Abstract
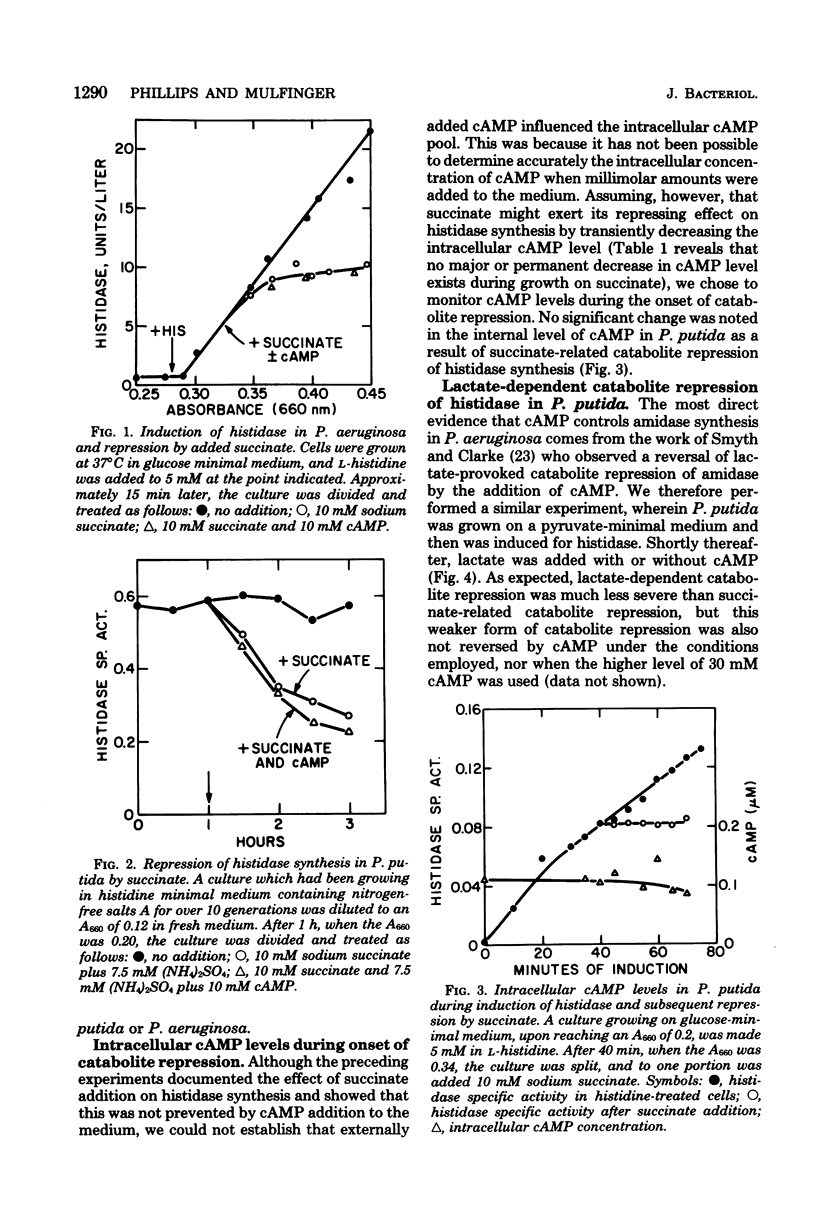
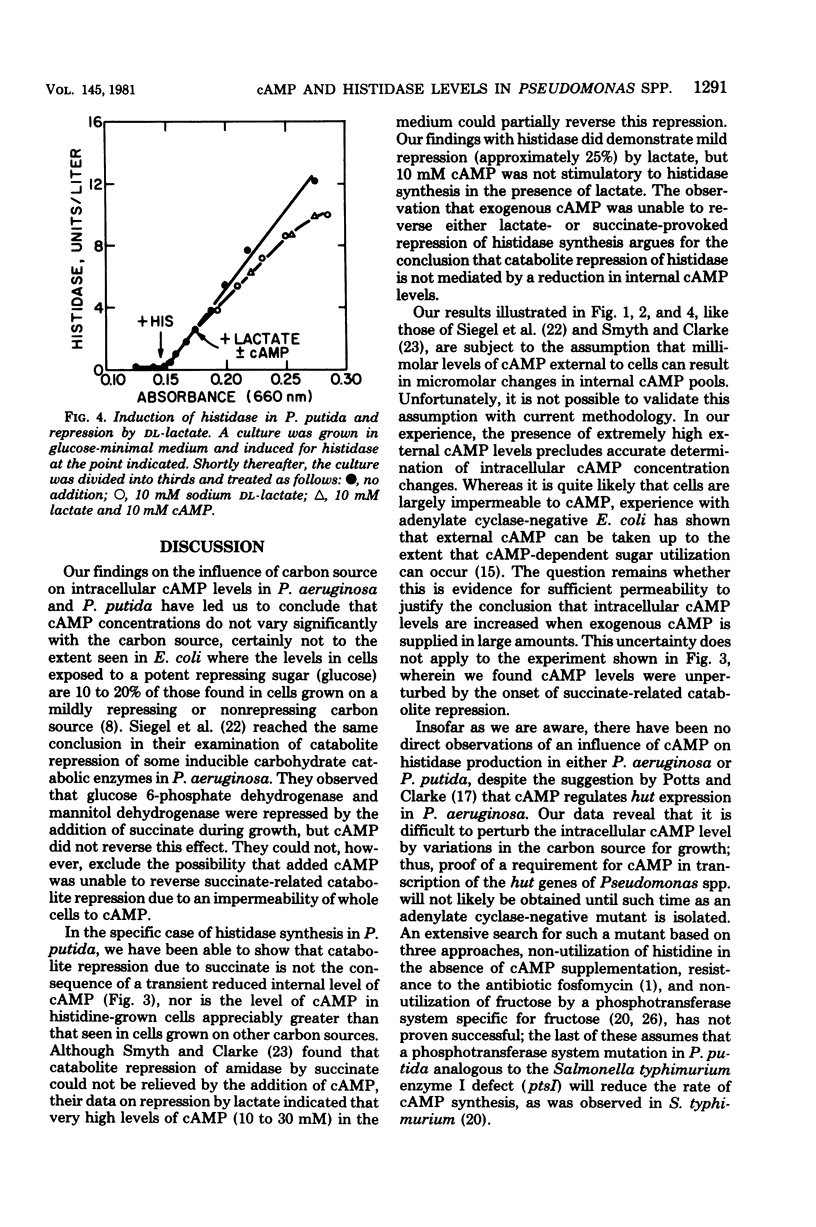
Inducibility of histidase (histidine ammonia-lyase, EC 4.3.1.3) in Pseudomonas putida and Pseudomonas aeruginosa was observed to be strongly affected by succinate-provoked catabolite repression, but this did not occur as a consequence of reduced intracellular cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate levels, and repression could not be alleviated by exogenously added cyclic adenosine 3,'5'-monophosphate. Milder repression of histidase by lactate was also not reversed by the addition of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate. These results, along with data showing intracellular cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate levels remained essentially constant during growth on such diverse carbon sources as histidine, acetamide, glucose, and succinate, indicated that catabolite repression of histidase synthesis by efficient carbon sources was not mediated through variations in internal cyclic adenosine 3,'5'-monophosphate.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alper M. D., Ames B. N. Transport of antibiotics and metabolite analogs by systems under cyclic AMP control: positive selection of Salmonella typhimurium cya and crp mutants. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):149–157. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.149-157.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAMMAR W. J., CLARKE P. H. INDUCTION AND REPRESSION OF PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA AMIDASE. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Dec;37:307–319. doi: 10.1099/00221287-37-3-307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buettner M. J., Spitz E., Rickenberg H. V. Cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1068–1073. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1068-1073.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook W. R., Kalb V. F., Jr, Peace A. A., Bernlohr R. W. Is cyclic guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate a cell cycle regulator? J Bacteriol. 1980 Mar;141(3):1450–1453. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.3.1450-1453.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coote J. G., Hassall H. The control of the enzymes degrading histidine and related imidazolyl derivates in Pseudomonas testosteroni. Biochem J. 1973 Mar;132(3):423–433. doi: 10.1042/bj1320423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein W., Rothman-Denes L. B., Hesse J. Adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate as mediator of catabolite repression in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2300–2304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hylemon P. B., Phibbs P. V., Jr Evidence against the presence of cyclic AMP and related enzymes in selected strains of Bacteroides fragilis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Sep 9;60(1):88–95. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90176-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leidigh B. J., Wheelis M. L. Genetic control of the histidine dissimilatory pathway in Pseudomonas putida. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Feb 2;120(3):201–210. doi: 10.1007/BF00267152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lessie T. G., Neidhardt F. C. Formation and operation of the histidine-degrading pathway in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jun;93(6):1800–1810. