Abstract
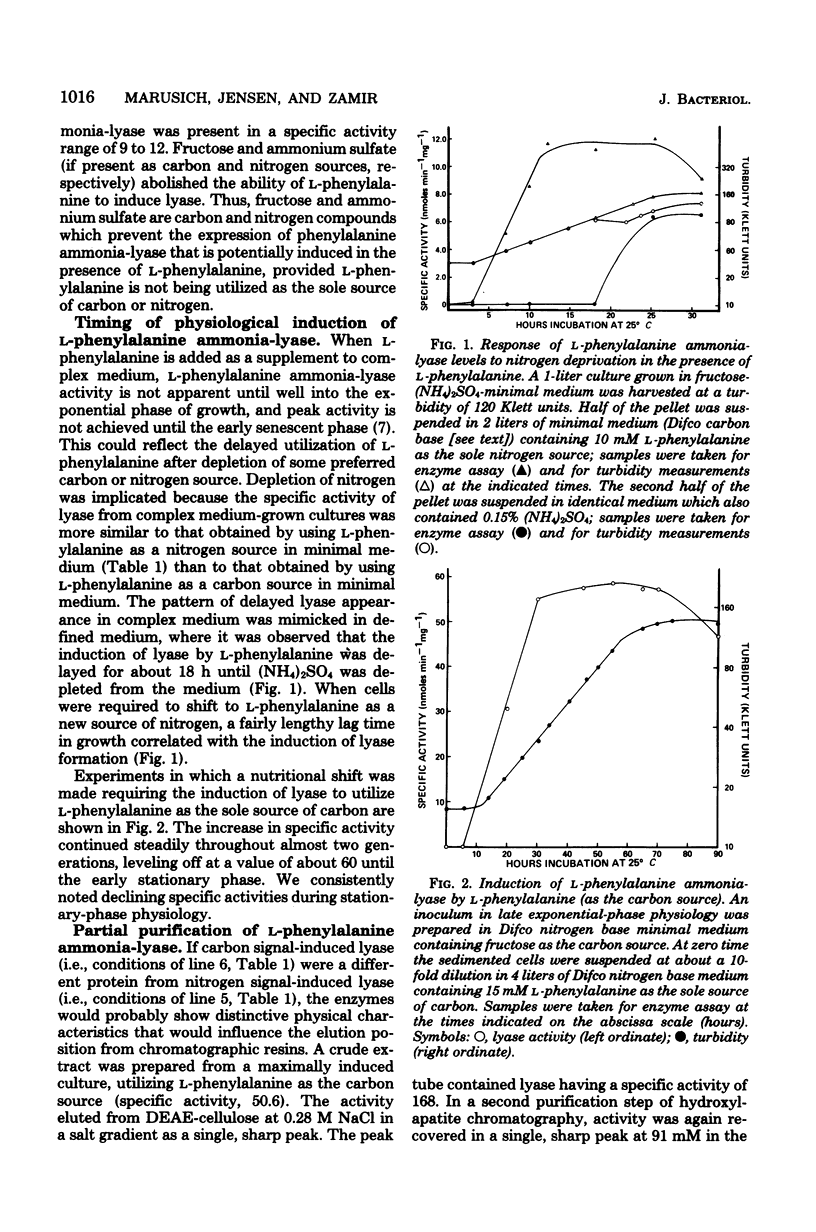
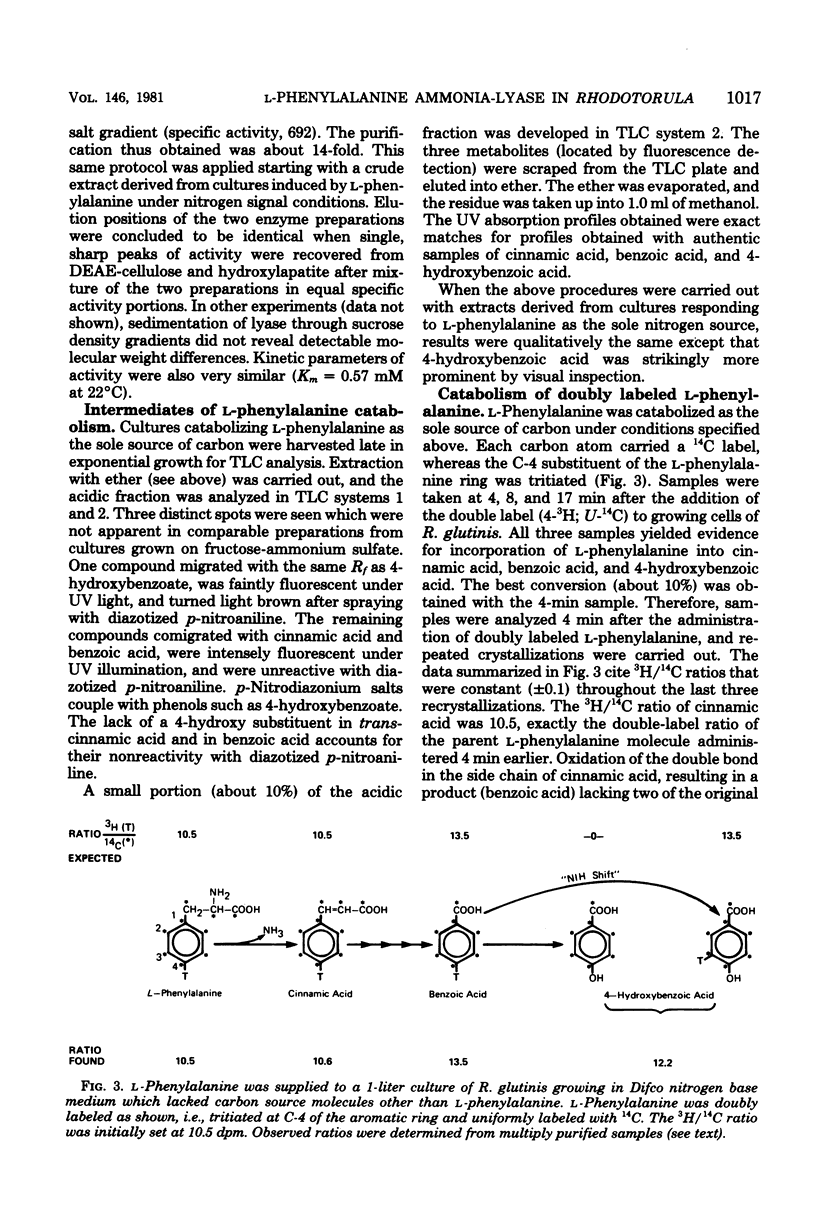
Rhodotorula glutinis is a convenient source of L-phenylalanine ammonia-lyase, an enzyme that is useful as a biochemical reagent in the assay of L-phenylalanine. There have been previous descriptions of induced lyase production in complex medium where induction occurs late in exponential growth, suggesting a role in secondary metabolism such as is the case in higher plants. A higher specific activity of L-phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (sixfold higher than a complex medium) can be obtained during midexponential growth in a defined medium containing L-phenylalanine as the sole source of carbon. L-Phenylalanine will also induce lyase synthesis during exponential growth in minimal in which L-phenylalanine is the sole source of nitrogen. The appearance of lyase in complex medium supplemented with L-phenylalanine is probably triggered fortuitously by exhaustion late in growth of a prime source of nitrogen. In this study, R. glutinis appeared to express a single lyase enzyme, regardless of whether induction was nitrogen signaled or carbon signaled. Thin-layer chromatographic analysis of ether extracts prepared from cultures induced with doubly labeled (U-14C; ring-4-3H) L-phenylalanine provided evidence of a catabolic sequence containing cinnamic acid, benzoic acid, and 4-hydroxybenzoic acid as degradative intermediates. 3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid was not identified as a catabolic intermediate.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bezanson G. S., Desaty D., Emes A. V., Vining L. C. Biosynthesis of cinnamamide and detection of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase in Streptomyces verticillatus. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Mar;16(3):147–151. doi: 10.1139/m70-026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford R. L. Pathways of 4-hydroxybenzoate degradation among species of Bacillus. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):204–210. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.204-210.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz R. R., Hodgins D. S., Abell C. W. Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase. Induction and purification from yeast and clearance in mammals. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 10;251(15):4646–4650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guroff G., Daly J. W., Jerina D. M., Renson J., Witkop B., Udenfriend S. Hydroxylation-induced migration: the NIH shift. Recent experiments reveal an unexpected and general result of enzymatic hydroxylation of aromatic compounds. Science. 1967 Sep 29;157(3796):1524–1530. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3796.1524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgins D. S. Yeast phenylalanine ammonia-lyase. Purification, properties, and the identification of catalytically essential dehydroalanine. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 10;246(9):2977–2985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyodo H., Kuroda H., Yang S. F. Induction of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and increase in phenolics in lettuce leaves in relation to the development of russet spotting caused by ethylene. Plant Physiol. 1978 Jul;62(1):31–35. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson C., Attridge T., Smith H. Regulation of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase synthesis by cinnamic acid. Its implication for the light mediated regulation of the enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 14;385(1):11–19. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90068-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOUKOL J., CONN E. E. The metabolism of aromatic compounds in higher plants. IV. Purification and properties of the phenylalanine deaminase of Hordeum vulgare. J Biol Chem. 1961 Oct;236:2692–2698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishore G., Sugumaran M., Vaidyanathan C. S. Metabolism of DL-(+/-)-phenylalanine by Aspergillus niger. J Bacteriol. 1976 Oct;128(1):182–191. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.1.182-191.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K., Rao P. V., Towers G. H. Degradation of phenylalanine and tyrosine by Sporobolomyces roseus. Biochem J. 1968 Jan;106(2):507–514. doi: 10.1042/bj1060507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparnins V. L., Burbee D. G., Dagley S. Catabolism of L-tyrosine in Trichosporon cutaneum. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):425–430. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.425-430.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker M. Induction of Phenylalanine Deaminase by Light and its Relation to Chlorogenic Acid Synthesis in Potato Tuber Tissue. Plant Physiol. 1965 Sep;40(5):779–784. doi: 10.1104/pp.40.5.779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


