Abstract
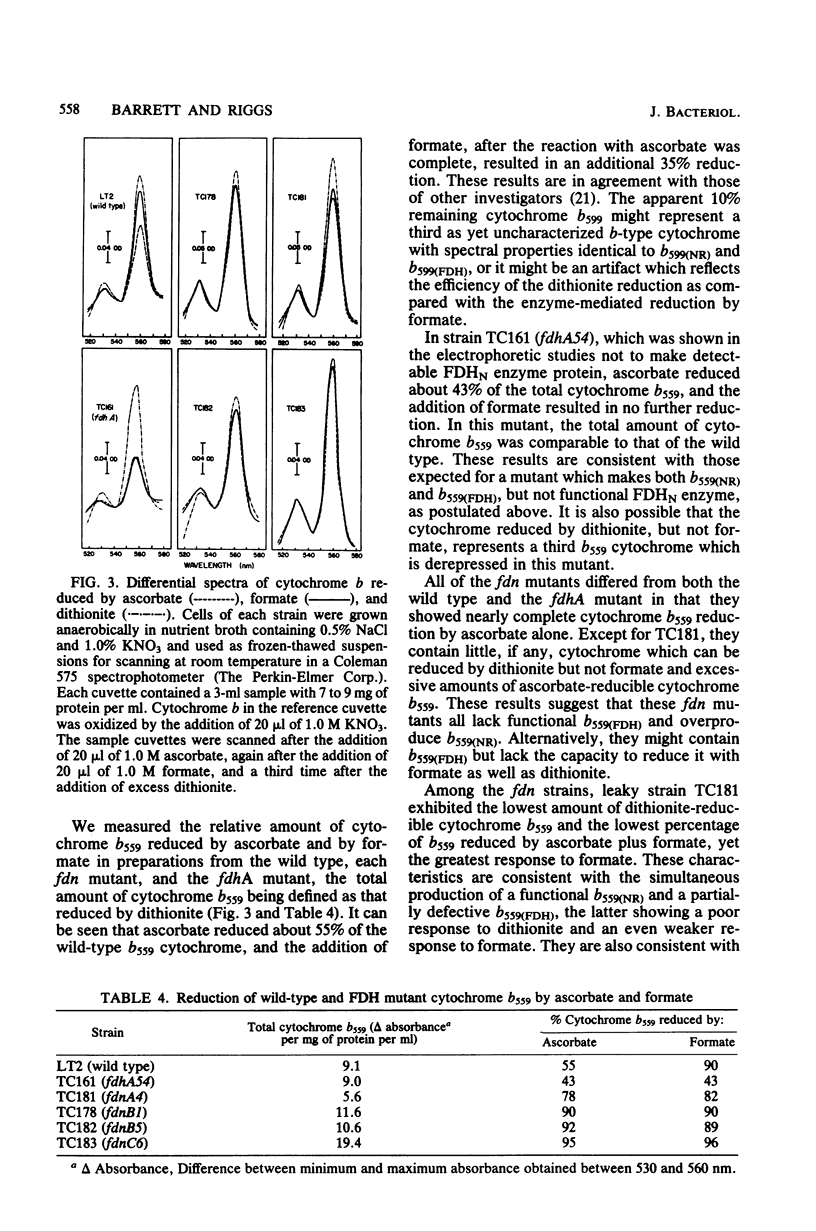
Six fdn mutants of Salmonella typhimurium defective in the formation of nitrate reductase-linked formate dehydrogenase (FDHN) but capable of producing both the hydrogenase-linked formate dehydrogenase (FDHH) and nitrate reductase were characterized. Results of phage P22 transduction experiments indicated that there may be three fdn genes located on the metE-metB chromosomal segment and distinct from all previously identified fdh and chl loci. All six FDHH+ FDHN- mutants were found to make FDHN enzyme protein which was indistinguishable from that of the wild type in electrophoretic studies. However, the results of the spectral studies indicated that all six mutants were defective in the anaerobic cytochrome b559 associated with FDHN. All contained the cytochrome b559 associated with nitrate reductase in amounts equal to or greater than the wild type. The results of the transduction experiments also indicated that the metE- metB segment of the Salmonella chromosome resembles that of Escherichia coli more than was originally thought.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J., Low K. B. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 6. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Mar;44(1):1–56. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.1.1-56.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett E. L., Jackson C. E., Fukumoto H. T., Chang G. W. Formate dehydrogenase mutants of Salmonella typhimurium: a new medium for their isolation and new mutant classes. Mol Gen Genet. 1979;177(1):95–101. doi: 10.1007/BF00267258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chippaux M., Casse F., Pascal M. C. Isolation and phenotypes of mutants from Salmonella typhimurium defective in formate hydrogenlyase activity. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):766–768. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.766-768.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chippaux M., Pascal M. C., Casse F. Formate hydrogenlyase system in Salmonella typhimurium LT2. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jan 3;72(1):149–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11234.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. C., Edwards E. S., DeMoss J. A. Resolution of distinct selenium-containing formate dehydrogenases from Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1317–1324. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1317-1324.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMoss J. A. Role of the chlC gene in formation of the formate-nitrate reductase pathway in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):626–630. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.626-630.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enoch H. G., Lester R. L. Effects of molybdate, tungstate, and selenium compounds on formate dehydrogenase and other enzyme systems in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jun;110(3):1032–1040. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.3.1032-1040.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enoch H. G., Lester R. L. The purification and properties of formate dehydrogenase and nitrate reductase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 10;250(17):6693–6705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enoch H. G., Lester R. L. The role of a novel cytochrome b-containing nitrate reductase and quinone in the in vitro reconstruction of formate-nitrate reductase activity of E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Dec 23;61(4):1234–1241. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80416-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser J. H., DeMoss J. A. Comparison of nitrate reductase mutants of Escherichia coli selected by alternative procedures. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;116(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF00334254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutnick D., Calvo J. M., Klopotowski T., Ames B. N. Compounds which serve as the sole source of carbon or nitrogen for Salmonella typhimurium LT-2. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):215–219. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.215-219.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackett C. S., MacGregor C. H. Synthesis and degradation of nitrate reductase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):352–359. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.352-359.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman P. E. Some improved methods in P22 transduction. Genetics. 1974 Apr;76(4):625–631. doi: 10.1093/genetics/76.4.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester R. L., DeMoss J. A. Effects of molybdate and selenite on formate and nitrate metabolism in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):1006–1014. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.1006-1014.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund K., DeMoss J. A. Association-dissociation behavior and subunit structure of heat-released nitrate reductase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 25;251(8):2207–2216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor C. H. Synthesis of nitrate reductase components in chlorate-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):1117–1121. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.1117-1121.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PECK H. D., Jr, GEST H. Formic dehydrogenase and the hydrogenlyase enzyme complex in coli-aerogenes bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1957 Jun;73(6):706–721. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.6.706-721.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Herrera J., DeMoss J. A. Nitrate reductase complex of Escherichia coli K-12: participation of specific formate dehydrogenase and cytochrome b1 components in nitrate reduction. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):720–729. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.720-729.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., Hartman P. E. Linkage map of Salmonella typhimurium, edition V. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Jun;42(2):471–519. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.2.471-519.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. H., DeMoss J. A. Formation of the formate-nitrate electron transport pathway from inactive components in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;126(1):478–486. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.1.478-486.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Levine M. A phage P22 gene controlling integration of prophage. Virology. 1967 Feb;31(2):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90164-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stouthamer A. H. A genetical and biochemical study of chlorate-resistant mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1969;35(4):505–521. doi: 10.1007/BF02219168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace B. J., Young I. G. Role of quinones in electron transport to oxygen and nitrate in Escherichia coli. Studies with a ubiA- menA- double quinone mutant. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jul 7;461(1):84–100. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(77)90071-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]