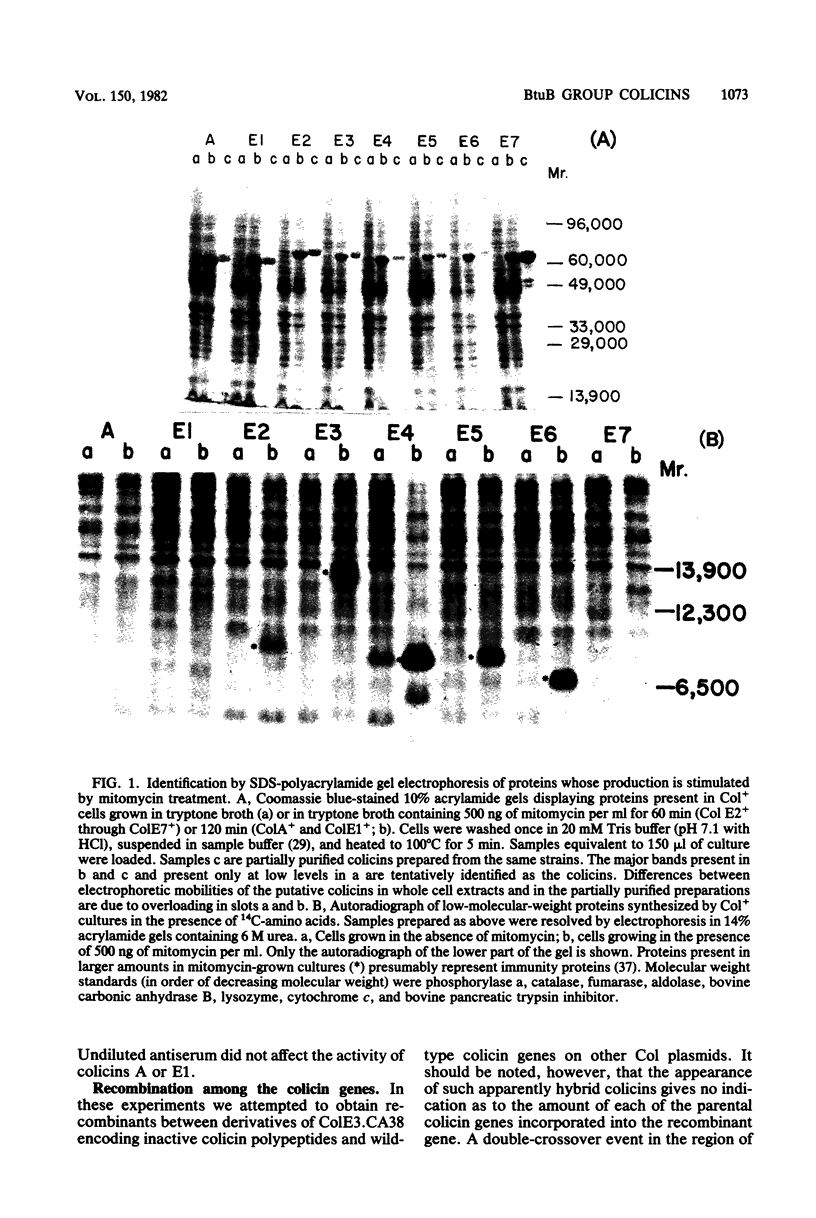
Colicins A, E1, E2, E3, E4, E5, E6, and E7 exhibited reduced activity against BtuB mutants of Escherichia coli K-12 and also against wild-type cells in the presence of vitamin B12. Plasmids encoding representatives of these colicins were specifically immune to high levels of the homologous colicin. Col+ cells grown in media containing mitomycin C accumulated large amounts of colicin polypeptide. ColE2+, ColE3+, ColE4+, ColE5+, and ColE6+ cultures also synthesized large amounts of second, lower-molecular-weight protein under these conditions. Colicins E2 through E7, but not A or E1, reacted with antiserum raised against purified colicin E3. Colicins E2 and E7 induced synthesis of β-galactosidase encoded by lacZ under the control of the colicin Ib gene promotor on a derivative of Col plasmid ColIb.P9. This promotor is usually active only when the cells are treated with agents which damage DNA or block replication. Plasmids encoding various mutant forms of colicin E3 (M. Mock and M. Schwartz, J. Bacteriol. 142:384-390, 1980) recombined with ColE2, ColE4, ColE5, or ColE6 plasmids at a frequency of 10−4 per cell to produce a colicin active against ColE2+, E4+, E5+, or E6+ cells. ColE5 and ColE6 plasmids recombined with ColE3 plasmids bearing mutations affecting colicin E3 receptor recognition, envelope penetration, and catalytic activities. ColE2 and ColE4 plasmids recombined only with ColE3 plasmids bearing mutations affecting receptor recognition and envelope penetration. Recombinants between mutant ColE3 plasmids and ColA, ColE1, or ColE7 plasmids were not detected. We propose the designation BtuB group for the colicins described here, and we divide the group into two classes comprising colicins A and E1, which act on the cytoplasmic membrane, and the related colicins E2 through E7, which have known or putative nuclease activities.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boon T. Inactivation of ribosomes in vitro by colicin E 3 . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2421–2425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavard D., Lazdunski C. J. Purification and molecular properties of a new colicin. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jun 1;96(3):519–524. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13065.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. K., Reeves P. Genetics of resistance to colicins in Escherichia coli K-12: cross-resistance among colicins of group A. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):102–117. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.102-117.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Graaf F. K. Mode of action of colicin E2, colicin E3 and cloacin DF13. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1979 Jun;244(1):121–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy K. G., Harwood C. R., Meynell G. G. Expression of colicin factor E2-P9. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;131(4):313–331. doi: 10.1007/BF00264862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horák V. Typing of Shigella sonnei colicins by means of specific indicators. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1975 Sep;233(1):58–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jetten A. M., Vogels G. D. Effects of colicin A and staphylococcin 1580 on amino acid uptake into membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli and staphylococcus aureus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jul 18;311(4):483–495. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90124-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luria S. E. The mistaken identity of colicin A. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):386–386. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.386-386.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Males B. M., Stocker B. A. Colicins E4, E5, E6 and A and properties of btuB+ colicinogenic transconjugants. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Jan;128(1):95–106. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-1-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Males B. M., Stocker B. A. Escherichia coli K317, formerly used to define colicin group E2, produces colicin E7, is immune to colicin E2, and carries a bacteriophage-restricting conjugative plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1980 Nov;144(2):524–531. