Abstract
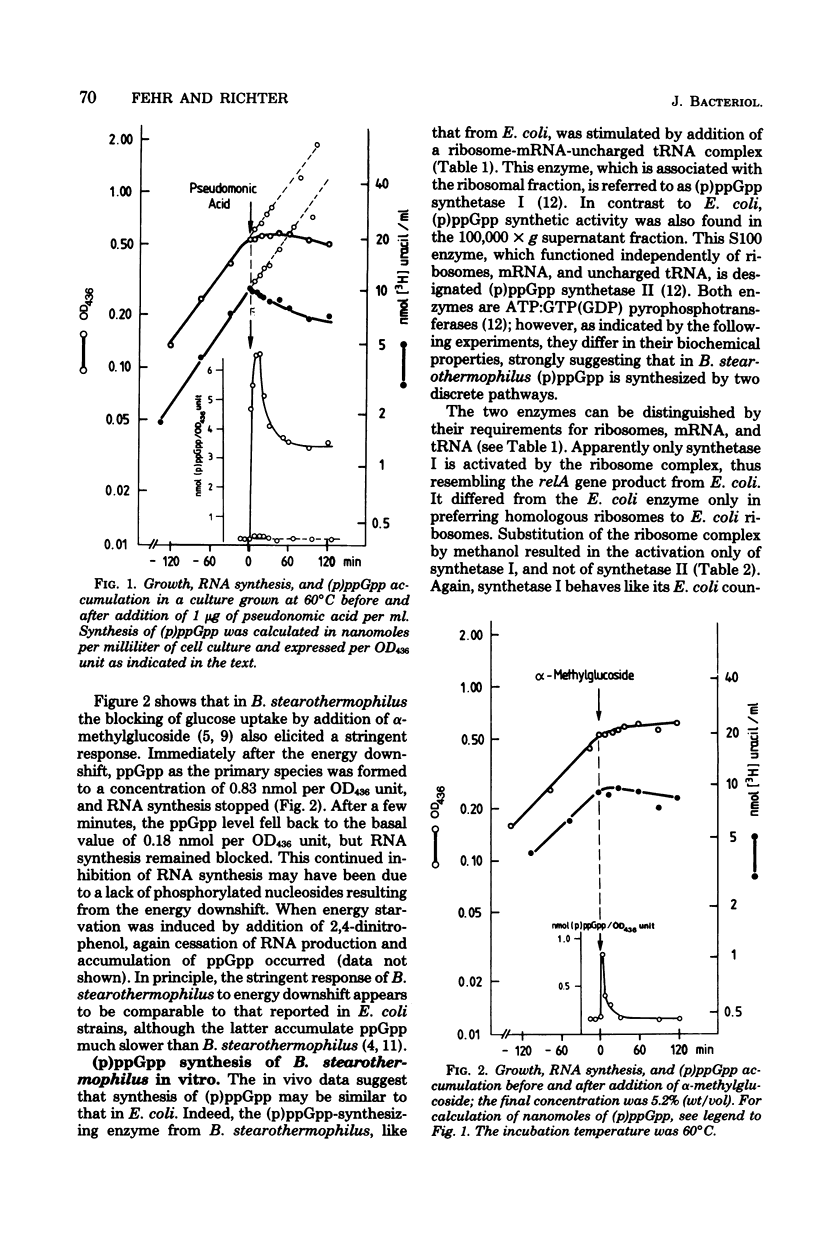
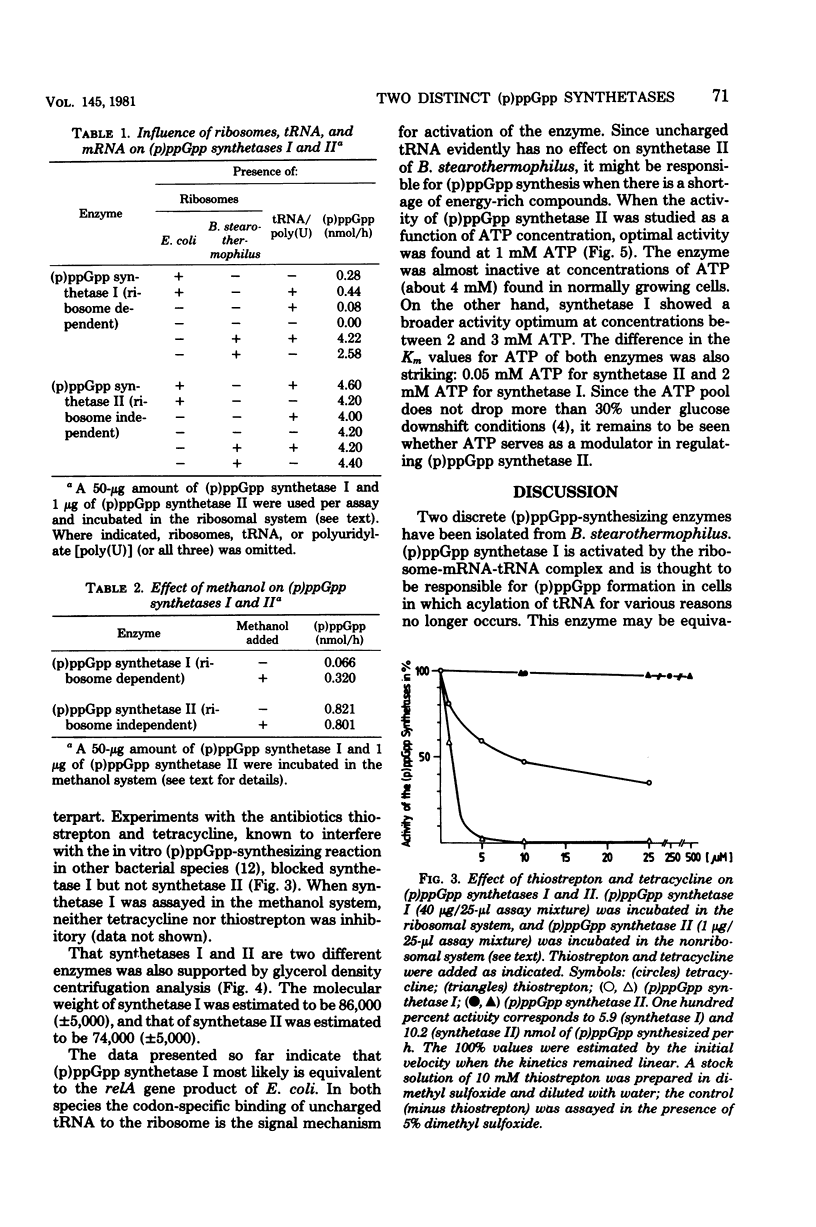
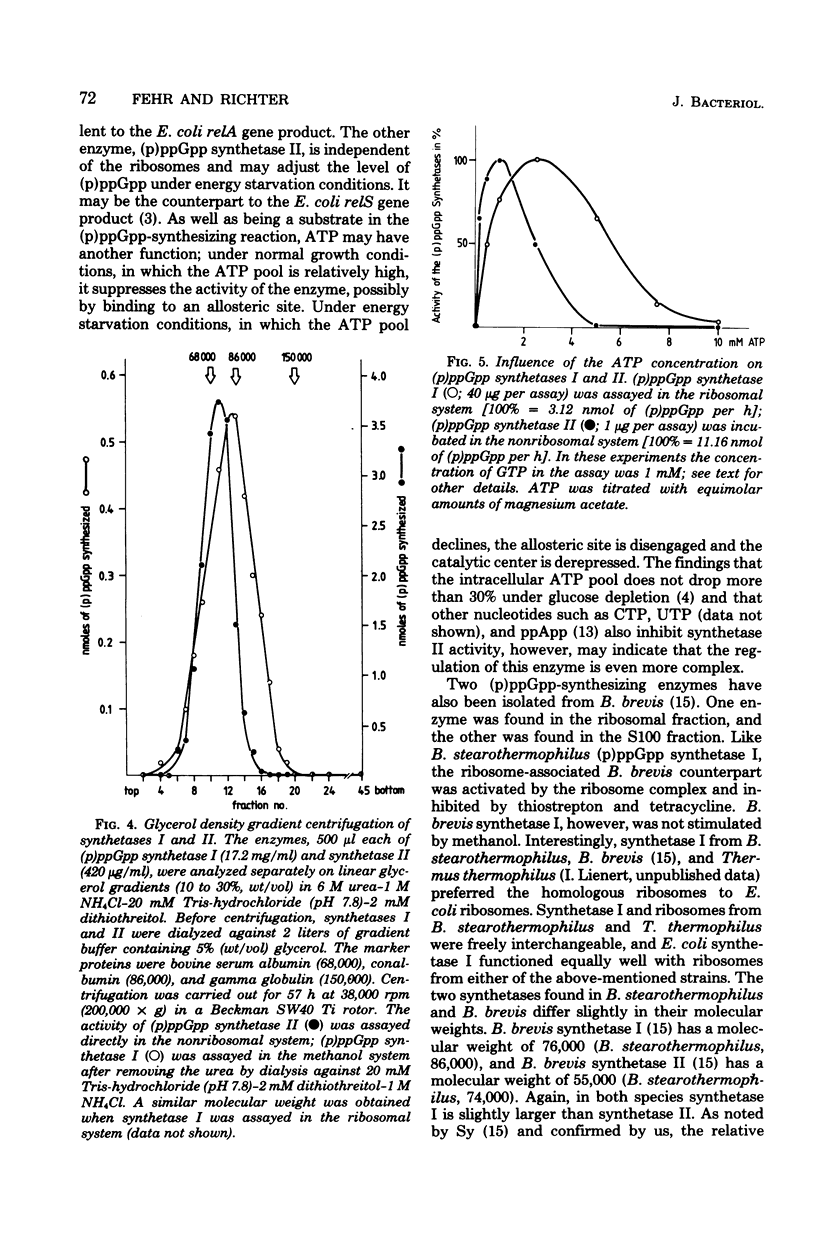
Bacillus stearothermophilus reacted to pseudomonic acid-induced inhibition of isoleucine-transfer ribonucleic acid (RNA) acylation and to energy downshift caused by alpha-methylglucoside addition with accumulation of guanosine 3',5'-polyphosphates [(p)ppGpp] and restriction of RNA synthesis. In vitro studies indicated that (p)ppGpp was synthesized by two different enzymes. One enzyme, (p)ppGpp synthetase I, was present in the ribosomal fraction, required the addition of a ribosome-messenger RNA-transfer RNA complex for activation, and was inhibited by tetracycline and thiostrepton. It is suggested that (p)ppGpp synthetase I is comparable to the relA gene product from Escherichia coli and is responsible for (p)ppGpp accumulation during amino acid starvation. The other enzyme, (p)ppGpp synthetase II, was found in the high-speed supernatant fraction (S100). It functioned independently of ribosomes, transfer RNA, and messenger RNA and was not inhibited by the above-mentioned antibiotics. (p)ppGpp synthetase II is thought to be responsible for (p)ppGpp accumulation during carbon source downshift. The two enzymes differ in their Km values for adenosine triphosphate (ATP):2mM ATP for synthetase I and 0.05 mM ATP for synthetase II. They also have different molecular weights: apparent Mr of 86,000 (+/- 5,000) for synthetase I and 74,000 (+/- 5,000) for synthetase II.