Abstract
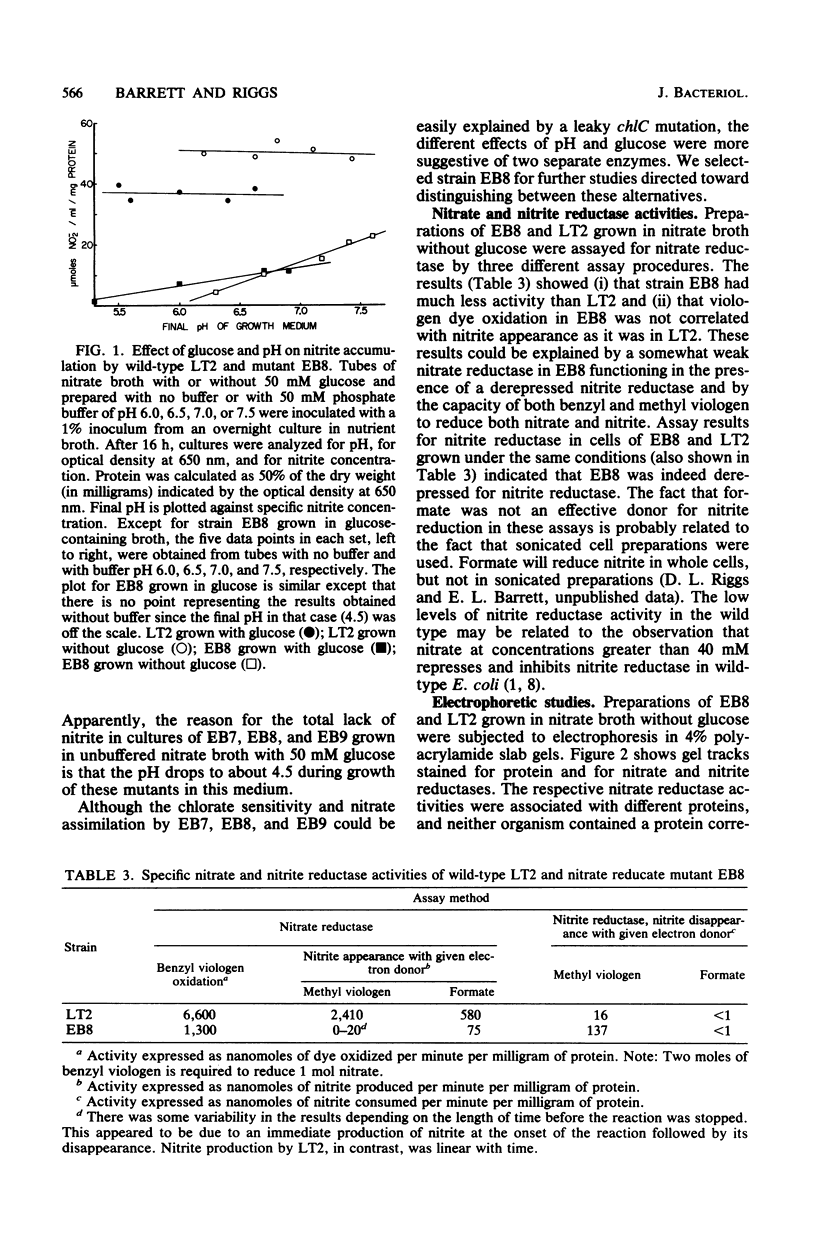
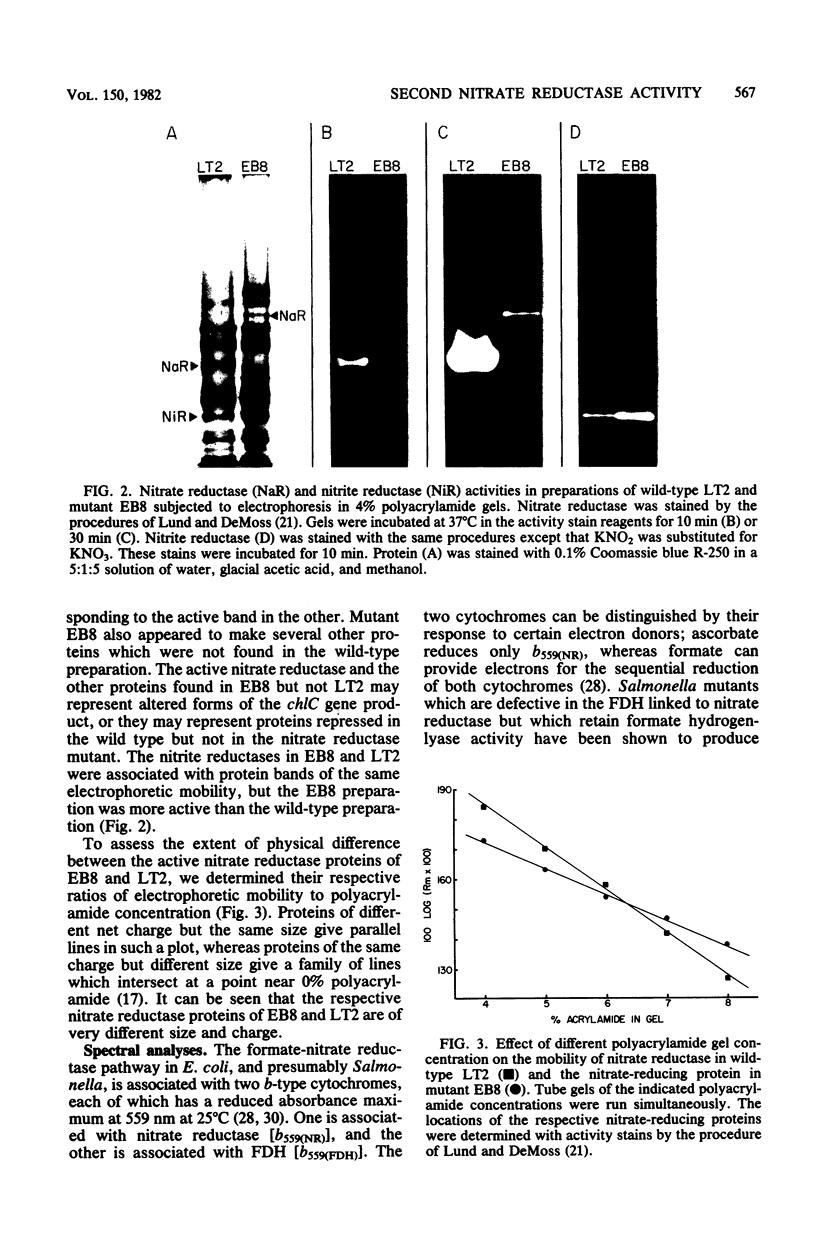
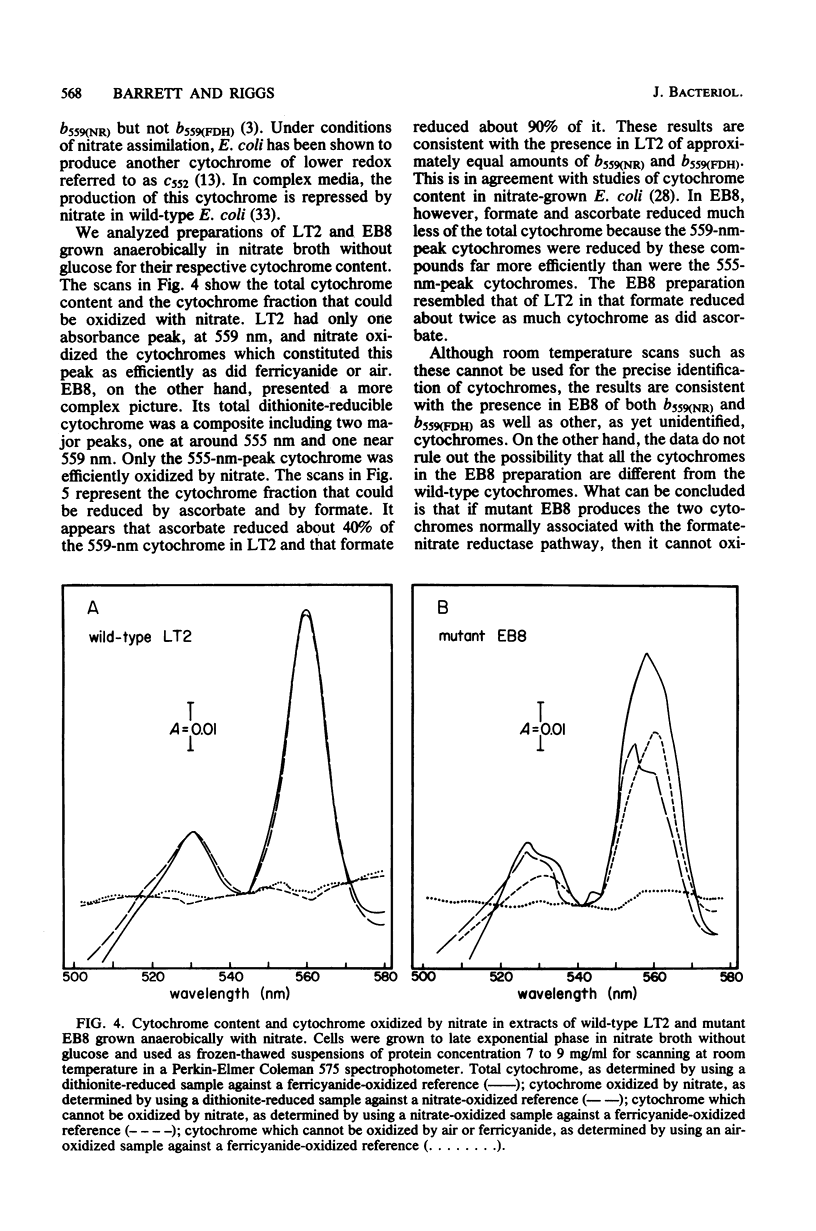
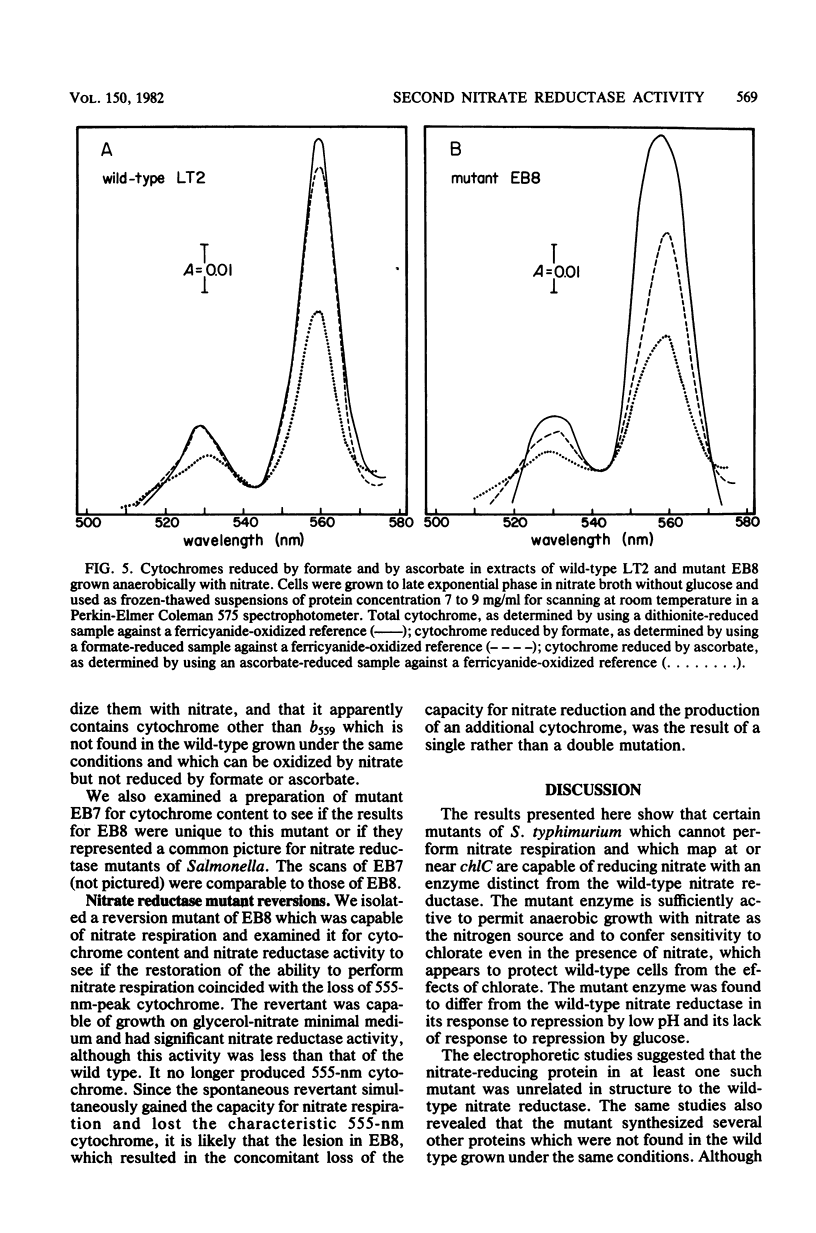
Significant nitrate reductase activity was detected in mutants of Salmonella typhimurium which mapped at or near chlC and which were incapable of growth with nitrate as electron acceptor. The same mutants were sensitive to chlorate and performed sufficient nitrate reduction to permit anaerobic growth with nitrate as the sole nitrogen source in media containing glucose. The mutant nitrate-reducing protein did not migrate with the wild-type nitrate reductase in polyacrylamide electrophoretic gels. Studies of the electrophoretic mobility in gels of different polyacrylamide concentration revealed that the wild-type and mutant nitrate reductases differed significantly in both size and charge. The second enzyme also differed from the wild-type major enzyme in its response to repression by low pH and its lack of response to repression by glucose. The same mutants were found to be derepressed for nitrite reductase and for a cytochrome with a maximal reduced absorbance at 555 nm at 25°C. This cytochrome was not detected in preparations of the wild type grown under the same conditions. Extracts of these mutants contained normal amounts of the b-type cytochromes which, in the wild type, were associated with nitrate reductase and formate dehydrogenase, respectively, although they could not mediate the oxidation of these cytochromes with nitrate. They were capable of oxidizing the derepressed 555-nm peak cytochrome with nitrate. It is suggested that these mutants synthesize a nitrate-reducing enzyme which is distinct from the chlC gene product and which is repressed in the wild type during anaerobic growth with nitrate.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ATKINSON D. E., MCNALL E. G. Nitrate reduction. I. Growth of Escherichia coli with nitrate as sole source of nitrogen. J Bacteriol. 1956 Aug;72(2):226–229. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.2.226-229.