Abstract
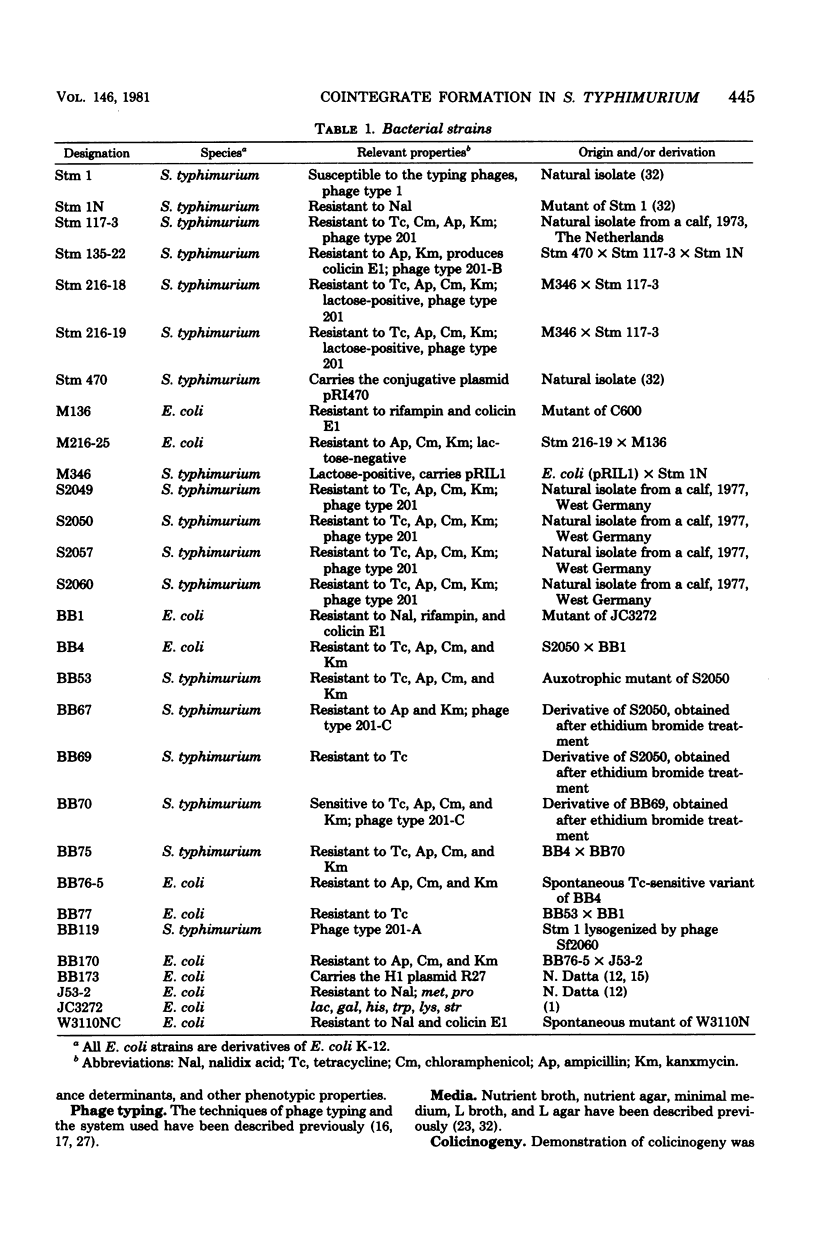
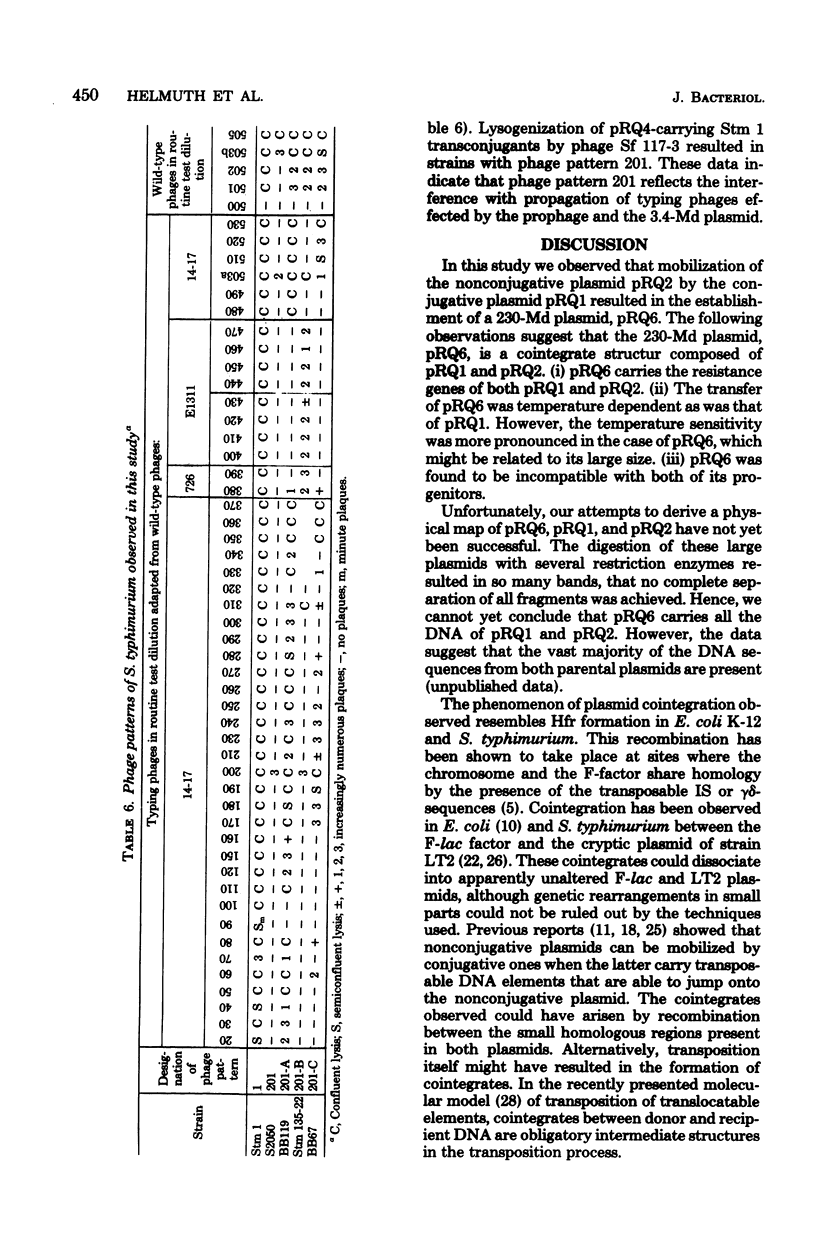
The genetic and molecular properties of the plasmids in Salmonella typhimurium phase type 201 isolated are described. Such strains are resistant to streptomycin, tetracycline, chloramphenicol, ampicillin, kanamycin, and several other antimicrobial drugs, and are highly pathogenic for calves. These strains have been encountered with increasing frequency since 1972 in West Germany and The Netherlands. We show that isolates of this phage type constitute a very homogeneous group with regard to their extrachromosomal elements. These bacteria carry three small plasmids: pRQ3, a 4.2-megadalton (Md) colicinogenic plasmid; pRQ4, 3.4-Md plasmid that interferes with the propagation of phages; and pRQ5, a 3.2-Md cryptic plasmid. Tetracycline resistance resides on a conjugative 120-MD plasmid pRQ1, belonging to the incompatibility class H2. Other antibiotic resistance determinants are encoded by a nonconjugative 108-Md plasmid pRQ2. Transfer of multiple-antibiotic resistance to appropriate recipient strains was associated with the appearance of a 230-Md plasmid, pRQ6. It appears that pRQ6 is a stable cointegrate of pRQ1 and pRQ2. This cointegrate plasmid was transferable with the same efficiency as pRQ1. Other conjugative plasmids could mobilize pRQ2, but stable cointegrates were not detected in the transconjugants. Phase type 201 strains carry a prophage, and we show that phage pattern 201 reflects the interference with propagation of typing phages effected by this prophage and plasmid pRQ4 in strains of phage type 201.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achtman M., Willetts N., Clark A. J. Beginning a genetic analysis of conjugational transfer determined by the F factor in Escherichia coli by isolation and characterization of transfer-deficient mutants. J Bacteriol. 1971 May;106(2):529–538. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.2.529-538.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson E. S. Influence of the delta transfer factor on the phage sensitivity of salmonellae. Nature. 1966 Nov 19;212(5064):795–799. doi: 10.1038/212795a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson E. S., Natkin E. Transduction of resistance determinants and R factors of the transfer systems by phage Plkc. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;114(3):261–265. doi: 10.1007/BF01788895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYD J. S. Immunity of lysogenic bacteria. Nature. 1956 Jul 21;178(4525):141–141. doi: 10.1038/178141a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabello F., Timmis K., Cohen S. N. Replication control in a composite plasmid constructed by in vitro linkage of two distinct replicons. Nature. 1976 Jan 29;259(5541):285–290. doi: 10.1038/259285a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Properties of a supercoiled deoxyribonucleic acid-protein relaxation complex and strand specificity of the relaxation event. Biochemistry. 1970 Oct 27;9(22):4428–4440. doi: 10.1021/bi00824a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis G. Transposition of Tn951 (Tnlac) and cointegrate formation are thermosensitive processes. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Mar;117(1):243–247. doi: 10.1099/00221287-117-1-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crisona N. J., Nowak J. A., Nagaishi H., Clark A. J. Transposon-mediated conjugational transmission of nonconjugative plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):701–713. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.701-713.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Olarte J. R factors in strains of Salmonella typhi and Shigella dysenteriae 1 isolated during epidemics in Mexico: classification by compatibility. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Mar;5(3):310–317. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.3.310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREDERICQ P. Colicins. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1957;11:7–22. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.11.100157.000255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREDERICQ P. Résistance et immunité aux colicines. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1956;150(7):1514–1517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grindley N. D., Humphreys G. O., Anderson E. S. Molecular studies of R factor compatibility groups. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jul;115(1):387–398. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.1.387-398.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinée P. A., Jansen W. H., van Schuylenburg A., van Leeuwen W. J. Mechanized technique for phage typing and determination of antibiograms. Zentralbl Bakteriol A. 1980 Mar;246(2):276–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinée P. A., van Leeuwen W. J., Pruys D. Phage typing of S. typhi murium in the Netherlands. 1. The phage typing system. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1974 Feb;226(2):194–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyer M. S. The gamma delta sequence of F is an insertion sequence. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 15;126(3):347–365. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90045-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. B., Olsen R. H. Isolation of large bacterial plasmids and characterization of the P2 incompatibility group plasmids pMG1 and pMG5. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):227–238. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.227-238.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooykaas P. J., den Dulk-Ras H., Schilperoort R. A. Molecular mechanism of Ti plasmid mobilization by R plasmids: isolation of Ti plasmids with transposon-insertions in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plasmid. 1980 Jul;4(1):64–75. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(80)90083-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida S. A cointegrate of the bacteriophage P1 genome and the conjugative R plasmid R100. Plasmid. 1980 May;3(3):278–290. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(80)90041-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manis J. J., Whitfield H. J. Physical characterization of a plasmid cointegrate containing an F'his gnd element and the Salmonella typhimurium LT2 cryptic plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1601–1606. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1601-1606.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milliken C. E., Clowes R. C. Molecular structure of an R factor, its component drug-resistance determinants and transfer factor. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):1026–1033. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.1026-1033.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsubo E., Zenilman M., Ohtsubo H. Plasmids containing insertion elements are potential transposons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):750–754. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez Lemoine V., Rowbury R. J. The formation of a dissociable plasmid cointegrate from the Flac factor and the resident plasmid of Salmonella typhimurium LT2. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Sep;96(1):109–116. doi: 10.1099/00221287-96-1-109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtens R. T., Rost J. A. Subdivision of "Salmonella typhi-murium" into phage types and biotypes. Characterization of transferable factors by means of phage typing. The increase of drug-resistance in Salmonellas. Ann Sclavo. 1972 May-Jun;14(3):309–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro J. A. Molecular model for the transposition and replication of bacteriophage Mu and other transposable elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1933–1937. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. R., Grindley N. D., Humphreys G. O., Anderson E. S. Interactions of group H resistance factors with the F factor. J Bacteriol. 1973 Aug;115(2):623–628. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.2.623-628.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Parsell Z., Green P. Thermosensitive antibiotic resistance plasmids in enterobacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Nov;109(1):37–47. doi: 10.1099/00221287-109-1-37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Embden J. D., van Leeuwen W. J., Guinée P. A. Interference with propagation of typing bacteriophages by extrachromosomal elements in Salmonella typhimurium: bacteriophage type 505. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1414–1426. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1414-1426.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Embden J., Cohen S. N. Molecular and genetic studies of an R factor system consisting of independent transfer and drug resistance plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):699–709. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.699-709.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Leeuwen W. J., van Embden J., Guinée P., Kampelmacher E. H., Manten A., van Schothorst M., Voogd C. E. Decrease of drug resistance in Salmonella in the Netherlands. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Aug;16(2):237–239. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.2.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