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- De Boer H. A., Bakker A. J., Weyer W. J., Gruber M. The role of energy-generating processes in the degradation of guanosine tetrophosphate, ppGpp, in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 19;432(3):361–368. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallant J. A. Stringent control in E. coli. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:393–415. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.002141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGIHIRA H., WILSON T. H., LIN E. C. STUDIES ON THE GLUCOSE-TRANSPORT SYSTEM IN ESCHERICHIA COLI WITH ALPHA-METHYLGLUCOSIDE AS SUBSTRATE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Nov 15;78:505–515. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90912-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemeyer E. A., Geis M., Richter D. Degradation of guanosine 3'-diphosphate 5'-diphosphate in vitro by the spoT gene product of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Aug 15;89(1):125–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb20904.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemeyer E. A., Richter D. Mechanism of the in vitro breakdown of guanosine 5'-diphosphate 3'-diphosphate in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4180–4183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J., Mellows G. Inhibition of isoleucyl-transfer ribonucleic acid synthetase in Escherichia coli by pseudomonic acid. Biochem J. 1978 Oct 15;176(1):305–318. doi: 10.1042/bj1760305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KESSLER D. P., RICKENBERG H. V. The competitive inhibition of alpha-methylglucoside uptake in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Mar 25;10:482–487. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90383-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Morgan E. A. Genetics of bacterial ribosomes. Annu Rev Genet. 1977;11:297–347. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.11.120177.001501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogilvie A., Wiebauer K., Kersten W. Inhibition of leucyl-transfer ribonucleic acid synthetasymol. Biochem J. 1975 Dec;152(3):511–515. doi: 10.1042/bj1520511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter D., Fehr S., Harder R. The guanosine 3',5'-bis(diphosphate) (ppGpp) cycle. Comparison of synthesis and degradation of guanosine 3',5'-bis(diphosphate) in various bacterial systems. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Aug 15;99(1):57–64. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13230.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe J. J., Goldberg I. D., Amelunxen R. E. Development of defined and minimal media for the growth of Bacillus stearothermophilus. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):279–284. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.279-284.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


