Abstract
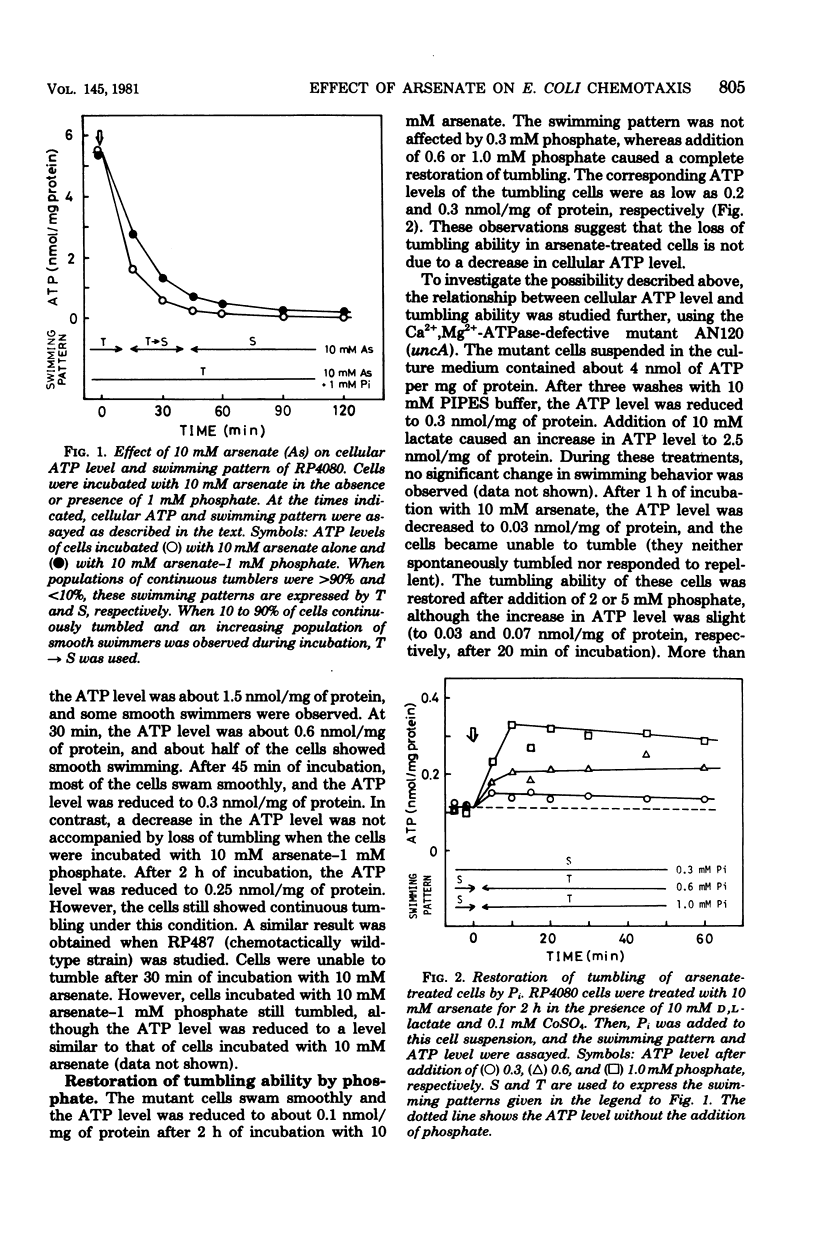
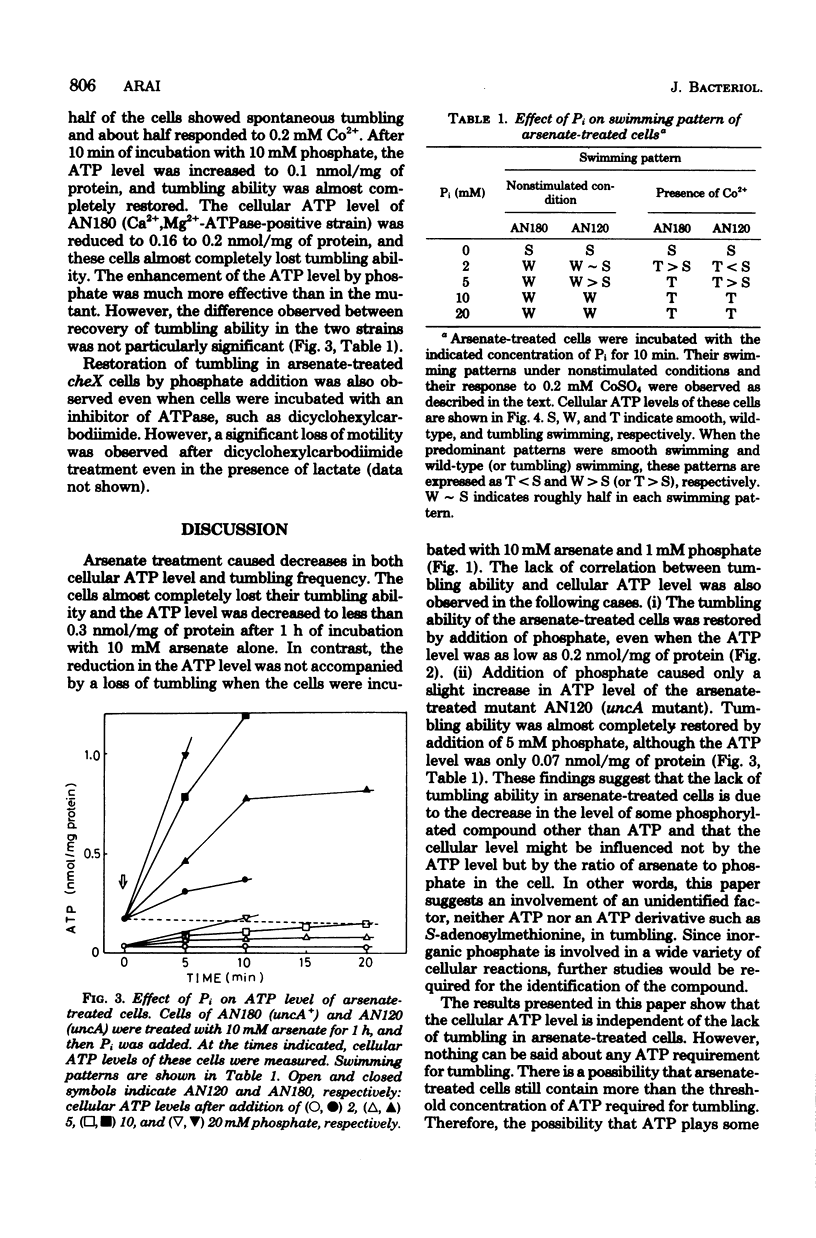
Escherichia coli cells treated with arsenate cannot tumble. The relationship between cellular adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP) level and the ability to tumble has been studied. (i) Cells incubated with arsenate completely lost their tumbling ability, and the cellular ATP level was decreased to less than 0.3 nmol/mg of protein. (ii) Incubation with 10 mM arsenate-1 mM phosphate reduced the cellular ATP level to less than 0.25 nmol/mg of protein. However, the cells were still able to tumble. (iii) Tumbling of the arsenate-treated cells was completely recovered after addition of a slight amount of phosphate, although the ATP level was still as low as 0.2 nmol/mg of protein. (iv) The cellular ATP level of an arsenate-treated uncA mutant (Ca2+,Mg2+-adenosine triphosphatase defective) was lower than 0.1 nmol/mg of protein even after the addition of 5 5 mM phosphate. However, tumbling ability was almost completely restored upon addition of the phosphate.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler J. Chemotaxis in bacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:341–356. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler J., Dahl M. M. A method for measuring the motility of bacteria and for comparing random and non-random motility. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Feb;46(2):161–173. doi: 10.1099/00221287-46-2-161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler J., Goy M. F., Springer M. S., Szmelcman S. On the mechanism of sensory transduction in bacterial chemotaxis. Soc Gen Physiol Ser. 1979;33:123–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J. B. An S-adenosylmethionine requirement for chemotaxis in Escherichia coli. Can J Microbiol. 1972 Nov;18(11):1695–1701. doi: 10.1139/m72-263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J. B. Chemotaxis and methionine metabolism in Escherichia coli. Can J Microbiol. 1972 May;18(5):591–596. doi: 10.1139/m72-093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aswad D., Koshland D. E., Jr Role of methionine in bacterial chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):640–645. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.640-645.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C. Chemotaxis in bacteria. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1975;4(00):119–136. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.04.060175.