Abstract
We describe the complete purification of aromatic aminotransferase I, the enzyme responsible for the ability of Klebsiella aerogenes to use tryptophan and phenylalanine as sole sources of nitrogen, as well as the partial purification of aromatic aminotransferase IV. An examination of the properties of these enzymes revealed that aminotransferase I had much greater affinity for the aromatic amino acids than aminotransferase IV, explaining the essential role of aminotransferase I in the utilization of exogenously supplied aromatic amino acids. The properties of aminotransferase IV suggest that this enzyme is actually an aspartate aminotransferase (EC 2.6.1.1), corresponding to the product of the aspC gene of Escherichia coli.
Full text
PDF
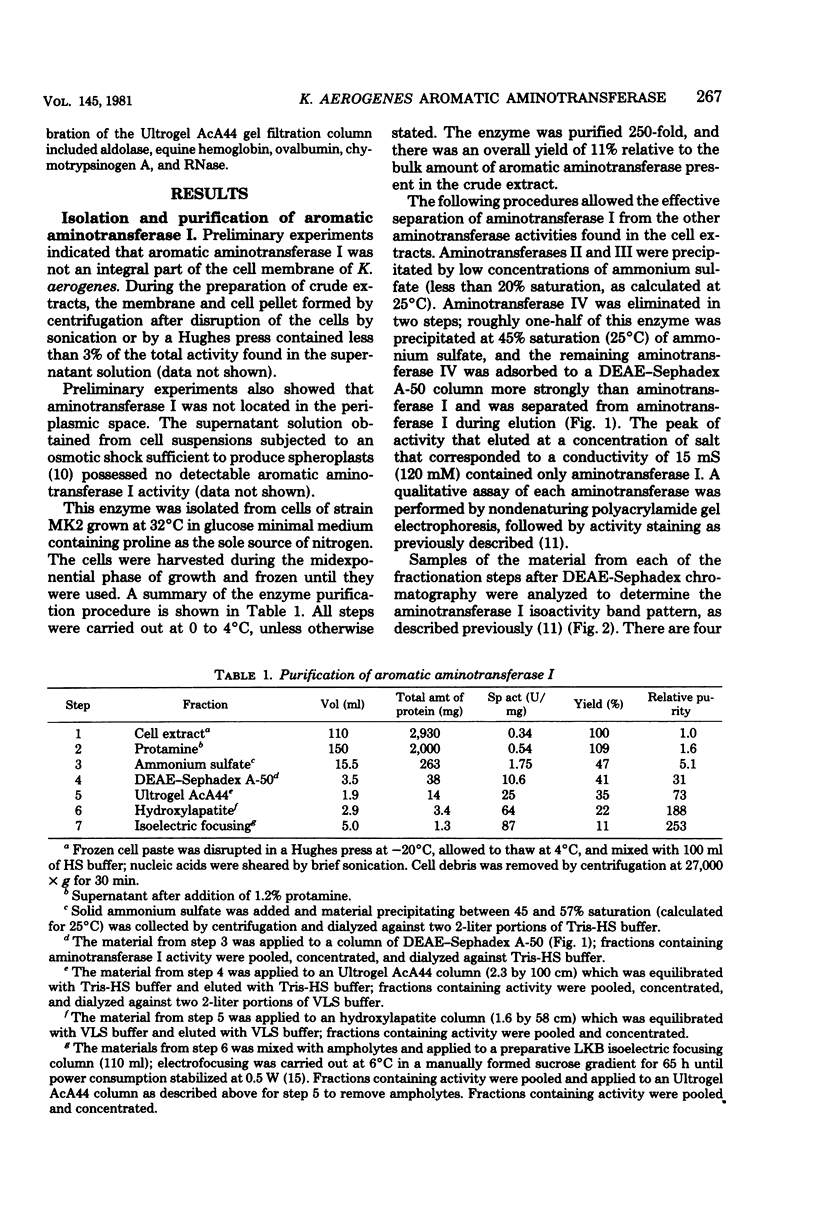
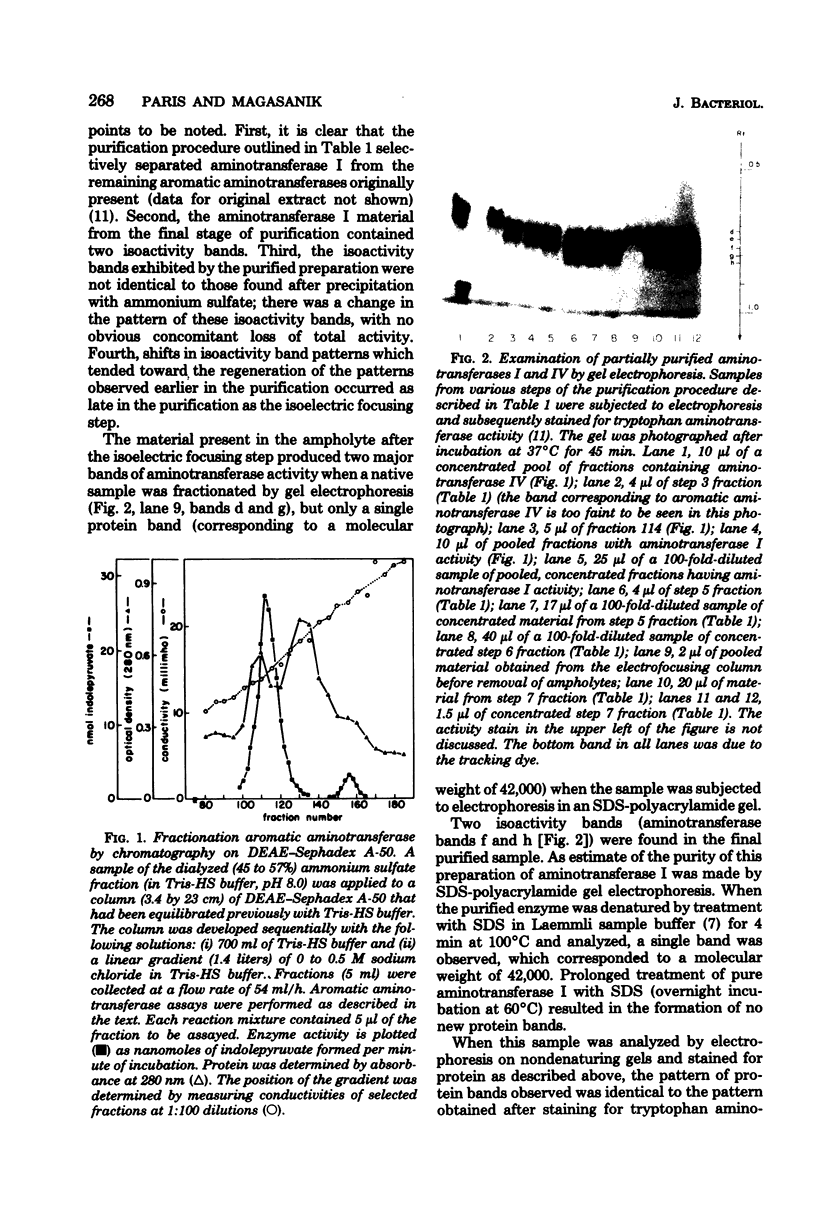



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Botsford J. L., DeMoss R. D. Catabolite repression of tryptophanase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):303–312. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.303-312.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand D. H., Steinberg R. A. Escherichia coli mutants deficient in the aspartate and aromatic amino acid aminotransferases. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):429–440. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.429-440.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOPPER S., SEGAL H. L. Kinetic studies of rat liver glutamicalanine transaminase. J Biol Chem. 1962 Oct;237:3189–3195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick J. L., Smith A. J. Size and charge isomer separation and estimation of molecular weights of proteins by disc gel electrophoresis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Jul;126(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90569-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavrides C., Orr W. Multispecific aspartate and aromatic amino acid aminotransferases in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4128–4133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Heppel L. A. The release of enzymes from Escherichia coli by osmotic shock and during the formation of spheroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3685–3692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paris C. G., Magasanik B. Tryptophan metabolism in Klebsiella aerogenes: regulation of the utilization of aromatic amino acids as sources of nitrogen. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):257–265. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.257-265.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prival M. J., Magasanik B. Resistance to catabolite repression of histidase and proline oxidase during nitrogen-limited growth of Klebsiella aerogenes. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6288–6296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUDMAN D., MEISTER A. Transamination in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1953 Feb;200(2):591–604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. R., Halpern Y. S., Magasanik B. Genetic and metabolic control of enzymes responsible for histidine degradation in Salmonella typhimurium. 4-imidazolone-5-propionate amidohydrolase and N-formimino-L-glutamate formiminohydrolase. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 25;246(10):3320–3329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickramasinghe R. H. Repressible histidine transamination in Escherichia coli and its retro-inhibition. Enzymologia. 1969 Aug 29;37(2):91–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickramasinghe R. H. Studies on the histidine transaminating enzyme of Escherichia coli. Enzymologia. 1969;36(3):161–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]