Abstract
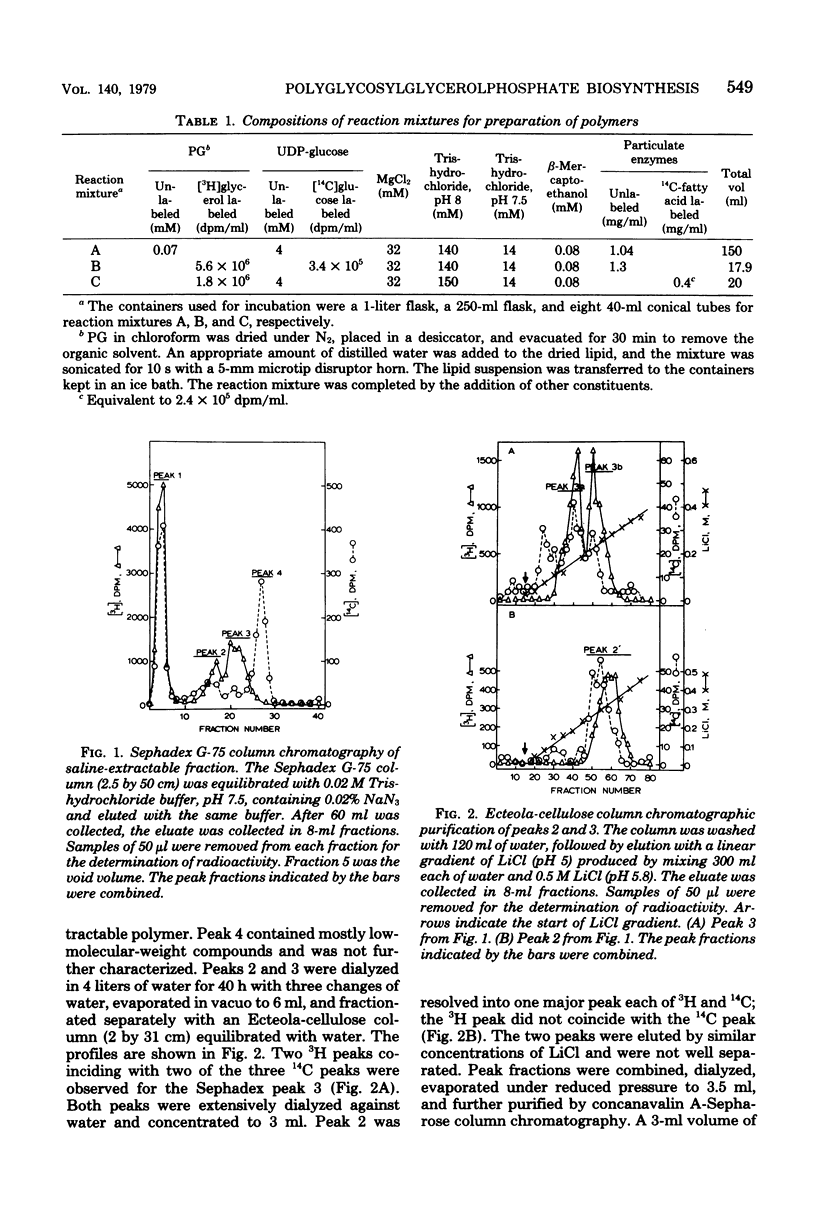
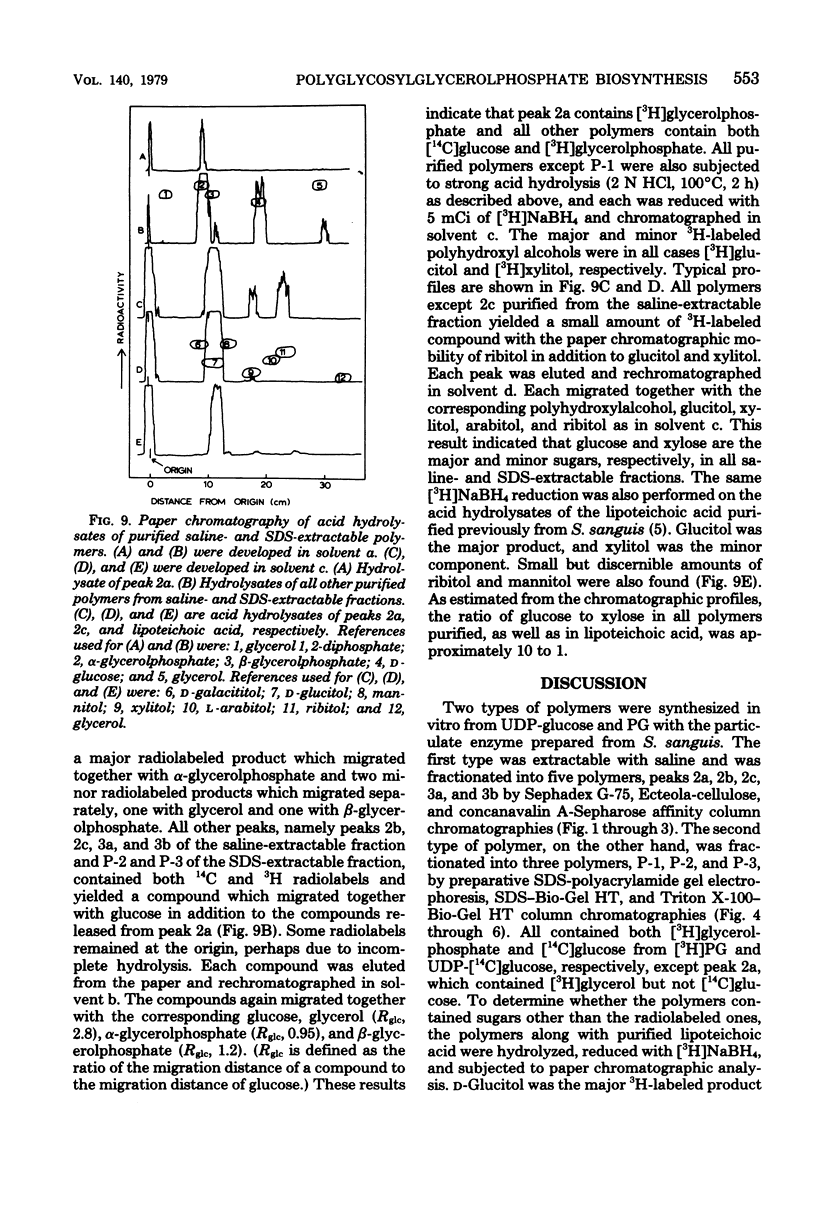
Two types of glycosylated glycerolphosphates were synthesized when a particulate enzyme prepared from Streptococcus sanguis was incubated with [3H]-phosphatidylglycerol and uridine diphosphate-[14C]glucose in the presence of MgCl2. The first type was extractable with saline and contained no fatty acid. The second type was pellet bound and could be extracted with 0.1% sodium dodecyl sulfate. Both types of polymers were purified and partially characterized. The first type of polymer was fractionated into five polymers, peaks 2a, 2b, 2c, 3a, and 3b. All except peak 2a, which contained only [3H]glycerol, contained both [3H]glycerol and [14C]glucose. [3H]NaBH4 reduction of acid hydrolysates of the polymers revealed that all of the polymers contained glucose as the major sugar componenta nd xylose as the minor sugar component. The second type of polymer was fractionated into three polymers, P-1, P-2, and P-3. All contained [3H]-glycerol, [14C]glucose, and fatty acids. P-1 appeared to be pure, whereas P-2 and P-3 contained two polymers each, as judged from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BANDURSKI R. S., AXELROD B. The chromatographic identification of some biologically important phosphate esters. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):405–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basch R. S. An improved method for counting tritium and carbon-14 in acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1968 Oct 10;26(1):184–188. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90044-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bracha R., Glaser L. In vitro system for the synthesis of teichoic acid linked to peptidoglycan. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):872–879. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.872-879.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu T. H., Emdur L. I., Platt D. Lipoteichoic acids from Streptococcus sanguis. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):471–479. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.471-479.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu T. H., Saralkar C. Biosynthesis of oligosaccharide-lipid in Streptococcus sanguis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):185–195. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.185-195.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland R. F., Holtje J. V., Wicken A. J., Tomasz A., Daneo-Moore L., Shockman G. D. Inhibition of bacterial wall lysins by lipoteichoic acids and related compounds. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Dec 1;67(3):1128–1135. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90791-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth M., Archibald A. R., Baddiley J. Lipoteichoic acid and lipoteichoic acid carrier in Staphylococcus aureus H. FEBS Lett. 1975 May 1;53(2):176–179. