Abstract
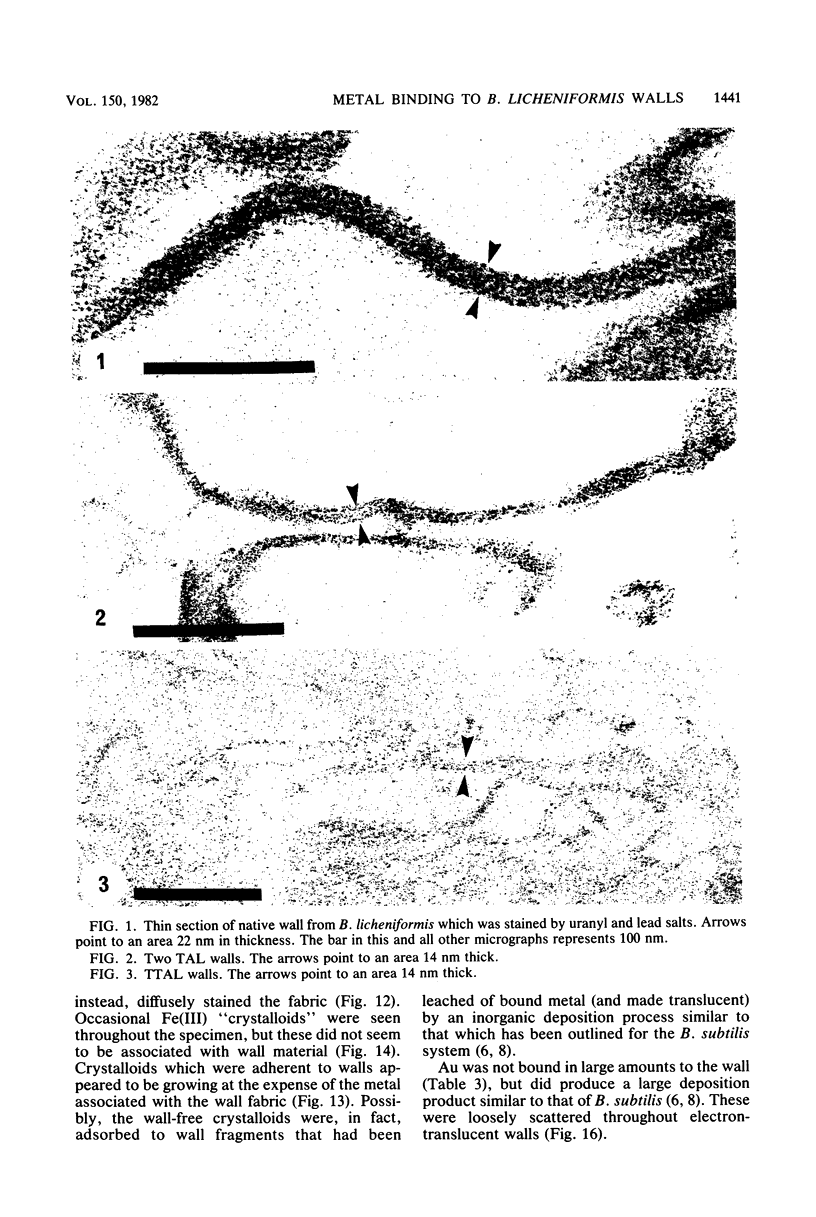
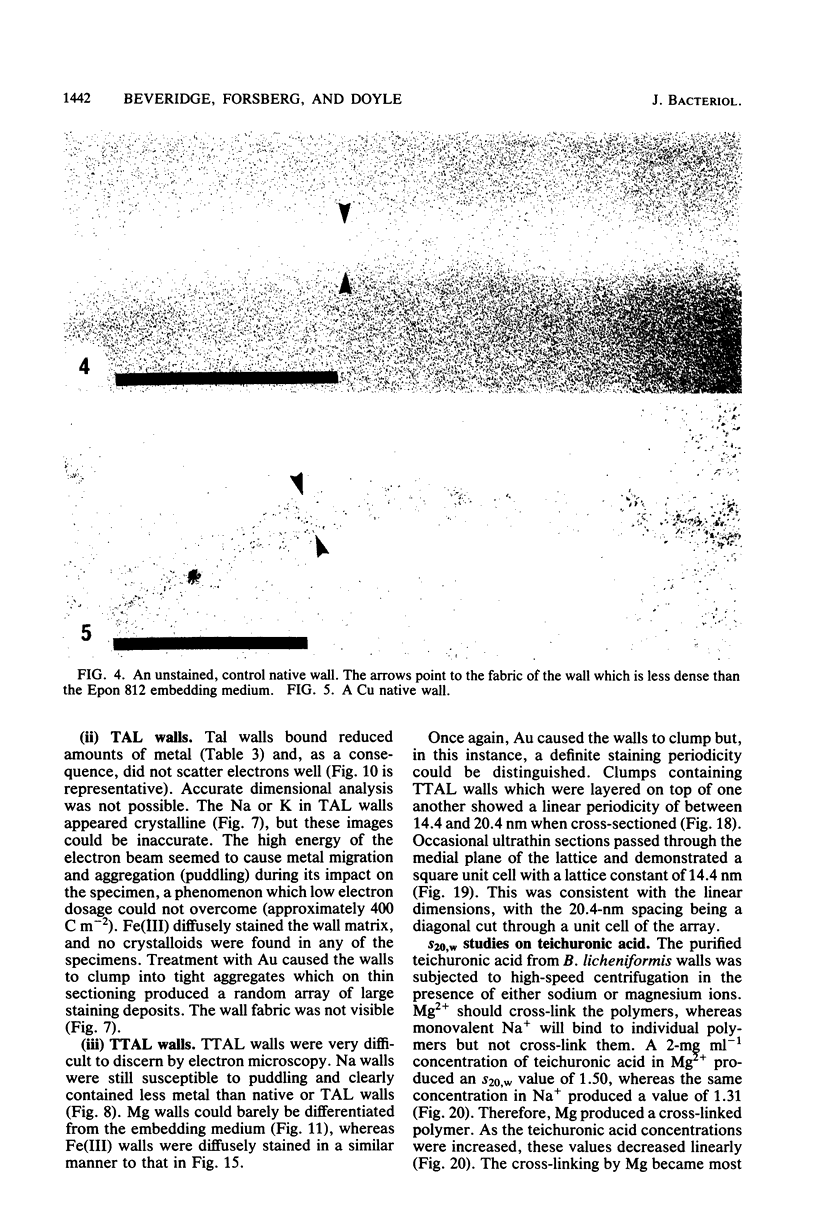
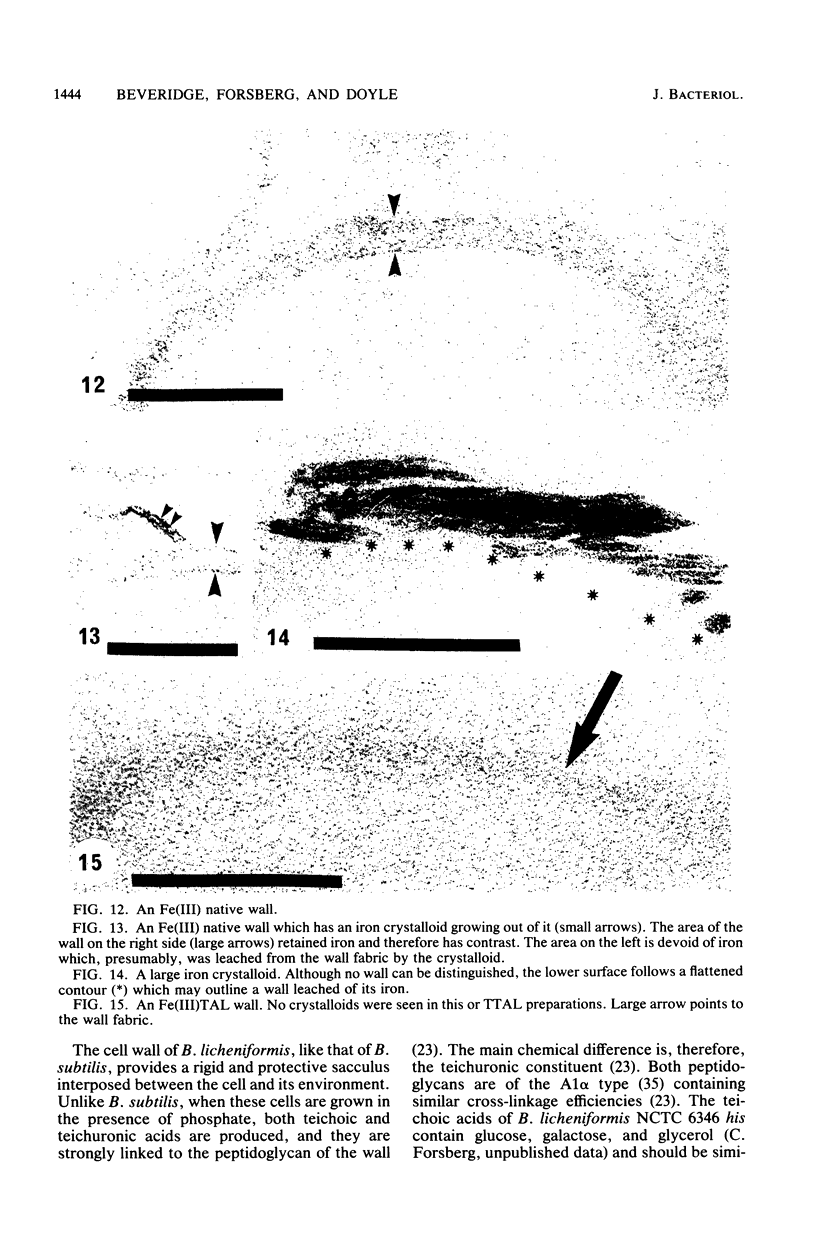
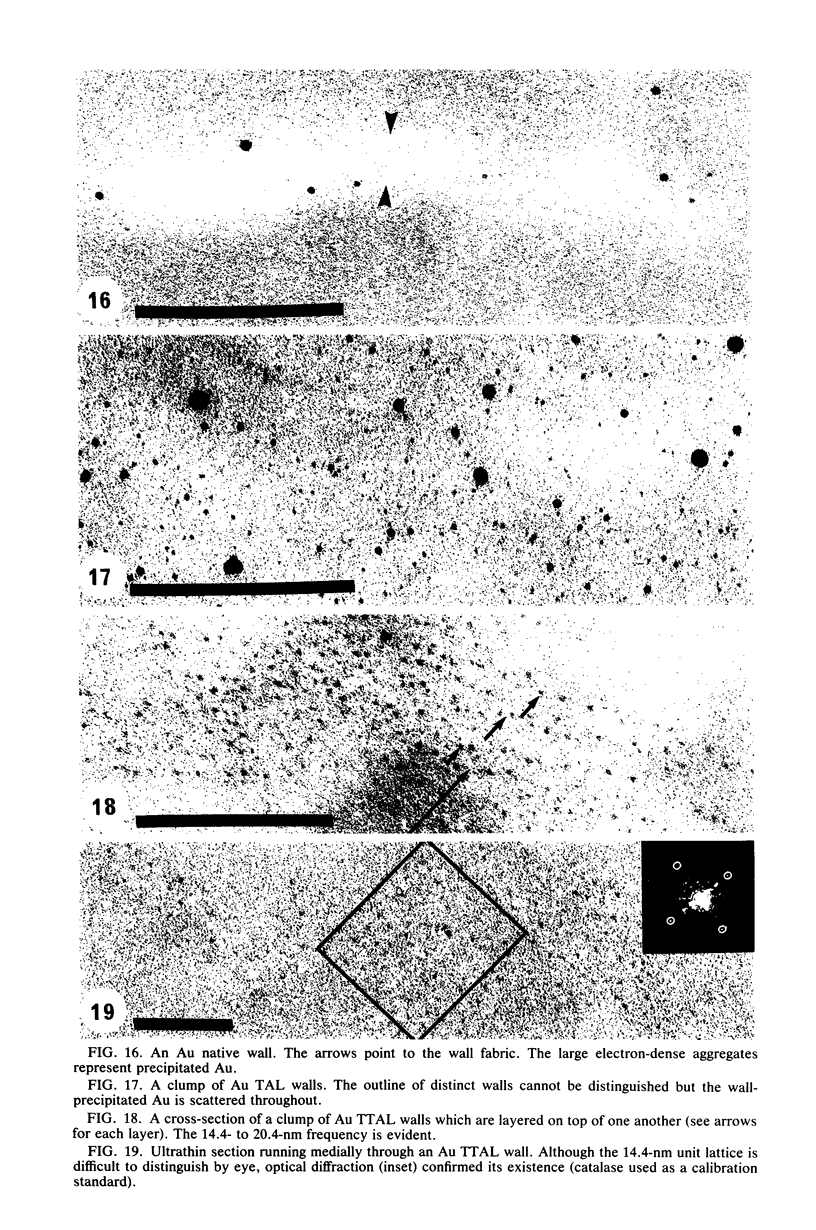
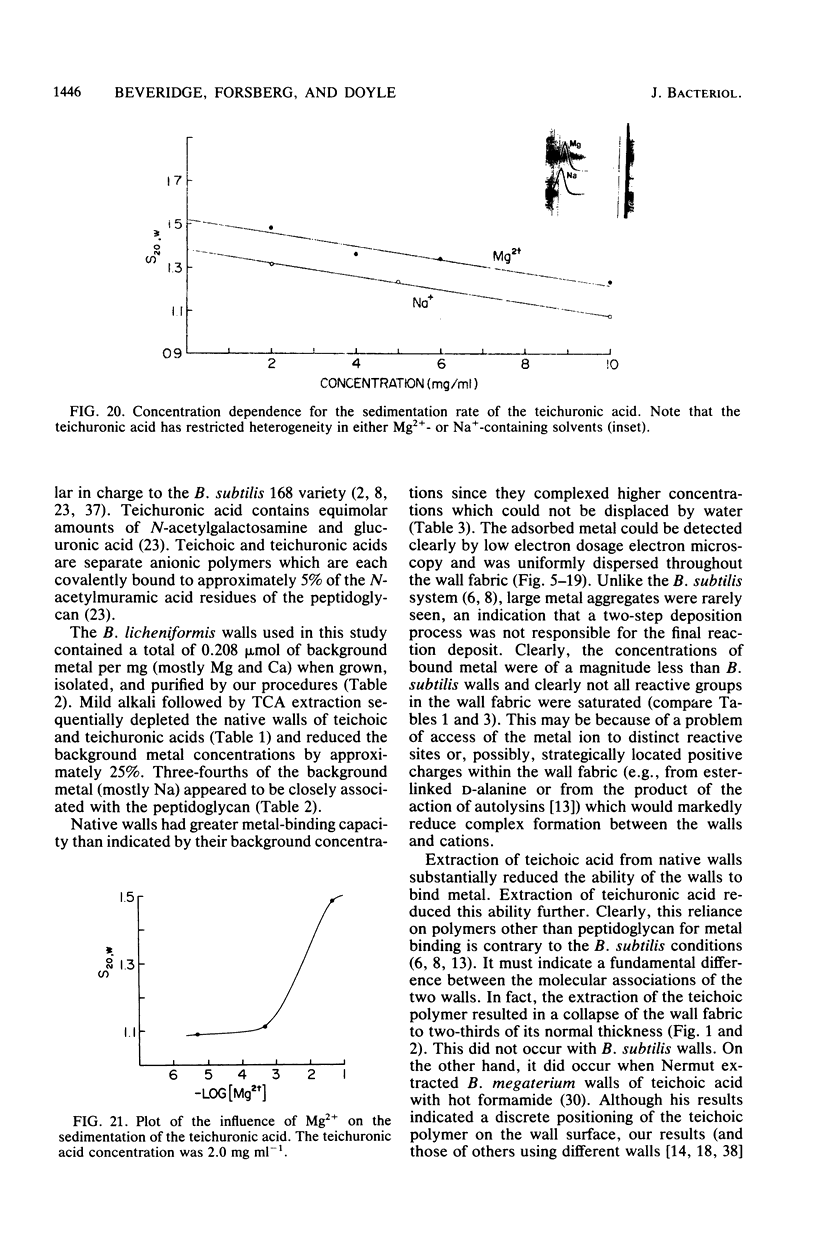
Isolated and purified walls of Bacillus licheniformis NCTC 6346 his contained peptidoglycan, teichoic acid, and teichuronic acid (0.36 mumol of diaminopimelic acid, 0.85 mumol of organic phosphorus, and 0.43 mumol of glucuronic acid per mg [dry weight] of walls, respectively). The walls also contained a total of 0.208 mumol of metal per mg. When these walls were subjected to metal-binding conditions (T. J. Beveridge and R. G. E. Murray, J. Bacteriol. 127:1502-1518, 1976) for nine metals, the amount of bound metal above background ranged from 0.910 mumol of Na to 0.031 mumol of Au per mg of walls. Most were in the 0.500-mumol mg-1 range. Electron-scattering profiles from unstained thin sections indicated that the metal was dispersed throughout the wall fabric. Mild alkali treatment extracted teichoic acid from the walls (97% based on phosphorus) but left the peptidoglycan and teichuronic acid intact. This treatment reduced their capacity for all metals but Au. Thin sections revealed that the wall thickness had been reduced by one-third, but metal was still dispersed throughout the wall fabric. Trichloroacetic acid treatment of the teichoic acid-less walls removed 95% of the teichuronic acid (based on glucuronic acid) but left the peptidoglycan intact (based on sedimentable diaminopimelic acid). The thickness of these walls was not further reduced, but little binding capacity remained (usually less than 10% of the original binding). The staining of these walls with Au produced a 14.4-nm repeat frequency within the peptidoglycan