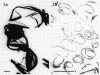Abstract
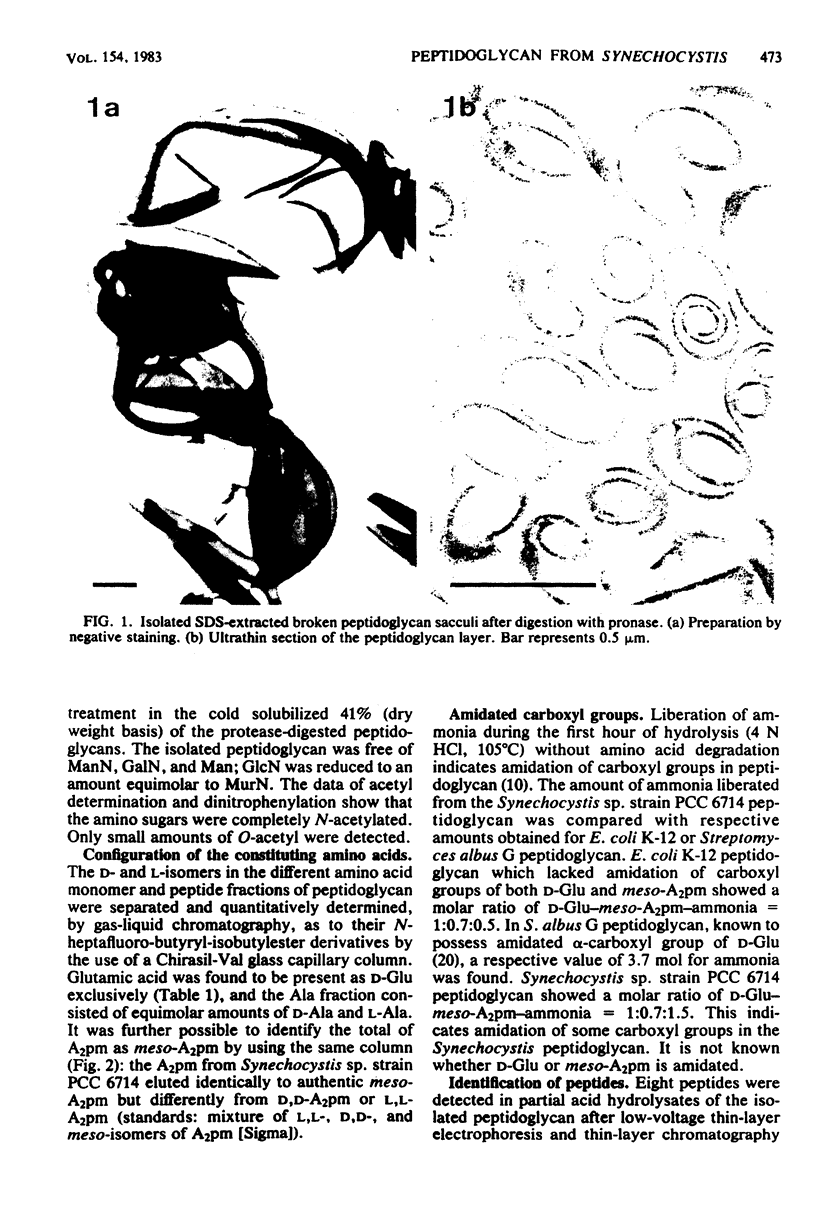
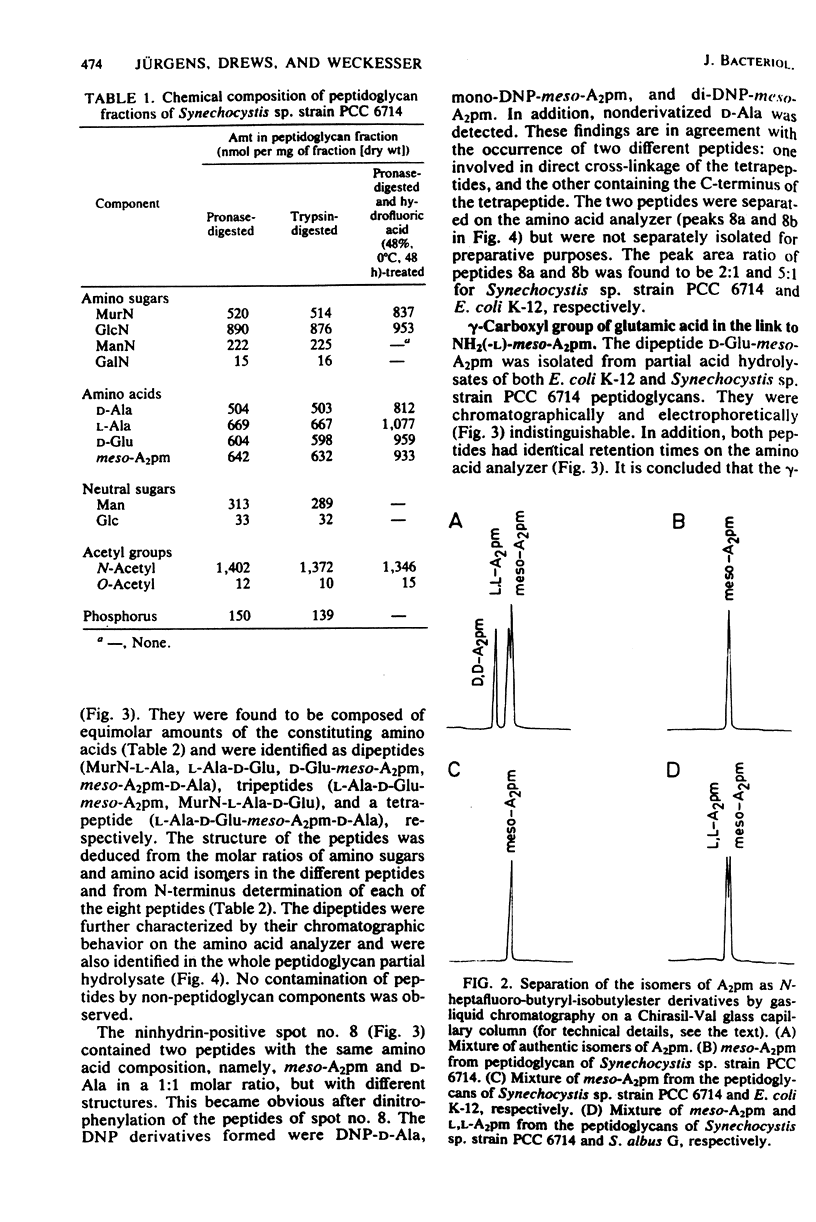
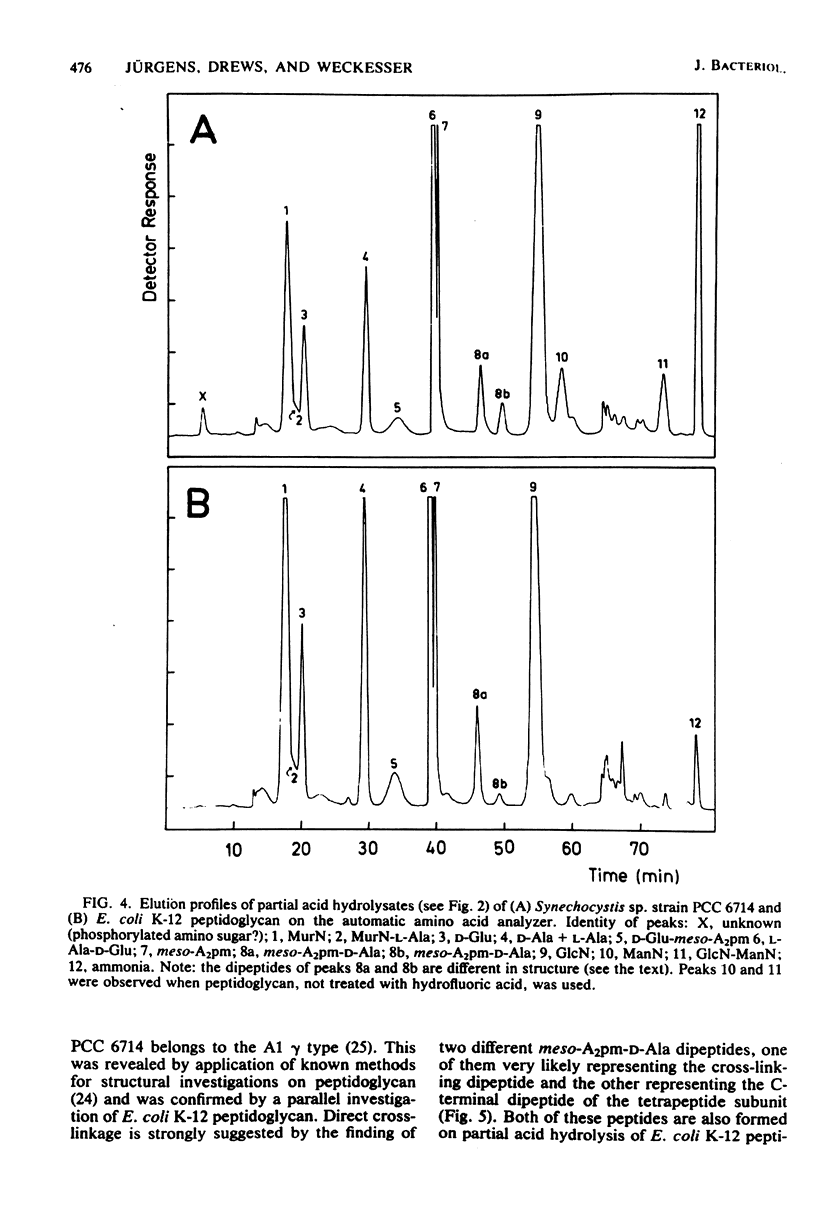
A peptidoglycan fraction free of non-peptidoglycan components was isolated from the unicellular cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6714. Hydrofluoric acid treatment (48%, 0 degrees C, 48 h) cleaved off from the peptidoglycan non-peptidoglycan glucosamine, mannosamine, and mannose. The purified peptidoglycan consists of N-acetyl muramic acid, N-acetyl glucosamine, L-alanine, D-alanine, D-glutamic acid, and meso-diaminopimelic acid in approximately equimolar amounts. At least partial amidation of carboxy groups in the peptide subunits is indicated. Peptide analyses and 2,4-dinitrophenyl studies of partial acid hydrolysates revealed the structure of the Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6714 peptidoglycan to belong to the A1 gamma type (direct cross-linkage) of peptidoglycan classification. The degree of cross-linkage is about 56% and thus is in the range of that found in gram-positive bacteria. Some of the peptide units are present as tripeptides lacking the carboxy-terminal D-alanine.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araki Y., Nakatani T., Nakayama K., Ito E. Occurrence of N-nonsubstituted glucosamine residues in peptidoglycan of lysozyme-resistant cell walls from Bacillus cereus. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 10;247(19):6312–6322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Rehn K. Chemical characterization, spatial distribution and function of a lipoprotein (murein-lipoprotein) of the E. coli cell wall. The specific effect of trypsin on the membrane structure. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Oct;10(3):426–438. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00707.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANK H., LEFORT M., MARTIN H. H. Chemical analysis of a mucopolymer component in cell walls of the blue-green alga Phormidium uncinatum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 May 4;7:322–325. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90200-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishbein J. C., Place A. R., Ropson I. J., Powers D. A., Sofer W. Thin-layer peptide mapping: quantitative analysis and sequencing at the nanomole level. Anal Biochem. 1980 Oct;108(1):193–201. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90712-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Stackebrandt E., Hespell R. B., Gibson J., Maniloff J., Dyer T. A., Wolfe R. S., Balch W. E., Tanner R. S., Magrum L. J. The phylogeny of prokaryotes. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):457–463. doi: 10.1126/science.6771870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromme I., Beilharz H. Gas chromatographic assay of total and O-acetyl groups in bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Anal Biochem. 1978 Feb;84(2):347–353. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90051-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghuysen J. M., Bricas E., Leyh-Bouille M., Lache M., Shockman G. D. The peptide N alpha-(L-alanyl-D-isoglutaminyl)-N epsilon-(D-isoasparaginyl)-L-lysyl-D-alanine and the disaccharide N-acetylglucosaminyl-beta-1,4-N-acetylmuramic acid in cell wall peptidoglycan of Streptococcus faecalis strain ATCC 9790. Biochemistry. 1967 Aug;6(8):2607–2619. doi: 10.1021/bi00860a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghuysen J. M. Use of bacteriolytic enzymes in determination of wall structure and their role in cell metabolism. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Dec;32(4 Pt 2):425–464. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi K. A rapid determination of sodium dodecyl sulfate with methylene blue. Anal Biochem. 1975 Aug;67(2):503–506. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90324-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandler O., König H. Chemical composition of the peptidoglycan-free cell walls of methanogenic bacteria. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Aug 1;118(2):141–152. doi: 10.1007/BF00415722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz W., Martin H. H. Peptide crosslinkage in cell wall murein of Proteus mirabilis and its penicillin-induced unstable L-form. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 May 22;39(4):744–749. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90268-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROBERTS N. R., LEINER K. Y., WU M. L., FARR A. L. The quantitative histochemistry of brain. I. Chemical methods. J Biol Chem. 1954 Mar;207(1):1–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen T. W., Thornton R. F. Analysis of the amino acid 3-methylhistidine by gas-liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):137–141. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedermeier W., Tomana M. Gas chromatographic analysis of hexosamines in glycoproteins. Anal Biochem. 1974 Feb;57(2):363–368. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleifer K. H., Kandler O. Peptidoglycan types of bacterial cell walls and their taxonomic implications. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):407–477. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.407-477.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleifer K. H., Kandler O. Zur chemischen Zusammensetzung der Zellwand der Streptokokken. I. Die Aminosäuresequenz des Mureins von Str. thermophilus und Str. faecalis. Arch Mikrobiol. 1967 Jul 6;57(4):335–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEBE I. EXTENT OF CROSS LINKAGE IN THE MUREIN SACCULUS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI B CELL WALL. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Mar 1;101:124–126. doi: 10.1016/0926-6534(65)90038-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udenfriend S., Stein S., Böhlen P., Dairman W., Leimgruber W., Weigele M. Fluorescamine: a reagent for assay of amino acids, peptides, proteins, and primary amines in the picomole range. Science. 1972 Nov 24;178(4063):871–872. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4063.871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]