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emdur L. I., Chiu T. H. Turnover of phosphatidylglycerol in Streptococcus sanguis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Aug 5;59(3):1137–1144. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80097-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emdur L., Chiu T. The role of phosphatidylglycerol in the in vitro biosynthesis of teichoic acid and lipoteichoic acid. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jul 15;55(1):216–219. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80995-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiedler F., Glaser L. The synthesis of polyribitol phosphate. I. Purification of polyribitol phosphate polymerase and lipoteichoic acid carrier. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 10;249(9):2684–2689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiedler F., Glaser L. The synthesis of polyribitol phosphate. II. On the mechanism of polyribitol phosphate polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 10;249(9):2690–2695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser L., Lindsay B. The synthesis of lipoteichoic acid carrier. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Aug 5;59(3):1131–1136. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80096-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtje J. V., Tomasz A. Biological effects of lipoteichoic acids. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):1023–1027. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.1023-1027.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. H., Hancock I. C., Baddiley J. The function of teichoic acids in cation control in bacterial membranes. Biochem J. 1973 Jan;132(1):83–93. doi: 10.1042/bj1320083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höltje J. V., Tomasz A. Lipoteichoic acid: a specific inhibitor of autolysin activity in Pneumococcus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1690–1694. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. A., Hancock I. C., Baddiley J. Occurrence and function of membrane teichoic acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 31;472(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(77)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partridge S. M. Filter-paper partition chromatography of sugars: 1. General description and application to the qualitative analysis of sugars in apple juice, egg white and foetal blood of sheep. with a note by R. G. Westall. Biochem J. 1948;42(2):238–250. doi: 10.1042/bj0420238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. L., Viñuela E., Maizel J. V., Jr Molecular weight estimation of polypeptide chains by electrophoresis in SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90391-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicken A. J., Knox K. W. Lipoteichoic acids: a new class of bacterial antigen. Science. 1975 Mar 28;187(4182):1161–1167. doi: 10.1126/science.46620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


