Abstract
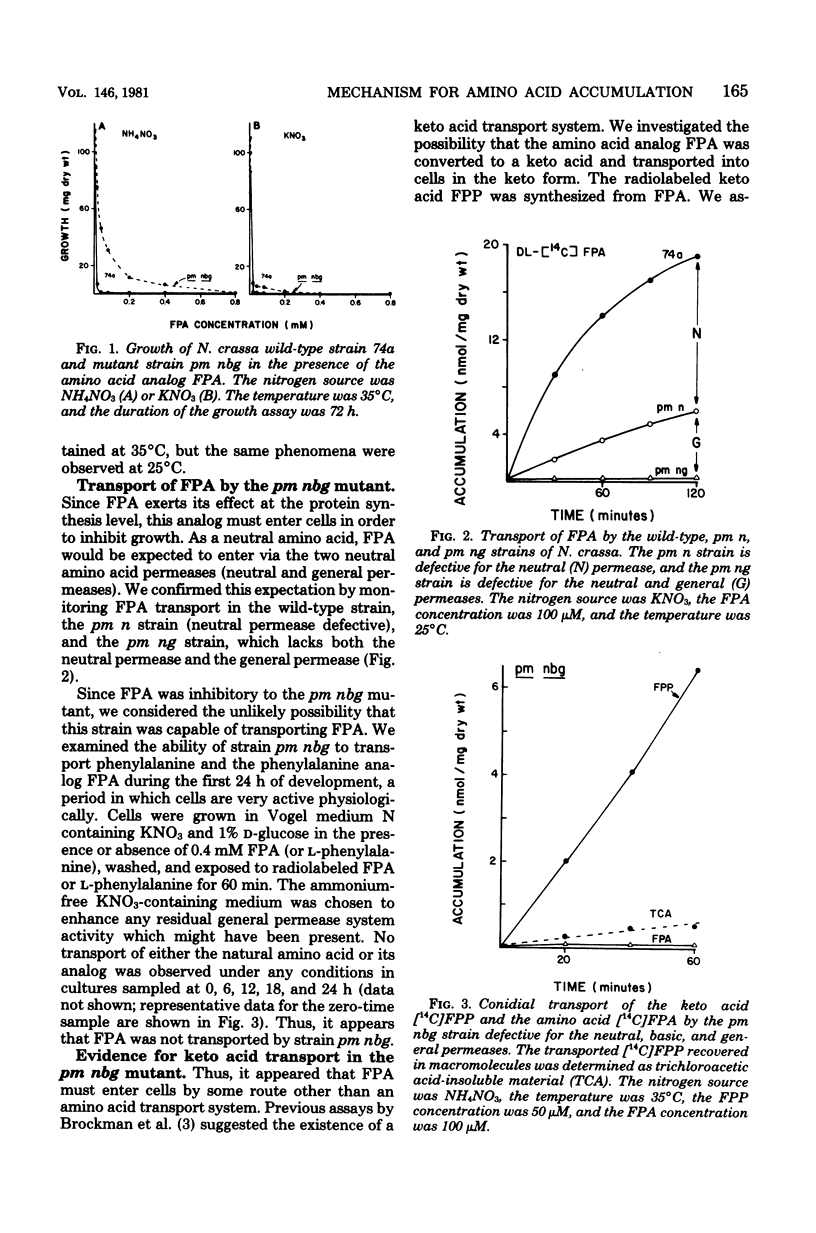
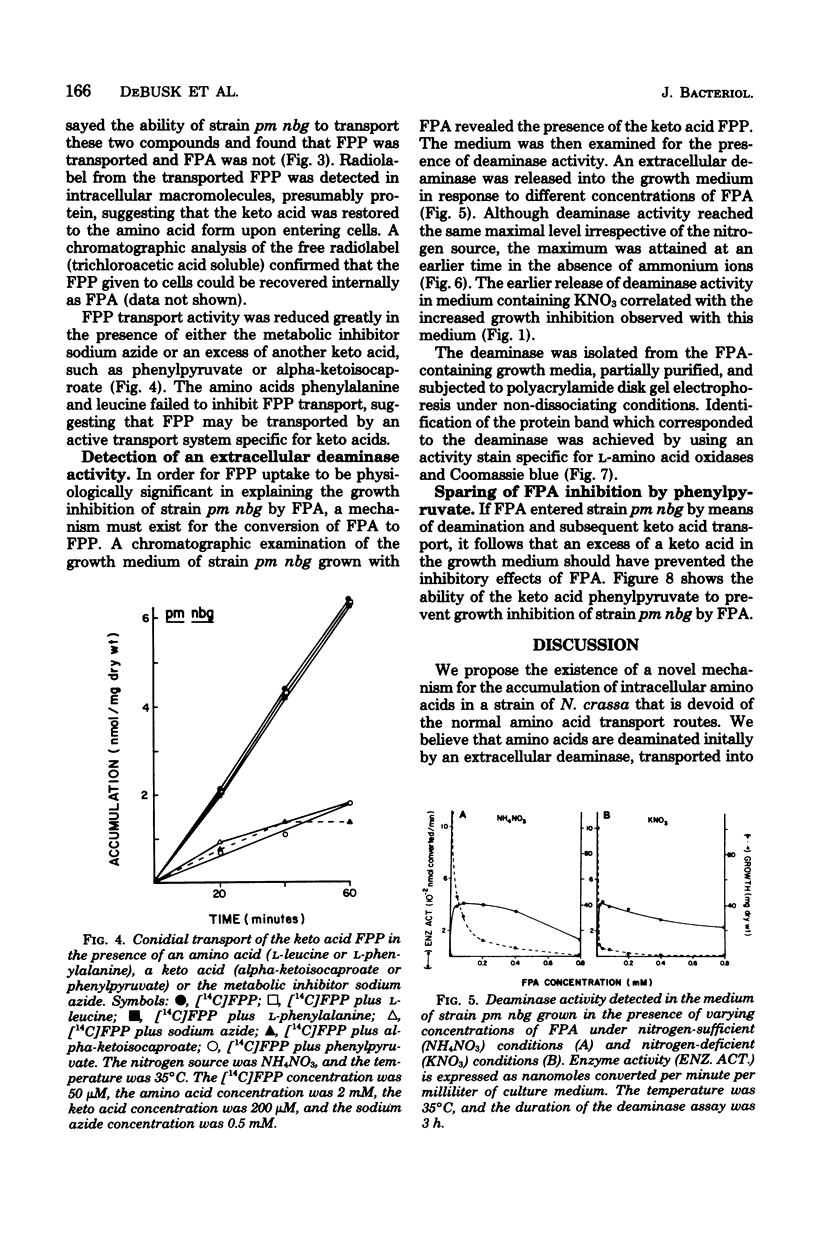
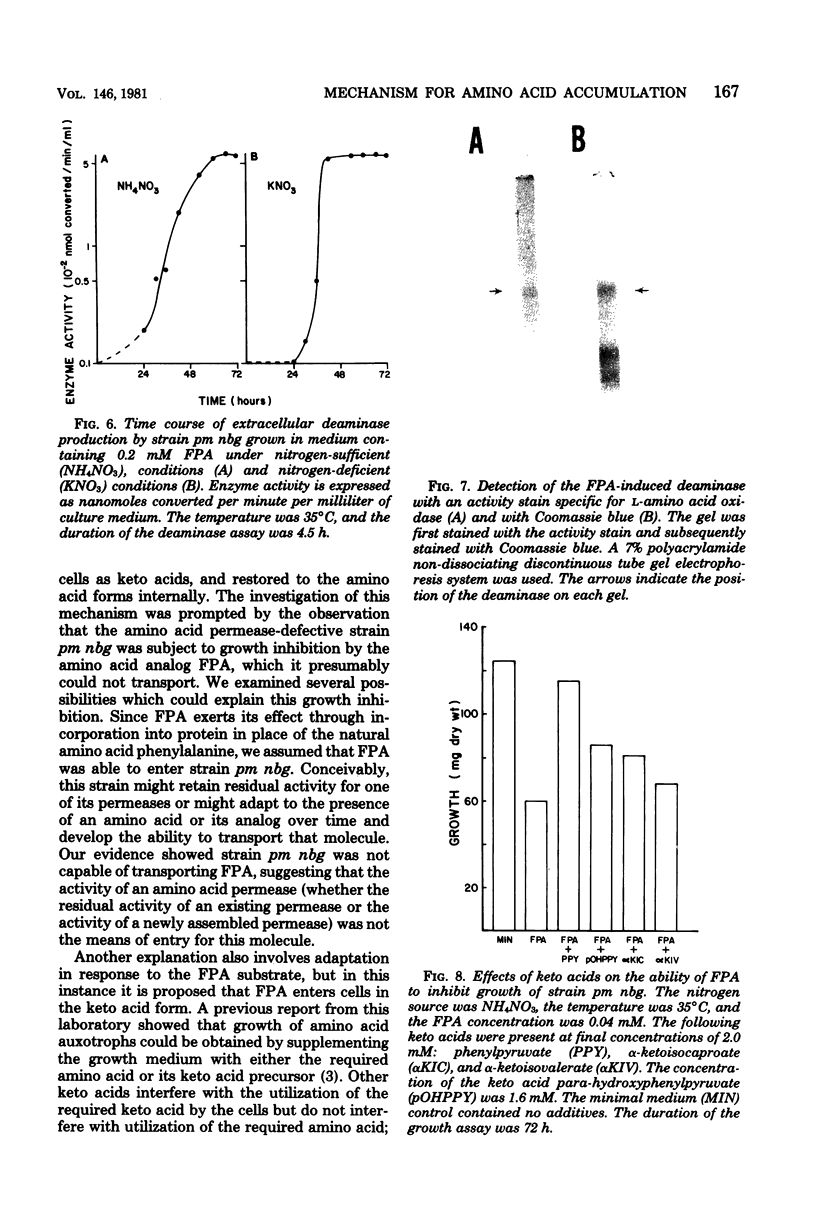
The growth of the pm nbg mutant strain of Neurospora crassa was inhibited by the amino acid analog para-fluorophenylalanine despite the fact that none of the three constitutive amino acid permeases is functional in this strain. This observation led to the detection of both a deaminase which was released into the growth medium in response to para-fluorophenylalanine and a keto acid transport system which allowed entry of the resulting keto acid into the cell. The transported keto acid was recovered in cellular protein, suggesting its regeneration as the amino acid. The cooperative activity of these two systems represents an additional mechanism for the intracellular accumulation of amino acids, which is distinct from the known amino acid permeases.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aurich H., Luppa D., Schücker G. Reinigung und eigenschaften der L-Aminosäureoxydase aus Neurospora. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1972;28(2):209–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCKMAN H. E., DeBUSK A. G., WAGNER R. P. Mutant-associated antagonisms in Neurospora crassa. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 Oct;84:455–461. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90607-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. The L-amino-acid oxidase of Neurospora. Biochem J. 1951 Dec;50(2):258–268. doi: 10.1042/bj0500258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns D. J., Beever R. E. Mechanisms controlling the two phosphate uptake systems in Neurospora crassa. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jul;139(1):195–204. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.1.195-204.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN G. N., MUNIER R. Incorporation d'analogues structuraux d'aminoacides dans les protéines bactériennes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Sep;21(3):592–593. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90207-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeBusk B. G., DeBusk A. G. Molecular transport in Neurospora crassa. I. Biochemical properties of a phenylalanine permease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jun 15;104(1):139–150. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90229-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeBusk R. M., DeBusk A. G. Physiological and regulatory properties of the general amino acid transport system of Neurospora crassa. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):188–197. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.188-197.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drucker H. Regulation of exocellular proteases in Neurospora crassa: induction and repression of enzyme synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jun;110(3):1041–1049. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.3.1041-1049.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein B. J., Zahler S. A. Uptake of branched-chain alpha-keto acids in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):667–670. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.667-670.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halestrap A. P., Brand M. D., Denton R. M. Inhibition of mitochondrial pyruvate transport by phenylpyruvate and alpha-ketoisocaproate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Oct 10;367(1):102–108. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90140-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson M. A., Marzluf G. A. Control of the synthesis of a single enzyme by multiple regulatory circuits in Neurospora crassa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1240–1244. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson M. A., Marzluf G. A. Regulation of a sulfur-controlled protease in Neurospora crassa. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):785–789. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.785-789.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
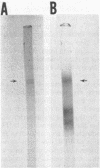
- Hayes M. B., Wellner D. Microheterogeneity of L-amino acid oxidase. Separation of multiple components by polyacrylamide gel electrofucusing. J Biol Chem. 1969 Dec 25;244(24):6636–6644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land J. M., Clark J. B. Inhibition of pyruvate and beta-hydroxybutyrate oxidation in rat brain mitochondria by phenylpyruvate and alpha-ketoisocaproate. FEBS Lett. 1974 Aug 30;44(3):348–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester G. Genetic control of amino acid permeability in Neurospora crassa. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):677–684. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.677-684.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockhart W R, Garner H R. Genetic Mechanisms Governing the Effect of Canavanine on Neurospora Crassa. Genetics. 1955 Sep;40(5):721–725. doi: 10.1093/genetics/40.5.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pall M. L. Amino acid transport in Neurospora crassa. IV. Properties and regulation of a methionine transport system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 9;233(1):201–214. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90372-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao E. Y., Rao T. K., Debusk A. G. Isolation and characterization of a mutant of Neurospora crassa deficient in general amino acid permease activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Nov 17;413(1):45–51. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90057-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarborough G. A. Sugar transport in Neurospora crassa. II. A second glucose transport system. J Biol Chem. 1970 Aug 10;245(15):3985–3987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R. P., Wiley W. R. Regulation of sugar transport in Neurospora crassa. J Bacteriol. 1971 May;106(2):487–492. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.2.487-492.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadler D. R. Genetic control of the uptake of amino acids in Neurospora. Genetics. 1966 Aug;54(2):677–685. doi: 10.1093/genetics/54.2.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THAYER P. S., HOROWITZ N. H. The L-amino acid oxidase of Neurospora. J Biol Chem. 1951 Oct;192(2):755–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan S. T., Marzluf G. A. Multiple intracellular peptidases in Neurospora crassa. J Bacteriol. 1979 Mar;137(3):1324–1332. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.3.1324-1332.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarpey M. M., Willis R. C., Seegmiller J. E. Uptake of alpha-ketoisocaproic acid in lymphoblast line WI-L2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jun 20;76(4):1267–1275. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90992-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thwaites W. M., Pendyala L. Regulation of amino acid assimilation in a strain of Neurospora crassa lacking basic amino acid transport activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Dec 30;192(3):455–461. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90394-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfinbarger L., Jr, Marzluf G. A. Specificity and regulation of peptide transport on Neurospora crassa. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Dec;171(2):637–644. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90074-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward J. R., Cirillo V. P. Amino acid transport and metabolism in nitrogen-starved cells of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):714–723. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.714-723.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]