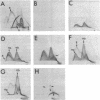
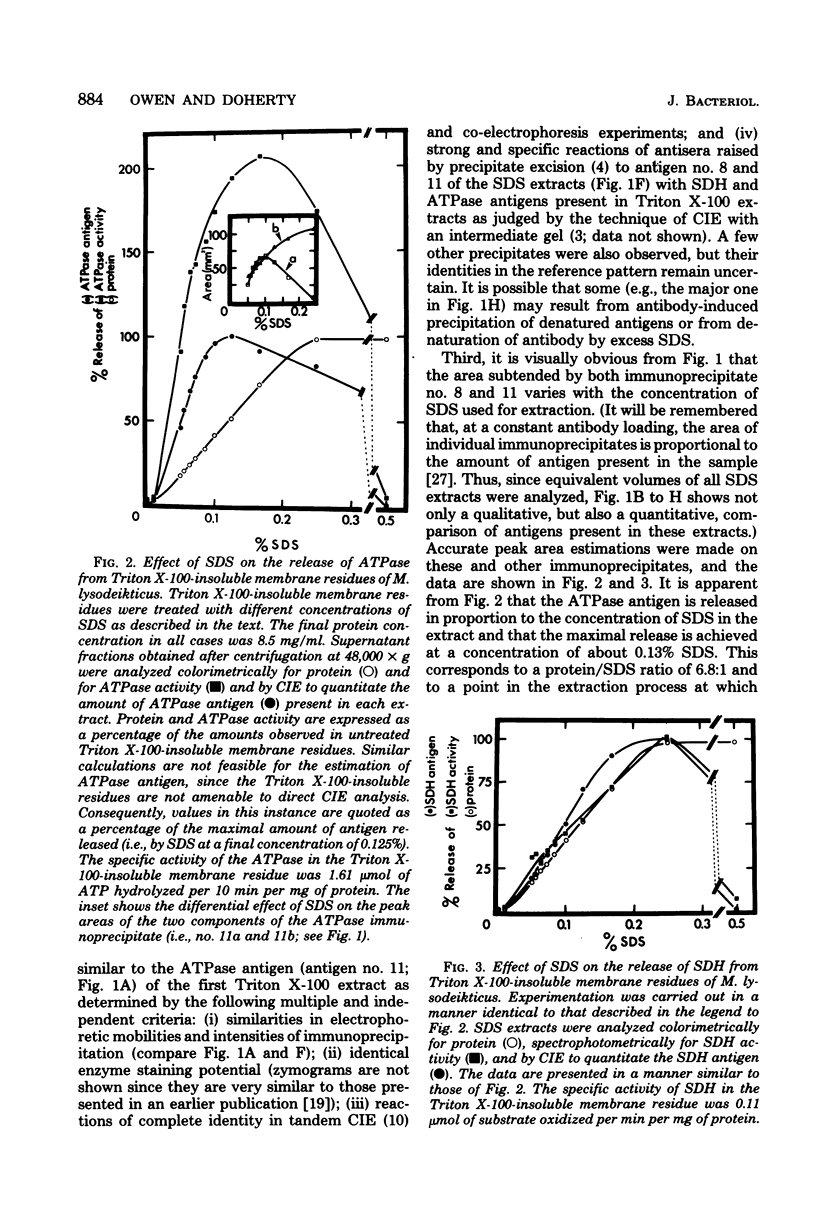
Abstract
Triton X-100-insoluble residues from Micrococcus lysodeikticus membranes were analyzed by crossed immunoelectrophoresis after dispersal of the residues in sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS). Conditions which produce no obvious distortion of the immunoprecipitate profile and which allow qualitative and quantitative analyses of the antigens present in the extracts are described. Two main antigens were detected; these were identified as succinate dehydrogenase (EC 1.3.99.1) and adenosine triphosphatase (EC 3.6.1.3). As determined by peak area estimations, the maximal release of succinate dehydrogenase and of adenosine triphosphatase from Triton X-100-insoluble membrane residues occurred at protein/SDS ratios of about 4.3:1 (0.2% SDS) and 6.8:1 (0.13% SDS), respectively. A comparison of enzyme activities of SDS extracts with those of untreated, control Triton X-100-insoluble membrane residues indicated that both the succinate dehydrogenase and the adenosine triphosphatase antigens were released with a full (or enhanced) catalytic potential at or below concentrations of SDS required to effect maximal solubilization of the enzyme in question. Evidence is also presented to suggest that the more acidic of the two components detected by crossed immunoelectrophoresis for the heterogeneous adenosine triphosphatase antigen is more sensitive to SDS than is the other. Both succinate dehydrogenase and adenosine triphosphatase lost catalytic activity and were denatured at protein/SDS ratios lower than 3.4:1.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander A. G., Kenny G. E. Application of charge shift electrophoresis to antigenic analysis of mycoplasmic membranes by two-dimensional (crossed) immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1978 Jun;20(3):861–863. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.3.861-863.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander A. G., Kenny G. E. Characterization of membrane and cytoplasmic antigens of Mycoplasma arginini by two-dimensional (crossed) immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):313–321. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.313-321.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowle A. J., Revis G. J., Jarrett K. Preparatory electroimmunodiffusion for making precipitins to selected native antigens. Immunol Commun. 1972;1(4):325–336. doi: 10.3109/08820137209022946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulley J. R., Grieve P. A. A simple technique for eliminating interference by detergents in the Lowry method of protein determination. Anal Biochem. 1975 Mar;64(1):136–141. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90415-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddock B. A., Jones C. W. Bacterial respiration. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Mar;41(1):47–99. doi: 10.1128/br.41.1.47-99.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Simons K. Solubilization of membranes by detergents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):29–79. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson K. E., Hjertén S. Localization of the Tween 20-soluble membrane proteins of Acholeplasma laidlawii by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jun 25;86(2):341–348. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll J. Tandem-crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:57–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin J., Meerovitch E. Immunochemical studies of the surface and cytoplasmic membranes of Entamoeba invadens (Rodhain 1934). Can J Microbiol. 