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butlin J. D., Cox G. B., Gibson F. Oxidative phosphorylation in Escherichia coli K12. Mutations affecting magnesium ion- or calcium ion-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase. Biochem J. 1971 Aug;124(1):75–81. doi: 10.1042/bj1240075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goy M. F., Springer M. S., Adler J. Failure of sensory adaptation in bacterial mutants that are defective in a protein methylation reaction. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1231–1240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90049-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerstedt R. H. An automated method for ATP analysis utilizing the luciferin-luciferase reaction. Anal Biochem. 1973 Apr;52(2):449–455. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondoh H. Tumbling chemotaxis mutants of Escherichia coli: possible gene-dependent effect of methionine starvation. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):527–534. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.527-534.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kort E. N., Goy M. F., Larsen S. H., Adler J. Methylation of a membrane protein involved in bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3939–3943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland D. E., Jr Chemotaxis as a model for sensory systems. FEBS Lett. 1974 Mar 23;40(0):suppl–suppl:S9. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80683-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen S. H., Adler J., Gargus J. J., Hogg R. W. Chemomechanical coupling without ATP: the source of energy for motility and chemotaxis in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1239–1243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M., Koshland D. E., Jr The gradient-sensing mechanism in bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2509–2512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S. cheA, cheB, and cheC genes of Escherichia coli and their role in chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1976 May;126(2):758–770. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.2.758-770.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer M. S., Kort E. N., Larsen S. H., Ordal G. W., Reader R. W., Adler J. Role of methionine in bacterial chemotaxis: requirement for tumbling and involvement in information processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4640–4644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strehler B. L. Bioluminescence assay: principles and practice. Methods Biochem Anal. 1968;16:99–181. doi: 10.1002/9780470110348.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