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.2.524-531.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mock M., Schwartz M. Mechanism of colicin E3 production in strains harboring wild-type or mutant plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1978 Nov;136(2):700–707. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.2.700-707.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mock M., Schwartz M. Mutations which affect the structure and activity of colicin E3. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):384–390. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.384-390.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno-Iwashita Y., Imahori K. Assignment of the functional loci in colicin E2 and E3 molecules by the characterization of their proteolytic fragments. Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 19;19(4):652–659. doi: 10.1021/bi00545a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P., Reeves P. Characterization of group B colicin-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli K-12: colicin resistance and the role of enterochelin. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):218–228. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.218-228.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P., Reeves P. Comparison of colicins B-K260 and D-CA23: purification and characterization of the colicins and examination of colicin immunity in the producing strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Feb;11(2):345–358. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.2.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P., Rosenbusch J. P. Release of colicin E2 from Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jul;147(1):186–192. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.1.186-192.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P., Schnaitman C. A. Outer membrane proteins of Escherichia coli. VII. Evidence that bacteriophage-directed protein 2 functions as a pore. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1181–1189. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1181-1189.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P. Transcription regulation of colicin Ib synthesis. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;183(3):522–527. doi: 10.1007/BF00268775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves P. Mode of action of colicins of types E1, E2, E3, and K. J Bacteriol. 1968 Nov;96(5):1700–1703. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.5.1700-1703.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller K., Nomura M. Colicin E2 is DNA endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3989–3993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schein S. J., Kagan B. L., Finkelstein A. Colicin K acts by forming voltage-dependent channels in phospholipid bilayer membranes. Nature. 1978 Nov 9;276(5684):159–163. doi: 10.1038/276159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider W. P., Nichols B. P., Yanofsky C. Procedure for production of hybrid genes and proteins and its use in assessing significance of amino acid differences in homologous tryptophan synthetase alpha polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2169–2173. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler J., Sherratt D. J. Synthesis of E colicins in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Oct 22;140(4):349–353. doi: 10.1007/BF00267325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uratani Y., Cramer W. A. Reconstitution of colicin E1 into dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):4017–4023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. H. Common inner membrane-specific domains of colicins E1, K, Ia and A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Apr 25;622(2):287–296. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90039-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. H., Sherratt D. J. In vivo proteolytic cleavage of colicins requires specific receptor binding. Nature. 1979 Mar 22;278(5702):362–364. doi: 10.1038/278362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]