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.6.1800-1810.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAKMAN R. S., SUTHERLAND E. W. ADENOSINE 3',5'-PHOSPHATE IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1309–1314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng F. M., Dawes E. A. Chemostat studies on the regulation of glucose metabolism in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by citrate. Biochem J. 1973 Feb;132(2):129–140. doi: 10.1042/bj1320129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Adhya S. Cyclic adenosine 5'-monophosphate in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Sep;40(3):527–551. doi: 10.1128/br.40.3.527-551.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips A. T., Egan R. M., Lewis B. Control of biodegradative threonine dehydratase inducibility by cyclic AMP in energy-restricted Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):828–840. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.828-840.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potts J. R., Clarke P. H. The effect of nitrogen limitation on catabolite repression of amidase, histidase and urocanase in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Apr;93(2):377–387. doi: 10.1099/00221287-93-2-377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M. The purification and characterization of L-histidine ammonia-lyse (Pseudomonas). J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 25;244(4):551–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Feucht B. U. Coordinate regulation of adenylate cyclase and carbohydrate permeases by the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system in Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 10;250(17):7078–7080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro L., Agabian-Keshishian N., Hirsch A., Rosen O. M. Effect of dibutyryladenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate on growth and differentiation in Caulobacter crescentus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1225–1229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. S., Hylemon P. B., Phibbs P. V., Jr Cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate levels and activities of adenylate cyclase and cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate phosphodiesterase in Pseudomonas and Bacteroides. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jan;129(1):87–96. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.1.87-96.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth P. F., Clarke P. H. Catabolite repression of Pseudomonas aeruginosa amidase: the effect of carbon source on amidase synthesis. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Sep;90(1):81–90. doi: 10.1099/00221287-90-1-81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler B. Regulation of the assimilation of nitrogen compounds. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:1127–1162. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.005403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dijken J. P., Quayle J. R. Fructose metabolism in four Pseudomonas species. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Sep 28;114(3):281–286. doi: 10.1007/BF00446874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


