Abstract
Threonine can be used aerobically as the sole source of carbon and energy by mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. The pathway used involves the conversion of threonine via threonine dehydrogenase to aminoketobutyric acid, which is further metabolized by aminoketobutyric acid ligase, forming acetyl coenzyme A and glycine. A strain devoid of serine transhydroxymethylase uses this pathway and excretes glycine as a waste product. Aminoketobutyric acid ligase activity was demonstrated after passage of crude extracts through Sephadex G100.
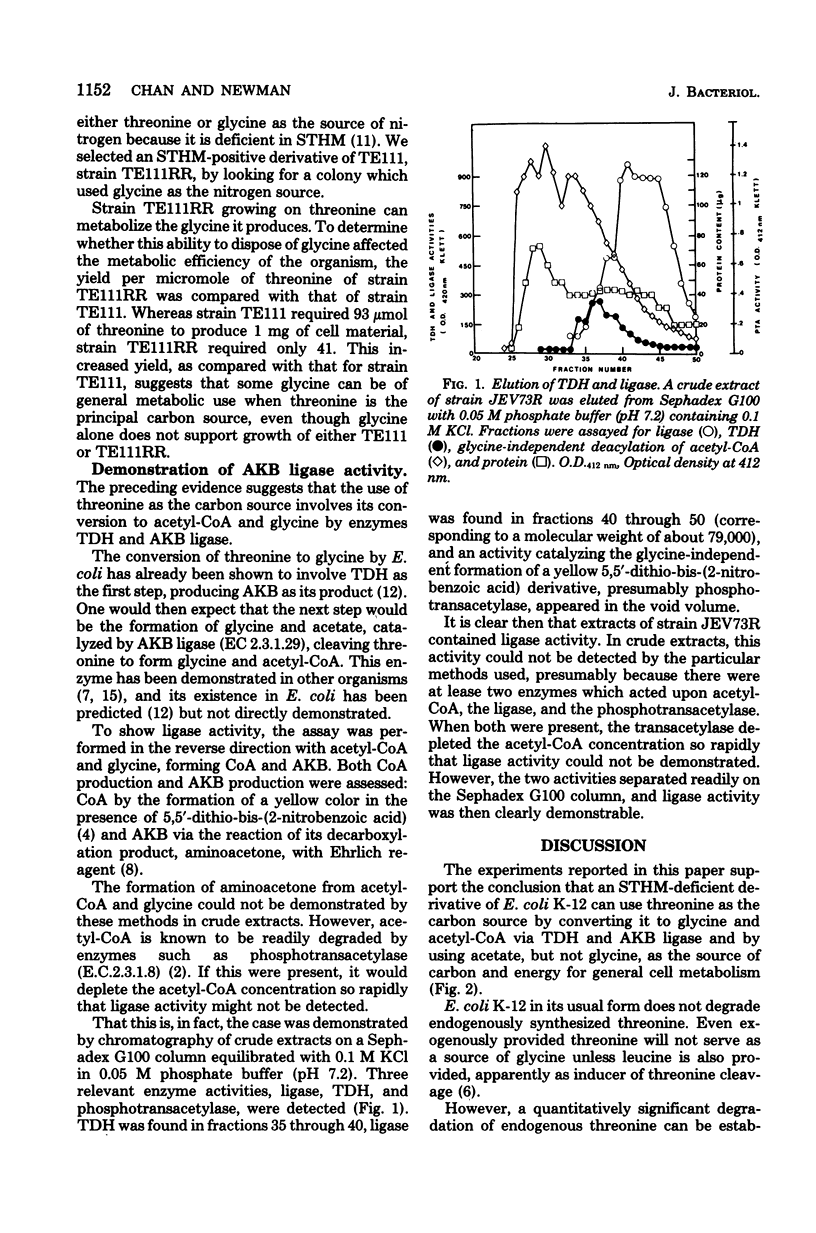
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell S. C., Turner J. M. Bacterial catabolism of threonine. Threonine degradation initiated by L-threonine acetaldehyde-lyase (aldolase) in species of Pseudomonas. Biochem J. 1977 Aug 15;166(2):209–216. doi: 10.1042/bj1660209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. D., Jones-Mortimer M. C., Kornberg H. L. The enzymic interconversion of acetate and acetyl-coenzyme A in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Oct;102(2):327–336. doi: 10.1099/00221287-102-2-327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns R. O., Hofler J. G., Luginbuhl G. H. Threonine deaminase from Salmonella typhimurium. Substrate-specific patterns of inhibition in an activator site-deficient form of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1074–1079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 May;82(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folk W. R., Berg P. Isolation and partial characterization of Escherichia coli mutants with altered glycyl transfer ribonucleic acid synthetases. J Bacteriol. 1970 Apr;102(1):193–203. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.1.193-203.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser J., Newman E. B. Derivation of glycine from threonine in Escherichia coli K-12 mutants. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):810–817. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.810-817.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGilvray D., Morris J. G. Utilization of L-threonine by a species of Arthrobacter. A novel catabolic role for "aminoacetone synthase". Biochem J. 1969 May;112(5):657–671. doi: 10.1042/bj1120657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. G. Utilization of L-threnonine by a pseudomonad: a catabolic role for L-threonine aldolase. Biochem J. 1969 Nov;115(3):603–605. doi: 10.1042/bj1150603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman E. B., Batist G., Fraser J., Isenberg S., Weyman P., Kapoor V. The use of glycine as nitrogen source by Escherichia coli K12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jan 14;421(1):97–105. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90173-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman E. B., Kapoor V., Potter R. Role of L-threonine dehydrogenase in the catabolism of threonine and synthesis of glycine by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1245–1249. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1245-1249.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter R., Kapoor V., Newman E. B. Role of threonine dehydrogenase in Escherichia coli threonine degradation. J Bacteriol. 1977 Nov;132(2):385–391. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.2.385-391.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong H. C., Lessie T. G. Hydroxy amino acid metabolism in Pseudomonas cepacia: role of L-serine deaminase in dissimilation of serine, glycine, and threonine. J Bacteriol. 1979 Oct;140(1):240–245. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.1.240-245.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


