Abstract
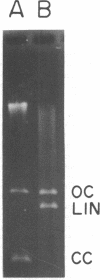
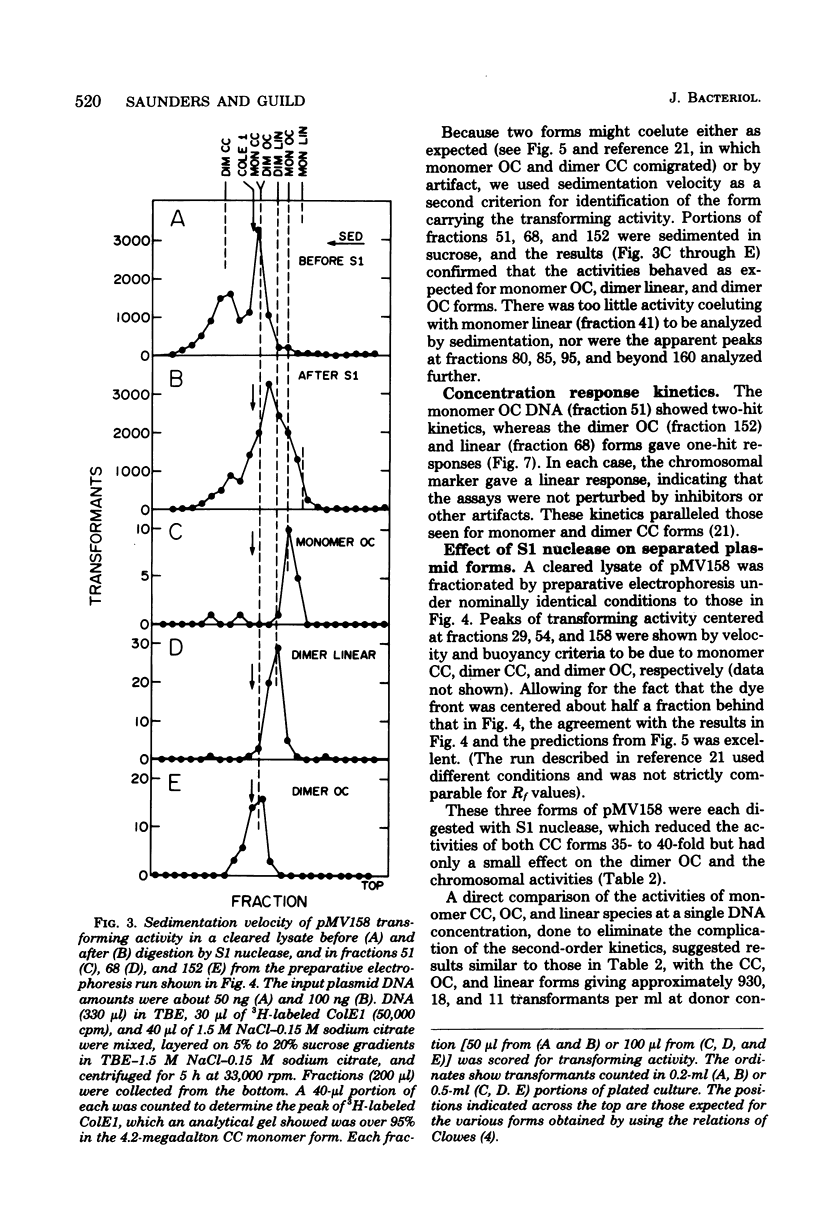
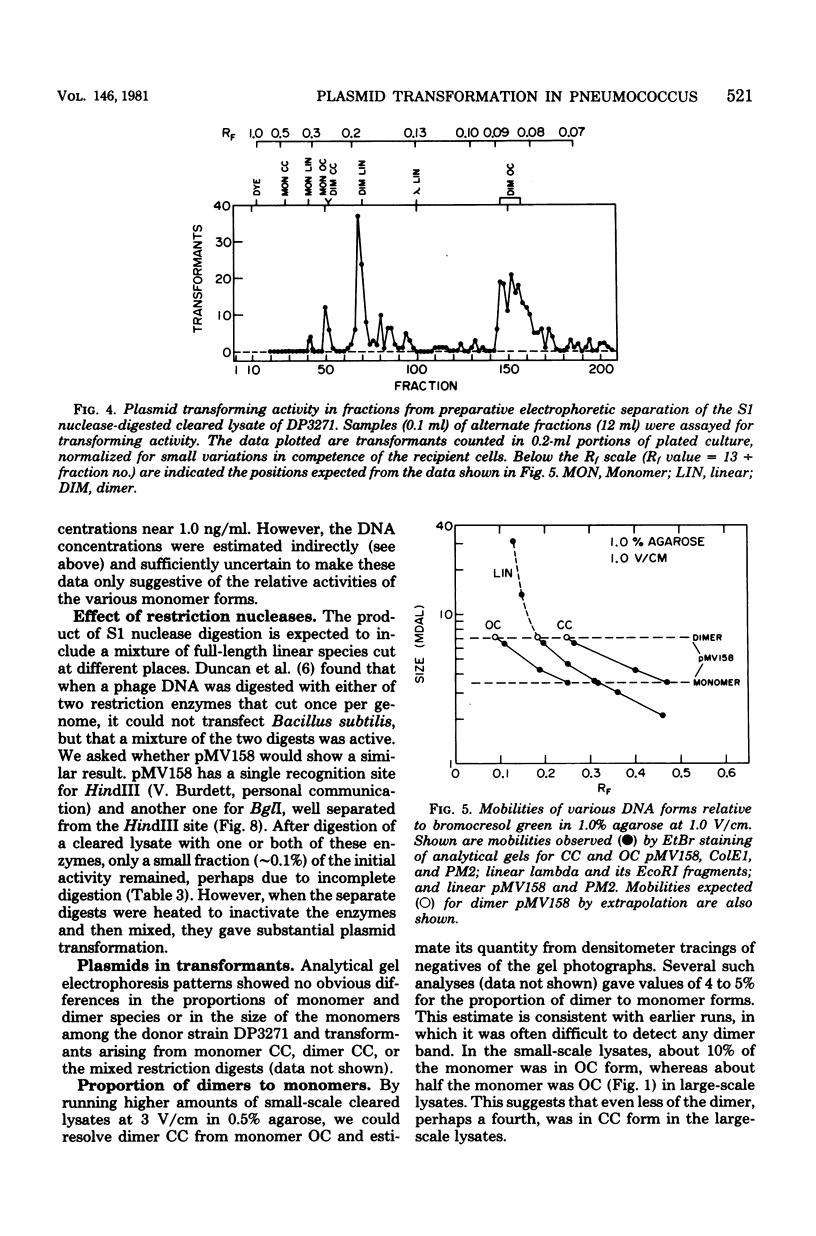
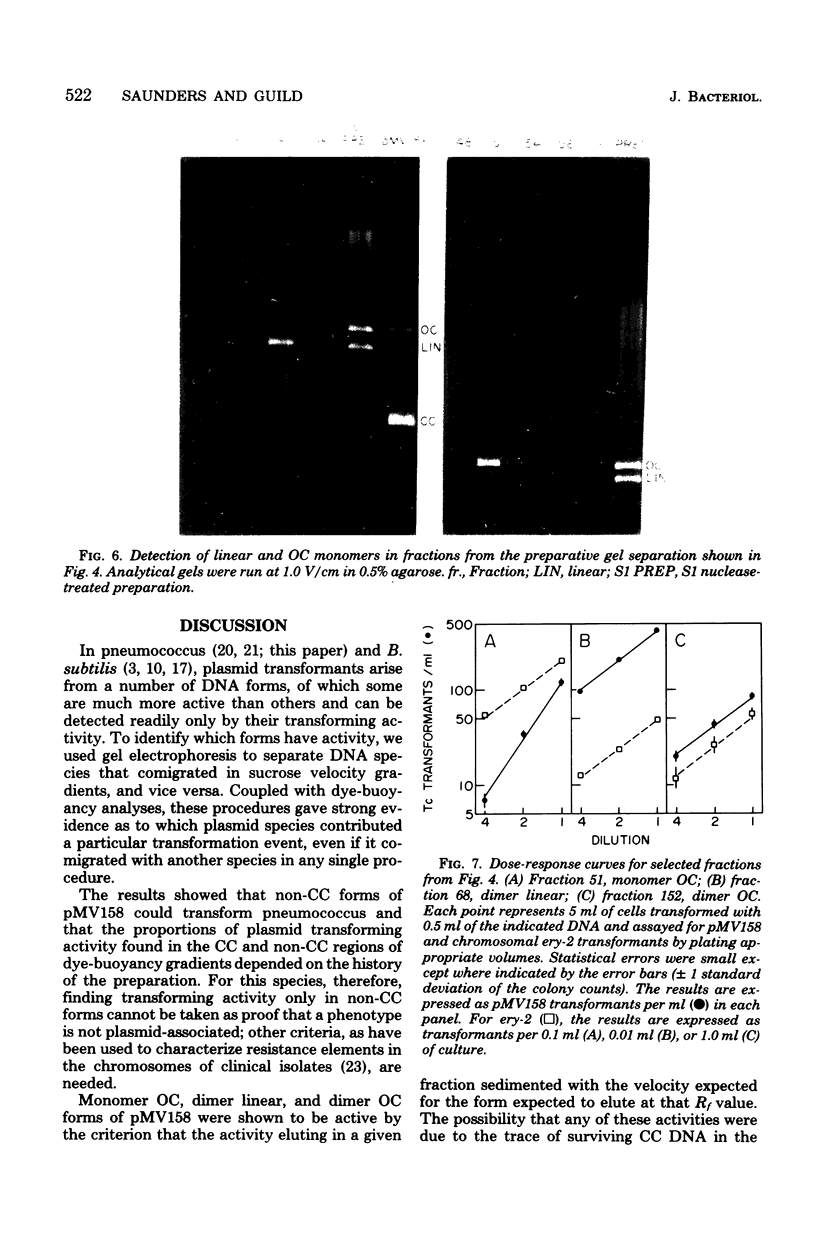
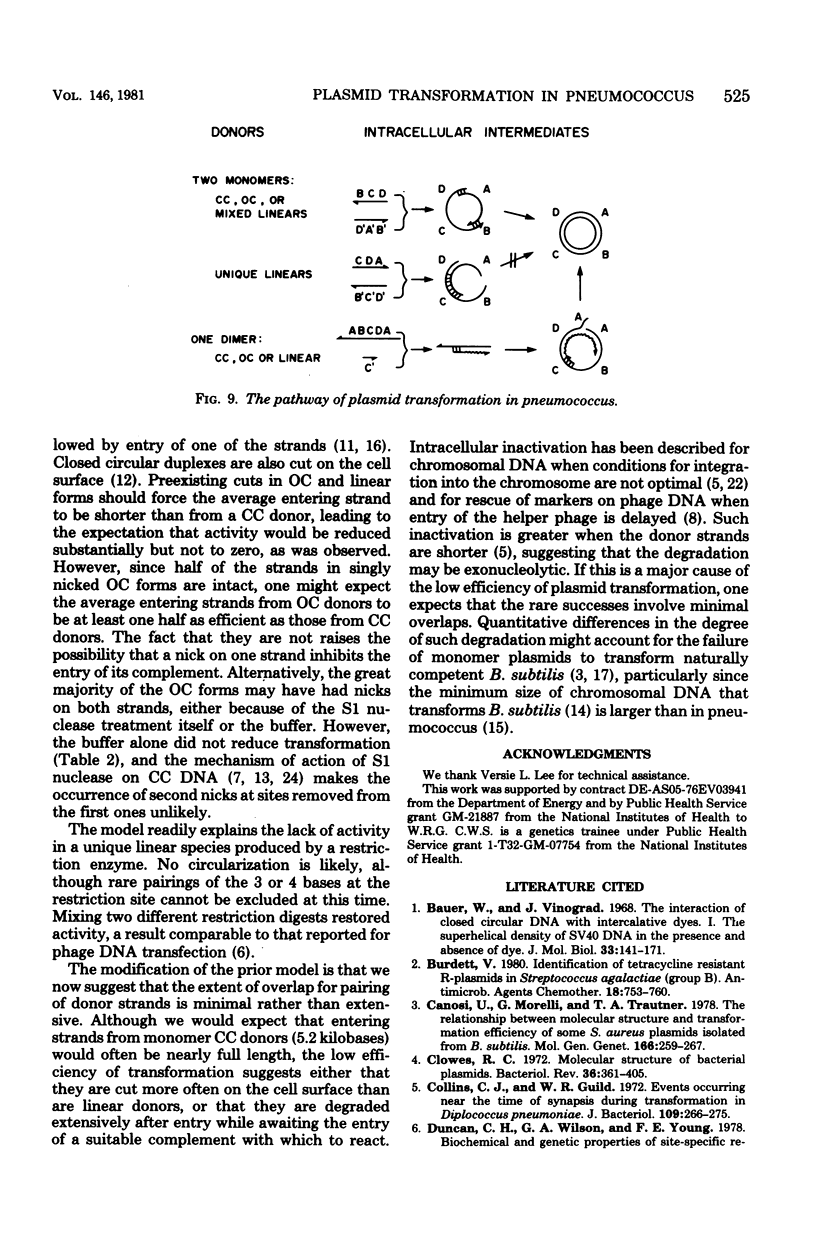
We have extended the analysis of plasmid transformation in Streptococcus pneumoniae by finding that monomeric and dimeric open circular and linear forms of pMV158 were active in transformation. Their efficiencies were at least 35-fold lower than those of the corresponding closed circular forms. The evidence came largely from analysis of S1 nuclease-digested plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid by combinations of dye-buoyancy, gel electrophoresis, and sedimentation velocity methods. As with closed circular forms, monomer open circular forms gave second-order kinetics and dimer forms gave first-order kinetics. Unique linear products of digestion by either of two restriction enzymes were inactive, but a mixture of the two digests was active, as was the mixture of linear monomer deoxyribonucleic acids produced by S1 nuclease. Absolute efficiencies of transformation were low even for closed circular donors. All of the results, including the low efficiencies, were consistent with the interpretation that plasmid replicons were assembled in the recipient cell by pairing of fragments of single strands that had entered the cell separately from duplex donors that had been cut on the cell surface.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer W., Vinograd J. The interaction of closed circular DNA with intercalative dyes. I. The superhelix density of SV40 DNA in the presence and absence of dye. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 14;33(1):141–171. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90286-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdett V. Identification of tetracycline-resistant R-plasmids in Streptococcus agalactiae (group B). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):753–760. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canosi U., Morelli G., Trautner T. A. The relationship between molecular structure and transformation efficiency of some S. aureus plasmids isolated from B. subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Nov 9;166(3):259–267. doi: 10.1007/BF00267617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clowes R. C. Molecular structure of bacterial plasmids. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Sep;36(3):361–405. doi: 10.1128/br.36.3.361-405.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins C. J., Guild W. R. Events occurring near the time of synapsis during transformation in Diplococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jan;109(1):266–275. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.1.266-275.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan C. H., Wilson G. A., Young F. E. Biochemical and genetic properties of site-specific restriction endonucleases in Bacillus globigii. J Bacteriol. 1978 Apr;134(1):338–344. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.1.338-344.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germond J. E., Vogt V. M., Hirt B. Characterization of the single-strand-specific nuclease S1 activity on double-stranded supercoiled polyoma DNA. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Apr 16;43(3):591–600. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03446.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryczan T., Contente S., Dubnau D. Molecular cloning of heterologous chromosomal DNA by recombination between a plasmid vector and a homologous resident plasmid in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1980 Feb;177(3):459–467. doi: 10.1007/BF00271485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guild W. R., Shoemaker N. B. Mismatch correction in pneumococcal transformation: donor length and hex-dependent marker efficiency. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jan;125(1):125–135. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.1.125-135.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S. Uptake of circular deoxyribonucleic acid and mechanism of deoxyribonucleic acid transport in genetic transformation of Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):404–409. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.404-409.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M. The inverted repeat as a recognizable structural feature in supercoiled DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6468–6472. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. A., Guild W. R. Activity of deoxyribonucleic acid fragments of defined size in Bacillus subtilis transformation. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):220–223. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.220-223.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. A., Guild W. R. Breakage prior to entry of donor DNA in Pneumococcus transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 11;299(4):545–556. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90226-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. A., Guild W. R. Transformation and deoxyribonucleic acid size: extent of degradation on entry varies with size of donor. J Bacteriol. 1972 Dec;112(3):1157–1168. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.3.1157-1168.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mottes M., Grandi G., Sgaramella V., Canosi U., Morelli G., Trautner T. A. Different specific activities of the monomeric and oligomeric forms of plasmid DNA in transformation of B. subtilis and E. coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jul 24;174(3):281–286. doi: 10.1007/BF00267800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polsky F., Edgell M. H., Seidman J. G., Leder P. High capacity gel preparative electrophoresis for purification of fragments of genomic DNA. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jul 1;87(2):397–410. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90689-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter R. D., Guild W. R. Transfection in pneumococcus: single-strand intermediates in the formation of infective centers. J Virol. 1978 Jan;25(1):60–72. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.1.60-72.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders C. W., Guild W. R. Monomer plasmid DNA transforms Streptococcus pneumoniae. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;181(1):57–62. doi: 10.1007/BF00339005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders C. W., Guild W. R. Properties and transforming activities of two plasmids in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;180(3):573–578. doi: 10.1007/BF00268062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shishido K. Relationship between S1 endonuclease-sensitivity and number of superhelical turns in a negatively-twisted DNA. FEBS Lett. 1980 Mar 10;111(2):333–336. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80821-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker N. B., Guild W. R. Kinetics of integration of transforming DNA in pneumococcus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3331–3335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker N. B., Smith M. D., Guild W. R. Organization and transfer of heterologous chloramphenicol and tetracycline resistance genes in pneumococcus. J Bacteriol. 1979 Aug;139(2):432–441. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.2.432-441.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. D., Shoemaker N. B., Burdett V., Guild W. R. Transfer of plasmids by conjugation in Streptococcus pneumonias. Plasmid. 1980 Jan;3(1):70–79. doi: 10.1016/s0147-619x(80)90035-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]