Abstract
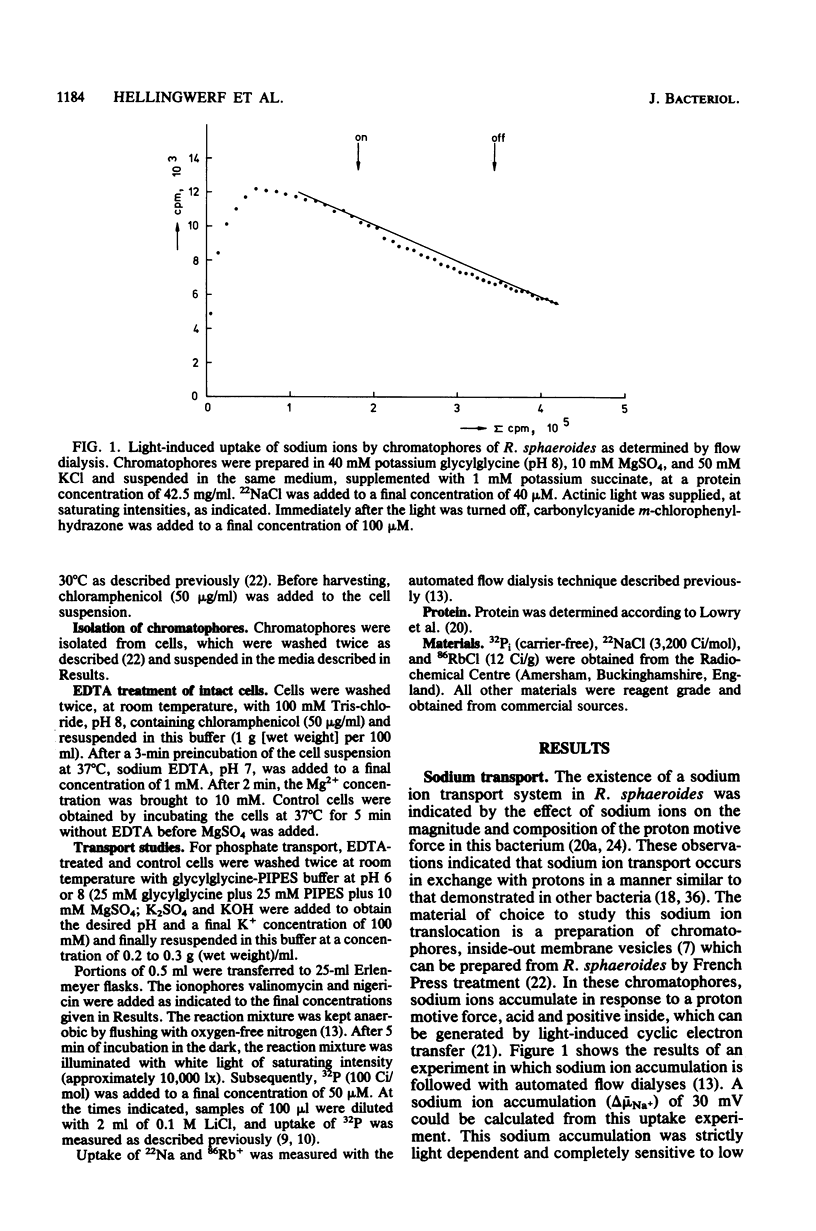
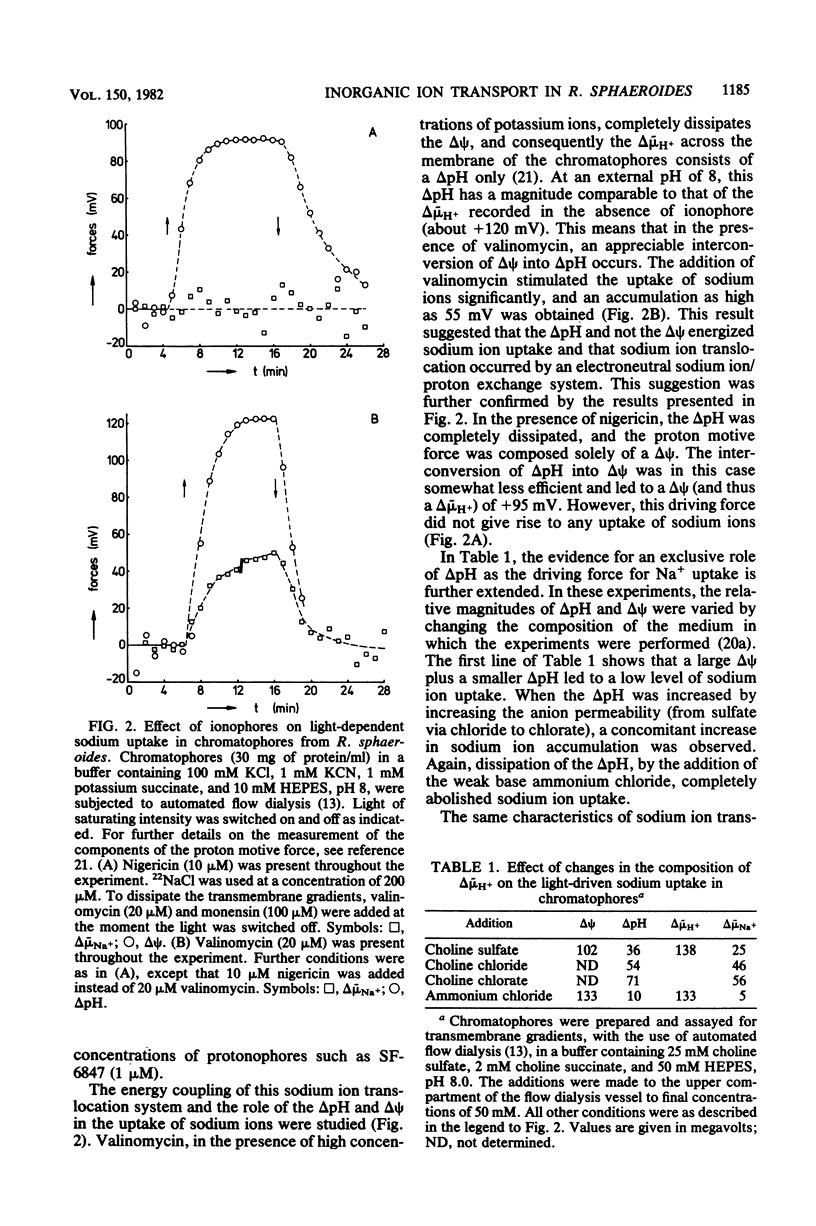
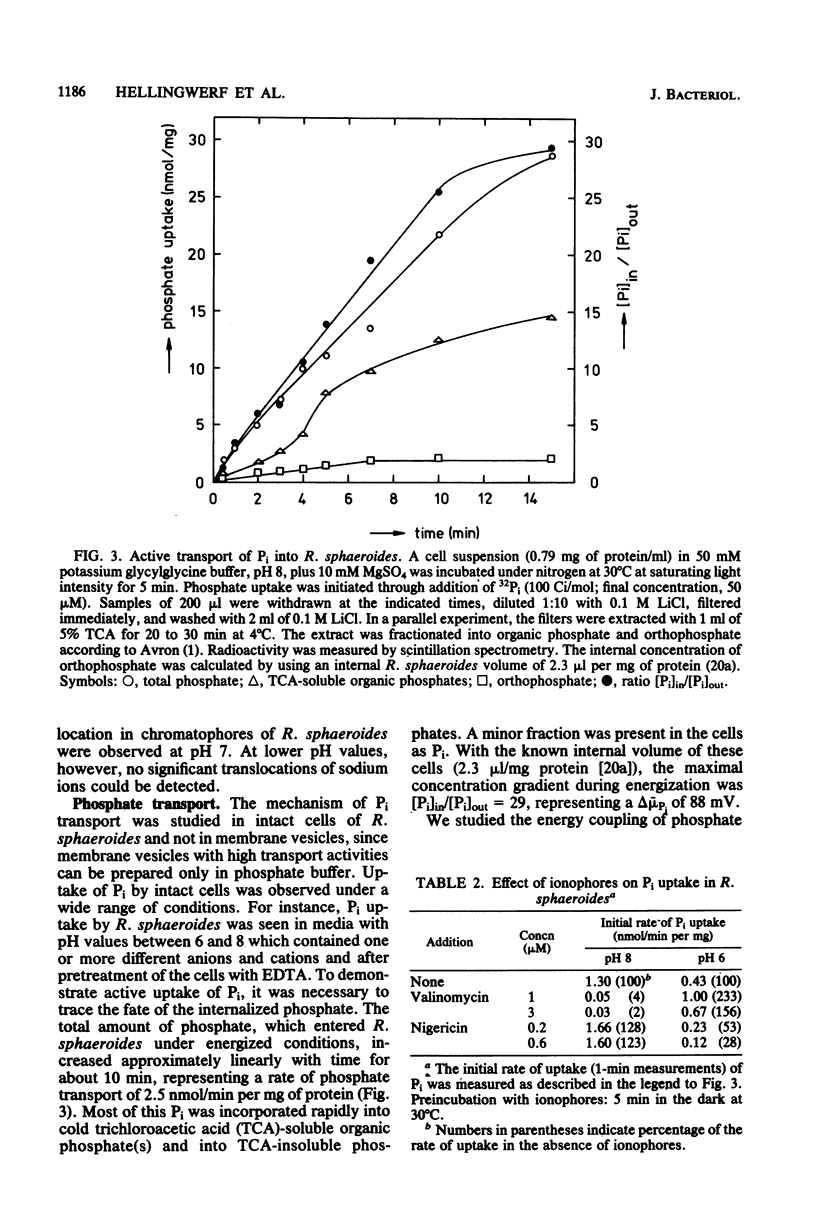
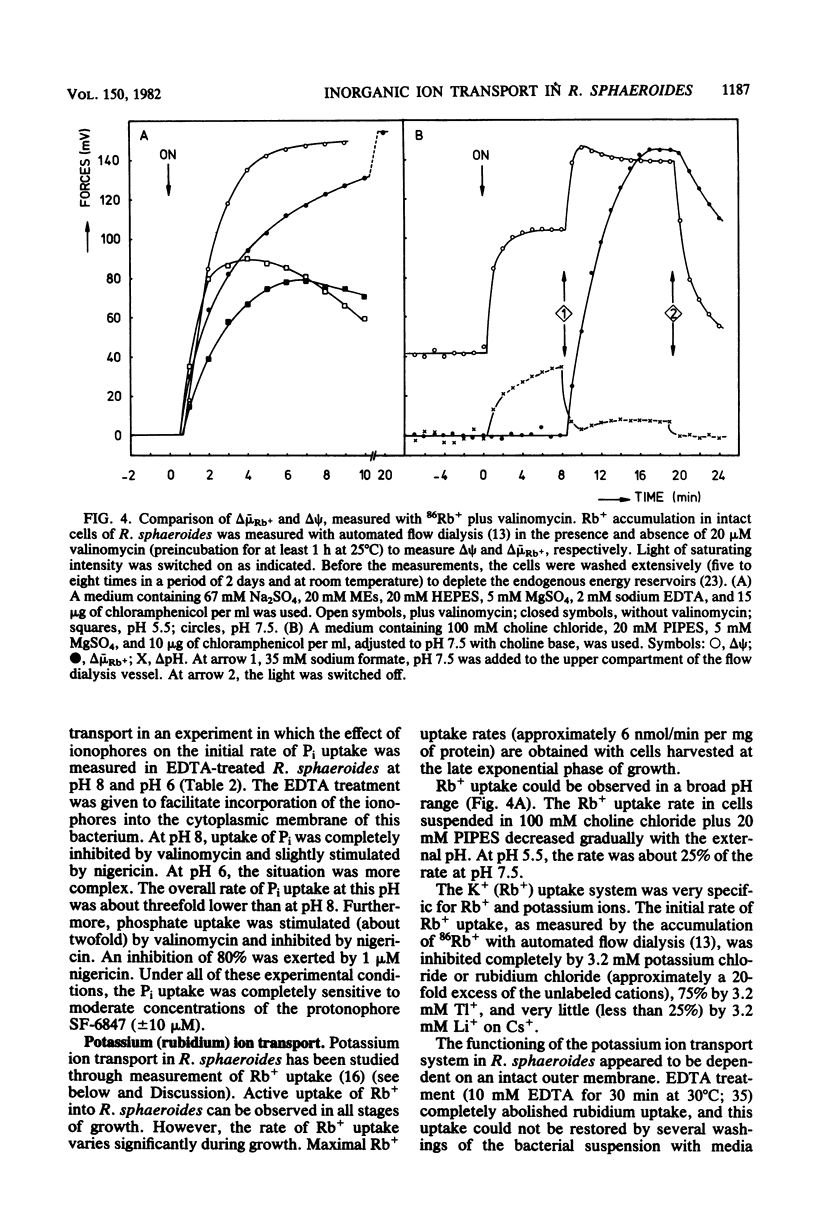
Within the scope of a study on the effects of changes in medium composition on the proton motive force in Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides, the energy coupling of sodium, phosphate, and potassium (rubidium) transport was investigated. Sodium was transported via an electroneutral exchange system against protons. The system functioned optimally at pH 8 and was inactive below pH 7. The driving force for the phosphate transport varied with the external pH. At pH 8, Pi transport was dependent exclusively on delta psi (transmembrane electrical potential), whereas at pH 6 only the delta pH (transmembrane pH gradient) component of the proton motive force was a driving force. Potassium (rubidium) transport was facilitated by a transport system which catalyzed the electrogenic transfer of potassium (rubidium) ions. However, in several aspects the properties of this transport system were different from those of a simple electrogenic potassium ionophore such as valinomycin: (i) accumulated potassium leaked very slowly out of cells in the dark; and (ii) the transport system displayed a threshold in the delta psi, below which potassium (rubidium) transport did not occur.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AVRON M. Photophosphorylation by swiss-chard chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 May 20;40:257–272. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91350-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker E. P., Harold F. M. Energy coupling to potassium transport in Streptococcus faecalis. Interplay of ATP and the protonmotive force. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):433–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger E. A., Heppel L. A. Different mechanisms of energy coupling for the shock-sensitive and shock-resistant amino acid permeases of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 25;249(24):7747–7755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brey R. N., Beck J. C., Rosen B. P. Cation/proton antiport systems in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Aug 29;83(4):1588–1594. