Abstract
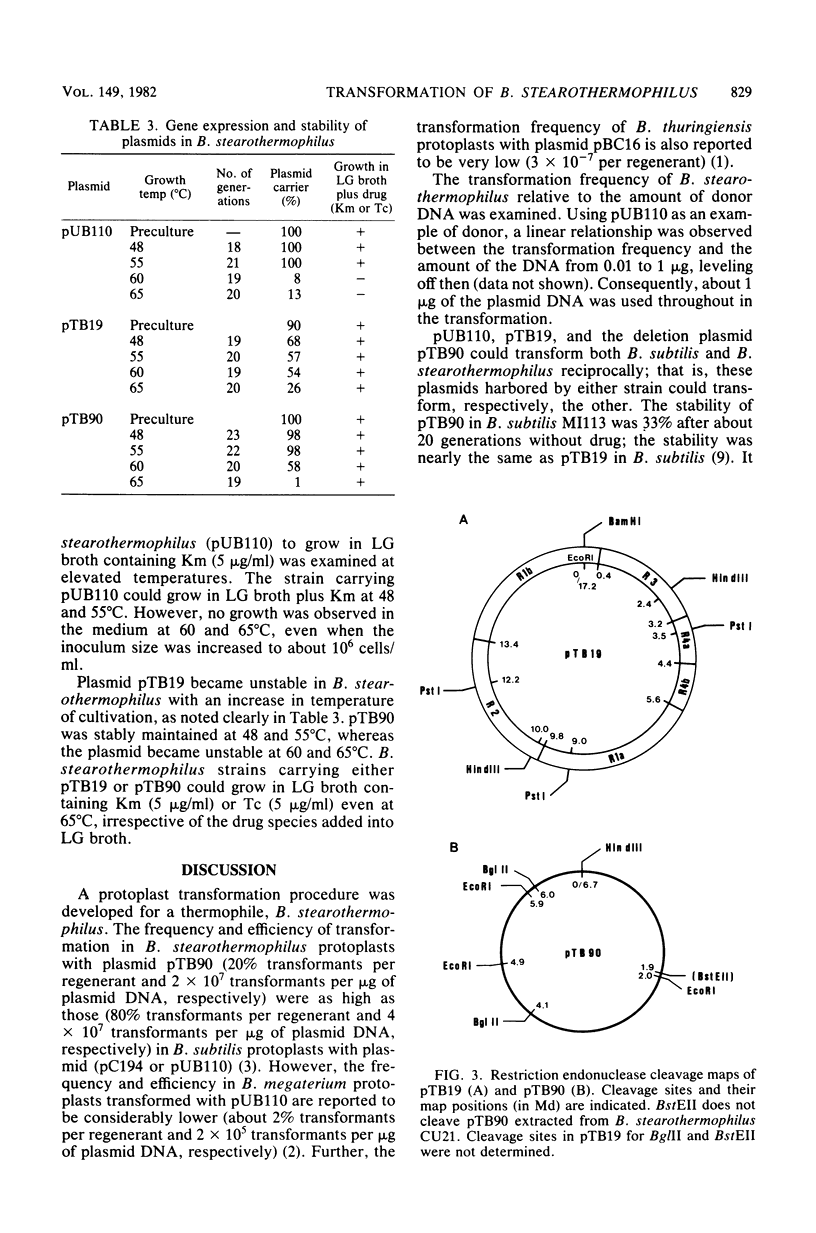
A thermophilic bacterium Bacillus stearothermophilus IFO 12550 (ATCC 12980) was transformed with each of the following plasmids, pUB110 (kanamycin resistance, Kmr), pTB19 (Kmr and tetracycline resistance [Tcr]), and its derivative pTB90 (Kmr Tcr), by the protoplast procedure in the presence of polyethylene glycol at 48 degrees C. The transformation frequencies per regenerant for pUB110, pTB19, and pTB90 were 5.9 x 10(-3), 5.5 x 10(-3), and 2.0 x 10(-1), respectively. Among these plasmids, pTB90 was newly derived, and the restriction endonuclease cleavage map was constructed. When tetracycline (5 micrograms/ml) was added into the culture medium, the copy number of pTB90 in B. stearothermophilus was about fourfold higher than that when kanamycin (5 micrograms/ml) was added instead of tetracycline. Bacillus subtilis could also be transformed with the plasmids extracted from B. stearothermophilus and vice versa. Accordingly, pUB110, pTB19, and pTB90 served as shuttle vectors between B. stearothermophilus and B. subtilis. The requirements for replication of pTB19 in B. subtilis and B. stearothermophilus appear to be different, because some deletion plasmids (pTB51, pTB52, and pTB53) derived from pTB19 could replicate only in B. subtilis, whereas another deletion plasmid pTB92 could replicate solely in B. stearothermophilus. Plasmids pTB19 and pTB90 could be maintained and expressed in B. stearothermophilus up to 65 degrees C, whereas the expression of pUB110 in the same strain was up to 55 degrees C.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alikhanian S. I., Ryabchenko N. F., Bukanov N. O., Sakanyan V. A. Transformation of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. galleria protoplasts by plasmid pBC16. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):7–9. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.7-9.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown B. J., Carlton B. C. Plasmid-mediated transformation in Bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):508–512. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.508-512.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S., Cohen S. N. High frequency transformation of Bacillus subtilis protoplasts by plasmid DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 5;168(1):111–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00267940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich S. D. DNA cloning in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1433–1436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabor M. H., Hotchkiss R. D. Parameters governing bacterial regeneration and genetic recombination after fusion of Bacillus subtilis protoplasts. J Bacteriol. 1979 Mar;137(3):1346–1353. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.3.1346-1353.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryczan T. J., Contente S., Dubnau D. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus plasmids introduced by transformation into Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Apr;134(1):318–329. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.1.318-329.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imanaka T., Fujii M., Aiba S. Isolation and characterization of antibiotic resistance plasmids from thermophilic bacilli and construction of deletion plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):1091–1097. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.1091-1097.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imanaka T., Tanaka T., Tsunekawa H., Aiba S. Cloning of the genes for penicillinase, penP and penI, of Bacillus licheniformis in some vector plasmids and their expression in Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, and Bacillus licheniformis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):776–786. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.776-786.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imanaka T., Tsunekawa H., Aiba S. Phenotypic stability of trp operon recombinant plasmids in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 May;118(1):253–261. doi: 10.1099/00221287-118-1-253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keggins K. M., Lovett P. S., Duvall E. J. Molecular cloning of genetically active fragments of Bacillus DNA in Bacillus subtilis and properties of the vector plasmid pUB110. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1423–1427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P. A., Lohr J. R., Dean D. H. Transformation of Bacillus thuringiensis protoplasts by plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):980–983. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.980-983.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. J. Restriction and modification enzymes and their recognition sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):r63–r80. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.197-d. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyrick P. B., Rogers H. J. Isolation and characterization of cell wall-defective variants of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis. J Bacteriol. 1973 Oct;116(1):456–465. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.1.456-465.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]