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abou-Jaoudé A., Chippaux M., Pascal M. C. Formate-nitrite reduction in Escherchia coli K12. 1. Physiological study of the system. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Apr 2;95(2):309–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12966.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett E. L., Jackson C. E., Fukumoto H. T., Chang G. W. Formate dehydrogenase mutants of Salmonella typhimurium: a new medium for their isolation and new mutant classes. Mol Gen Genet. 1979;177(1):95–101. doi: 10.1007/BF00267258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett E. L., Riggs D. L. Salmonella typhimurium mutants defective in the formate dehydrogenase linked to nitrate reductase. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):554–560. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.554-560.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck C. F., Ingraham J. L., Neuhard J. Location on the chromosome of Salmonella typhimurium of genes governing pyrimidine metabolism. II. Uridine kinase, cytosine deaminase and thymidine kinase. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;115(3):208–215. doi: 10.1007/BF00268884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casse F., Chippaux M., Pascal M. C. Isolation from Salmonella typhimurium LT2 of mutants lacking specifically nitrate reductase activity and mapping of the chl-C gene. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Aug 17;124(3):247–251. doi: 10.1007/BF00293095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casse F., Pascal M. C., Chippaux M. A mutant of Salmonella typhimurium deficient in tetrathionate reductase activity. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;119(1):71–74. doi: 10.1007/BF00270446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole J. A., Coleman K. J., Compton B. E., Kavanagh B. M., Keevil C. W. Nitrite and ammonia assimilation by anaerobic continuous cultures of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Nov;85(1):11–22. doi: 10.1099/00221287-85-1-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole J. A., Wimpenny J. W. Metabolic pathways for nitrate reduction in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jul 16;162(1):39–48. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(68)90212-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman K. J., Cornish-Bowden A., Cole J. A. Purification and properties of nitrite reductase from Escherichia coli K12. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 1;175(2):483–493. doi: 10.1042/bj1750483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMoss J. A. Role of the chlC gene in formation of the formate-nitrate reductase pathway in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):626–630. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.626-630.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Sato R. Studies on soluble cytochromes in Enterobacteriaceae. IV. Possible involvement of cytochrome c-552 in anaerobic nitrite metabolism. J Biochem. 1966 Dec;60(6):691–700. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser J. H., DeMoss J. A. Comparison of nitrate reductase mutants of Escherichia coli selected by alternative procedures. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;116(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF00334254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guest J. R. Biochemical and genetic studies with nitrate reductase C-gene mutants of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1969;105(4):285–297. doi: 10.1007/BF00277583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutnick D., Calvo J. M., Klopotowski T., Ames B. N. Compounds which serve as the sole source of carbon or nitrogen for Salmonella typhimurium LT-2. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):215–219. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.215-219.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman P. E. Some improved methods in P22 transduction. Genetics. 1974 Apr;76(4):625–631. doi: 10.1093/genetics/76.4.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick J. L., Smith A. J. Size and charge isomer separation and estimation of molecular weights of proteins by disc gel electrophoresis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Jul;126(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90569-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWE R. H., EVANS H. J. PREPARATION AND SOME PROPERTIES OF A SOLUBLE NITRATE REDUCTASE FROM RHIZOBIUM JAPONICUM. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jun 1;85:377–389. doi: 10.1016/0926-6569(64)90301-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester R. L., DeMoss J. A. Effects of molybdate and selenite on formate and nitrate metabolism in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):1006–1014. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.1006-1014.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund K., DeMoss J. A. Association-dissociation behavior and subunit structure of heat-released nitrate reductase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 25;251(8):2207–2216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor C. H. Synthesis of nitrate reductase components in chlorate-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):1117–1121. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.1117-1121.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orth V., Chippaux M., Pascal M. C. A mutant defective in electron transfer to nitrate in Escherichia coli K12. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Mar;117(1):257–262. doi: 10.1099/00221287-117-1-257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pichinoty F., Chippaux M. Recherches sur des mutants bactériens ayant perdu les activités catalytiques liées à la nitrate-réductase A. 3. Caractères biochimiques. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1969 Aug;117(2):145–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piéchaud M., Puig J., Pichinoty F., Azoulay E., Le Minor L. Mutations affectant la nitrate-réductase A et d'autres enzymes bactériennes d'oxydoréduction. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1967 Jan;112(1):24–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Herrera J., DeMoss J. A. Nitrate reductase complex of Escherichia coli K-12: participation of specific formate dehydrogenase and cytochrome b1 components in nitrate reduction. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):720–729. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.720-729.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Herrera J., Showe M. K., DeMoss J. A. Nitrate reductase complex of Escherichia coli K-12: isolation and characterization of mutants unable to reduce nitrate. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1291–1297. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1291-1297.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. H., DeMoss J. A. Formation of the formate-nitrate electron transport pathway from inactive components in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;126(1):478–486. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.1.478-486.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Levine M. A phage P22 gene controlling integration of prophage. Virology. 1967 Feb;31(2):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90164-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stouthamer A. H. A genetical and biochemical study of chlorate-resistant mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1969;35(4):505–521. doi: 10.1007/BF02219168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venables W. A., Wimpenny J. W., Cole J. A. Enzymic properties of a mutant of Escherichia coli K12 lacking nitrate reductase. Arch Mikrobiol. 1968;63(2):117–121. doi: 10.1007/BF00412166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimpenny J. W., Cole J. A. The regulation of metabolism in facultative bacteria. 3. The effect of nitrate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Oct 9;148(1):233–242. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90298-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