fabric. Sedimentation velocity experiments with the extracted teichuronic acid in the presence of metal confirmed it to be a potent metal-complexing polymer. These results indicated that teichoic and teichuronic acids are the prime sites of metal binding in B. licheniformis walls.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES B. N., DUBIN D. T. The role of polyamines in the neutralization of bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:769–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J., Jack T. Binding of an inert, cationic osmium probe to walls of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):1120–1123. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.1120-1123.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J., Murray R. G. Sites of metal deposition in the cell wall of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):876–887. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.876-887.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J., Murray R. G. Uptake and retention of metals by cell walls of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1502–1518. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1502-1518.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J. The response of cell walls of Bacillus subtilis to metals and to electron-microscopic stains. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Feb;24(2):89–104. doi: 10.1139/m78-018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J. Ultrastructure, chemistry, and function of the bacterial wall. Int Rev Cytol. 1981;72:229–317. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61198-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birdsell D. C., Doyle R. J., Morgenstern M. Organization of teichoic acid in the cell wall of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Feb;121(2):726–734. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.2.726-734.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Gnirke H., Henning U., Rehn K. Model for the structure of the shape-maintaining layer of the Escherichia coli cell envelope. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1264–1270. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1264-1270.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle R. J., Matthews T. H., Streips U. N. Chemical basis for selectivity of metal ions by the Bacillus subtilis cell wall. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):471–480. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.471-480.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle R. J., McDannel M. L., Helman J. R., Streips U. N. Distribution of teichoic acid in the cell wall of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Apr;122(1):152–158. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.1.152-158.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle R. J., McDannel M. L., Streips U. N., Birdsell D. C., Young F. E. Polyelectrolyte nature of bacterial teichoic acids. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):606–615. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.606-615.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einolf C. W., Jr, Carstensen E. L. Passive electrical properties of microorganisms. V. Low-frequency dielectric dispersion of bacteria. Biophys J. 1973 Jan;13(1):8–13. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(73)85966-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg C. W., Rogers H. J. Characterization of Bacillus licheniformis 6346 mutants which have altered lytic enzyme activities. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):358–368. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.358-368.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garland J. M., Archibald A. R., Baddiley J. An electron microscopic study of the location of teichoic acid and its contribution to staining reactions in walls of Streptococcus faecalis 8191. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Jul;89(1):73–86. doi: 10.1099/00221287-89-1-73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckels J. E., Lambert P. A., Baddiley J. Binding of magnesium ions to cell walls of Bacillus subtilis W23 containing teichoic acid or teichuronic acid. Biochem J. 1977 Feb 15;162(2):359–365. doi: 10.1042/bj1620359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heptinstall S., Archibald A. R., Baddiley J. Teichoic acids and membrane function in bacteria. Nature. 1970 Feb 7;225(5232):519–521. doi: 10.1038/225519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. H., Hancock I. C., Baddiley J. The function of teichoic acids in cation control in bacterial membranes. Biochem J. 1973 Jan;132(1):83–93. doi: 10.1042/bj1320083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R. C., Pavlik J. G., Rogers H. J., Tanner P. J. Organization of polymers in the cell walls of some bacilli. Nature. 1968 Aug 10;219(5154):642–644. doi: 10.1038/219642a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R. C., Tanner P. J. The action of dilute alkali on some bacterial cell walls. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Oct 10;33(1):22–28. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90248-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R. C. The isolation of structural components present in the cell wall of Bacillus licheniformis N.C.T.C. 6346. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):700–709. doi: 10.1042/bj0960700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R. C., Thurman P. F., Stokes E. Estimates of the porosity of Bacillus licheniformis and Bacillus subtilis cell walls. Z Immunitatsforsch Exp Klin Immunol. 1975 Jul;149(2-4):126–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. A., Hancock I. C., Baddiley J. The interaction of magnesium ions with teichoic acid. Biochem J. 1975 Sep;149(3):519–524. doi: 10.1042/bj1490519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquis R. E., Mayzel K., Carstensen E. L. Cation exchange in cell walls of gram-positive bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Jul;22(7):975–982. doi: 10.1139/m76-142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millward G. R., Reaveley D. A. Electron microscope observations on the cell walls of some gram-positive bacteria. J Ultrastruct Res. 1974 Mar;46(3):309–326. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(74)90059-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou L. T., Marquis R. E. Coccal cell-wall compactness and the swelling action of denaturants. Can J Microbiol. 1972 May;18(5):623–629. doi: 10.1139/m72-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaveley D. A., Rogers H. J. Some enzymic activities and chemical properties of the mesosomes and cytoplasmic membranes of Bacillus licheniformis 6346. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(1):67–79. doi: 10.1042/bj1130067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson R. L., Baddiley J. Role of teichuronic acid in Bacillus licheniformis: defective autolysis due to deficiency of teichuronic acid in a novobiocin-resistant mutant. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):1051–1058. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.1051-1058.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleifer K. H., Kandler O. Peptidoglycan types of bacterial cell walls and their taxonomic implications. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):407–477. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.407-477.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M., Beveridge T. J., Murray R. G. Structure of the regular surface layer of Spirillum putridiconchylium. J Mol Biol. 1980 Feb 15;137(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90153-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien H. C., Shockman G. D., Higgins M. L. Structural arrangement of polymers within the wall of Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):372–386. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.372-386.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WORK E. Reaction of ninhydrin in acid solution with straight-chain amino acids containing two amino groups and its application to the estimation of alpha epsilon-diaminopimelic acid. Biochem J. 1957 Nov;67(3):416–423. doi: 10.1042/bj0670416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. B. Teichoic and teichuronic acids: biosynthesis, assembly, and location. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Jun;45(2):211–243. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.2.211-243.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warth A. D., Strominger J. L. Structure of the peptidoglycan from vegetative cell walls of Bacillus subtilis. Biochemistry. 1971 Nov 23;10(24):4349–4358. doi: 10.1021/bi00800a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]