Abstract
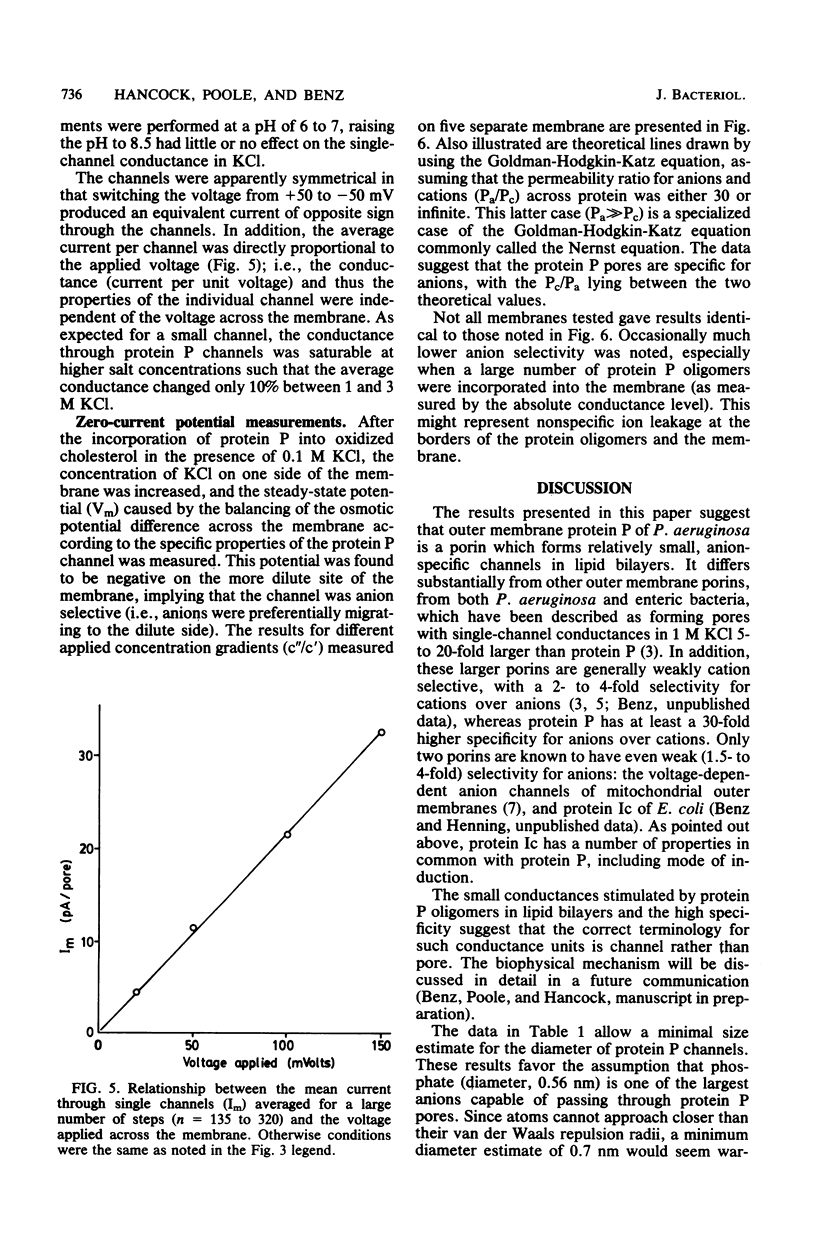
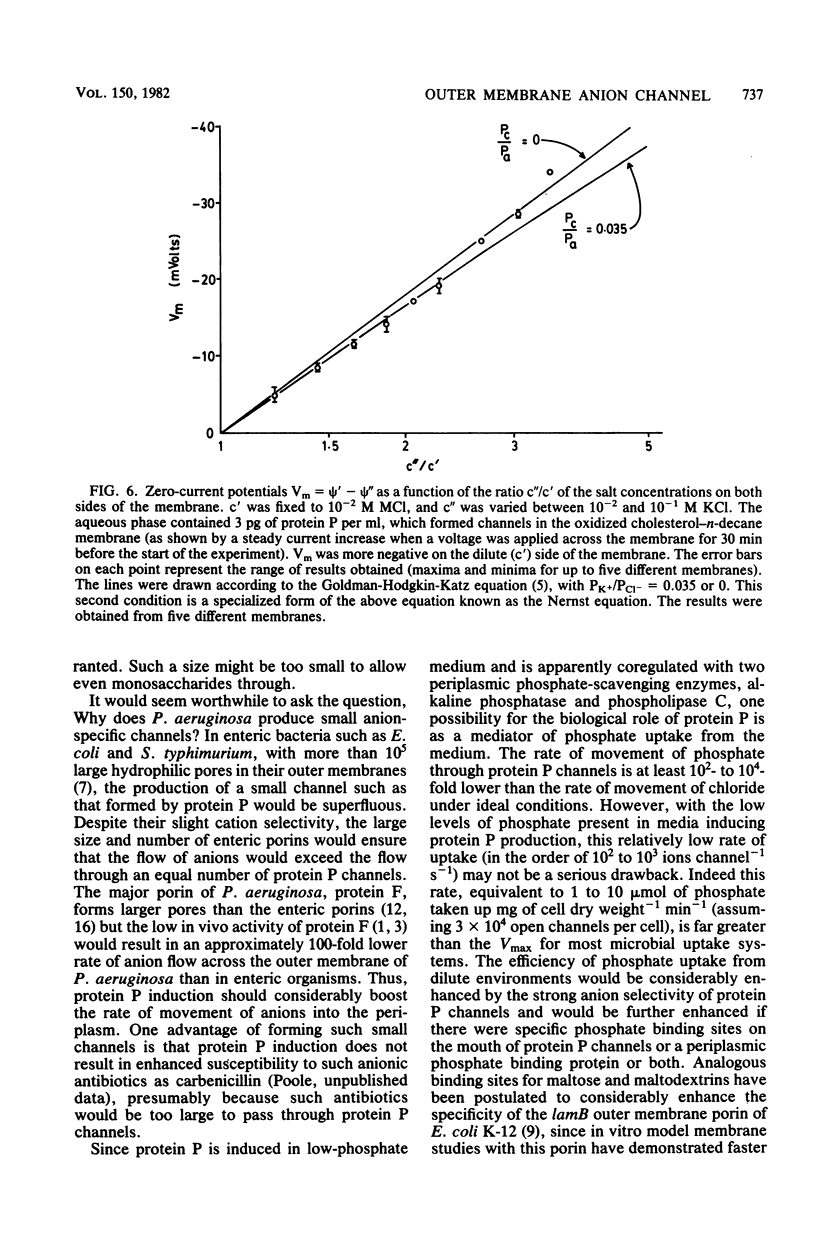
A new major outer membrane protein, P, was induced in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 upon growth in medium containing 0.2 mM or less inorganic phosphate. Studies with media containing different levels of phosphate and with mutants of PAO1 suggested that protein P was coregulated with alkaline phosphatase and phospholipase C. Protein P was substantially purified and shown to form sodium dodecyl sulfate-resistant oligomers on polyacrylamide gels. The incorporation of purified protein P into artificial lipid bilayers resulted in an increase of the membrane conductance by many orders of magnitude. Single-channel experiments demonstrated that protein P channels were substantially smaller than all previously studied porins from P. aeruginosa and enteric bacteria, with an average single-channel conductance in 1 M NaCl of 0.25 nS. The protein P channel was apparently not voltage induced or regulated. The results of single-channel conductance experiments, using a variety of different salts, allowed a minimum channel diameter estimate of 0.7 nm. Furthermore, from these results it was concluded that the protein P channel was highly specific for anions. Zero-current potential measurements confirmed that protein P was at least 30-fold more permeable for Cl- than for K+ ions. The possible biological role of the small, anion-specific protein P channels in phosphate uptake from the medium is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angus B. L., Carey A. M., Caron D. A., Kropinski A. M., Hancock R. E. Outer membrane permeability in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: comparison of a wild-type with an antibiotic-supersusceptible mutant. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Feb;21(2):299–309. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Boehler-Kohler B. A., Dieterle R., Boos W. Porin activity in the osmotic shock fluid of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):1080–1090. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.1080-1090.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Hancock R. E. Properties of the large ion-permeable pores formed from protein F of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in lipid bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Aug 20;646(2):298–308. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90336-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Ishii J., Nakae T. Determination of ion permeability through the channels made of porins from the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium in lipid bilayer membranes. J Membr Biol. 1980 Aug 21;56(1):19–29. doi: 10.1007/BF01869348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Janko K., Boos W., Läuger P. Formation of large, ion-permeable membrane channels by the matrix protein (porin) of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Aug 17;511(3):305–319. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90269-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Janko K., Läuger P. Ionic selectivity of pores formed by the matrix protein (porin) of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 8;551(2):238–247. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90002-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. J., Ingram J. M., Costerton J. W. Release of alkaline phosphatase from cells of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by manipulation of cation concentration and of pH. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):748–753. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.748-753.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombini M. A candidate for the permeability pathway of the outer mitochondrial membrane. Nature. 1979 Jun 14;279(5714):643–645. doi: 10.1038/279643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferenci T., Boos W. The role of the Escherichia coli lambda receptor in the transport of maltose and maltodextrins. J Supramol Struct. 1980;13(1):101–116. doi: 10.1002/jss.400130110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Carey A. M. Outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: heat- 2-mercaptoethanol-modifiable proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):902–910. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.902-910.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Decad G. M., Nikaido H. Identification of the protein producing transmembrane diffusion pores in the outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA01. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jul 5;554(2):323–331. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90373-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Irvin R. T., Costerton J. W., Carey A. M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane: peptidoglycan-associated proteins. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):628–631. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.628-631.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Raffle V. J., Nicas T. I. Involvement of the outer membrane in gentamicin and streptomycin uptake and killing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 May;19(5):777–785. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.5.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckey M., Nikaido H. Specificity of diffusion channels produced by lambda phage receptor protein of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):167–171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakae T., Ishii J., Tokunaga M. Subunit structure of functional porin oligomers that form permeability channels in the other membrane of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 10;254(5):1457–1461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler H., Rosenbusch J. P. Matrix protein from Escherichia coli outer membranes forms voltage-controlled channels in lipid bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3751–3755. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson M. W., Hayden C. Secretion of phospholipase C by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):558–564. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.558-564.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tommassen J., Lugtenberg B. Outer membrane protein e of Escherichia coli K-12 is co-regulated with alkaline phosphatase. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):151–157. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.151-157.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]