1975 Oct;21(10):1635–1646. doi: 10.1139/m75-238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz E., Nachbar M. S., Schor M. T., Salton M. R. Adenosinetriphosphatase of Micrococcus lysodeikticus: selective release and relationship to membrane structure. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Aug 13;32(3):539–546. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90696-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz E., Salton M. R., Ng M. H., Schor M. T. Membrane adenosine triphosphatase of Micrococcus lysodeikticus. Purification, properties of the "soluble" enzyme and properties of the membrane-bound enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Feb;7(4):490–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen P., Freer J. H. Isolation and properties of mesosomal membrane fractions from Micrococcus lysodeikticus. Biochem J. 1972 Oct;129(4):907–917. doi: 10.1042/bj1290907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen P., Kaback H. R. Antigenic architecture of membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 17;18(8):1422–1426. doi: 10.1021/bi00575a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen P., Kaback H. R. Immunochemical analysis of membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 17;18(8):1413–1422. doi: 10.1021/bi00575a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen P., Kaback H. R. Molecular structure of membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3148–3152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen P., Salton M. R. Antigenic and enzymatic architecture of Micrococcus lysodeikticus membranes established by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3711–3715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen P., Salton M. R. Membrane asymmetry and expression of cell surface antigens of Micrococcus lysodeikticus established by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1977 Dec;132(3):974–978. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.3.974-985.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutberg B., Hederstedt L., Holmgren E., Rutberg L. Characterization of succinic dehydrogenase mutants of Bacillus subtilis by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):304–311. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.304-311.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt M., Rittinghaus K., Scheurich P., Schwulera U., Dose K. Immunological properties of membrane-bound adenosine triphosphatase: immunological identification of rutamycin-sensitive F0.F1ATPase from Micrococcus luteus ATCC 4698 established by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jun 2;509(3):410–418. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90235-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth C. J., Friedman-Kien A. E., Salton M. R. Antigenic analysis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1273–1288. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1273-1288.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth C. J., Siegel J., Salton M. R., Owen P. Immunochemical analysis of inner and outer membranes of Escherichia coli by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):306–319. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.306-319.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeke B. Crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:47–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03778.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]