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91403-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenbach M., Cooper S., Garty H., Johnstone R. M., Rottenberg H., Caplan S. R. Light-driven sodium transport in sub-bacterial particles of Halobacterium halobium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 17;465(3):599–613. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90276-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elferink M. G., Hellingwerf K. J., Michels P. A., Seÿen H. G., Konings W. N. Immunochemical analysis of membrane vesicles and chromatophoresis of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. FEBS Lett. 1979 Nov 15;107(2):300–307. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80395-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedberg I. Phosphate transport in Micrococcus lysodeikticus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 2;466(3):451–460. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90338-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedberg I. The effect of ionophores on phosphate and arsenate transport in Micrococcus lysodeikticus. FEBS Lett. 1977 Sep 15;81(2):264–266. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80531-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M., Spitz E. Accumulation of arsenate, phosphate, and aspartate by Sreptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Apr;122(1):266–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.1.266-277.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellingwerf K. J., Arents J. C., Scholte B. J., Westerhoff H. V. Bacteriorhodopsin in liposomes. II. Experimental evidence in support of a theoretical model. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Sep 11;547(3):561–582. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(79)90034-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong J. S., Hunt A. G., Masters P. S., Lieberman M. A. Requirements of acetyl phosphate for the binding protein-dependent transport systems in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1213–1217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasper P. Potassium transport system of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1314–1322. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1314-1322.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasper P., Silver S. Divalent cation transport systems of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1323–1328. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1323-1328.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K., Silverman M. P. Gating effects in Halobacterium halobium membrane transport. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4750–4755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K., Yearwood-Drayton V., MacDonald R. E. Light-induced glutamate transport in Halobacterium halobium envelope vesicles. I. Kinetics of the light-dependent and the sodium-gradient-dependent uptake. Biochemistry. 1976 Apr 20;15(8):1595–1603. doi: 10.1021/bi00653a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michels P. A., Konings W. N. The electrochemical proton gradient generated by light in membrane vesicles and chromatophores from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(1):147–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12222.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolay K., Kaptein R., Hellingwerf K. J., Konings W. N. 31P nuclear magnetic resonance studies of energy transduction in Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. Eur J Biochem. 1981 May;116(1):191–197. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05318.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolay K., Lolkema J., Hellingwerf K. J., Kaptein R., Konings W. N. Quantitative agreement between the values for the light-induced delta pH in Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides measured with automated follow-dialysis and 31P NMR. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jan 26;123(2):319–323. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80318-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Schuldiner S., Kaback H. R. The electrochemical gradient of protons and its relationship to active transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1892–1896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads D. B., Epstein W. Energy coupling to net K+ transport in Escherichia coli K-12. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1394–1401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads D. B., Woo A., Epstein W. Discrimination between Rb+ and K+ by Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 15;469(1):45–51. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90324-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robillard G. T., Konings W. N. Physical mechanism for regulation of phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent glucose transport activity in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1981 Aug 18;20(17):5025–5032. doi: 10.1021/bi00520a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romano A. H., Voytek A., Bruskin A. M. Energization of glucose transport by Pseudomonas fluorescens. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jun;142(3):755–762. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.3.755-762.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell L. M., Rosenberg H. The nature of the link between potassium transport and phosphate transport in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1980 Jun 15;188(3):715–723. doi: 10.1042/bj1880715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuldiner S., Fishkes H. Sodium-proton antiport in isolated membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1978 Feb 21;17(4):706–711. doi: 10.1021/bi00597a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen E. N., Rosen B. P. Effects of sodium and lithium ions on the potassium ion transport systems of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 1;19(7):1458–1462. doi: 10.1021/bi00548a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szmelcman S., Adler J. Change in membrane potential during bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4387–4391. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West I. C., Mitchell P. Proton/sodium ion antiport in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1974 Oct;144(1):87–90. doi: 10.1042/bj1440087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


