Abstract
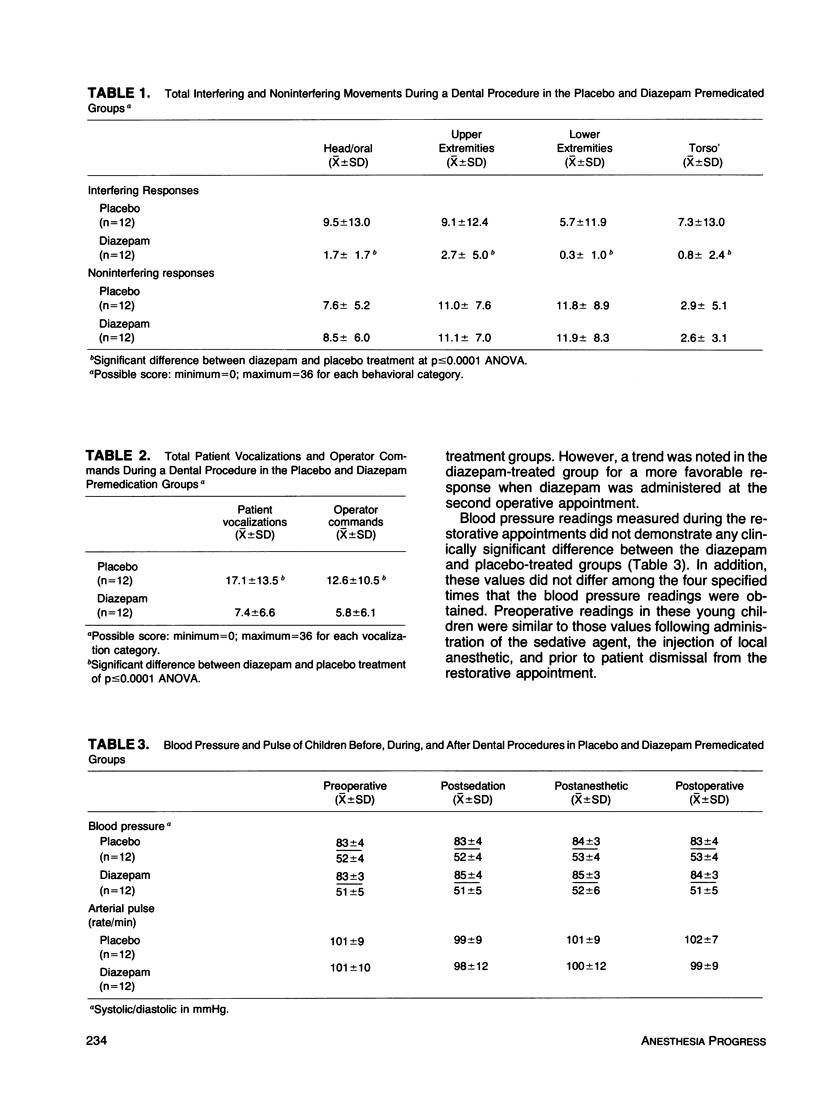
The sedative and cardiovascular effects of rectally administered diazepam (0.6 mg/kg) were compared to placebo in uncooperative children who required sedation during dental treatment. Twelve healthy preschool children, who required amalgam restorations, were treated during two standardized restorative appointments in a double-blind, crossover study. Blood pressure and pulse were obtained during four specified intervals during the appointment. The behavior of the children during the treatment visits was videotaped and later statistically analyzed using a kinesics/vocalization instrument. Behavioral ratings of cooperation were significantly improved during the treatment visit following diazepam. All interfering bodily movements, patient vocalizations and operator commands for the diazepam group were reduced significantly (p≤0.0001). No significant differences were observed for noninterfering behavioral response. Rectally administered diazepam did not alter blood pressure or pulse significantly in these sedated children when compared to the placebo. These findings indicate that rectal diazepam is an effective sedative agent with minimal effect on the cardiovascular system for the management of the young pediatric dental patient.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agurell S., Berlin A., Ferngren H., Hellström B. Plasma levels of diazepam after parenteral and rectal administration in children. Epilepsia. 1975 Jun;16(2):277–283. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1975.tb06058.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahn N. C., Andersen G. W., Thomsen A., Valentin N. Preanaesthetic medication with rectal diazepam in children. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1981 Apr;25(2):158–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1981.tb01627.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blom H., Schmidt J. F., Rytlander M. Rectal diazepam compared to intramuscular pethidine/promethazine/chlorpromazine with regard to gastric contents in paediatric anaesthesia. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1984 Dec;28(6):652–653. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1984.tb02139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulac O., Aicardi J., Rey E., Olive G. Blood levels of diazepam after single rectal administration in infants and children. J Pediatr. 1978 Dec;93(6):1039–1041. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)81254-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howitt J. W., Stricker G. Sequential changes in response to dental procedures. J Dent Res. 1970 Sep-Oct;49(5):1074–1077. doi: 10.1177/00220345700490051201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen F. U. Plasma-diazepam in infants after rectal administration in solution and by suppository. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1977 Sep;66(5):563–567. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1977.tb07947.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langslet A., Meberg A., Bredesen J. E., Lunde P. K. Plasma concentrations of diazepam and N-desmethyldiazepam in newborn infants after intravenous, intramuscular, rectal and oral administration. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1978 Nov;67(6):699–704. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1978.tb16246.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren S., Ekman A., Blombäck U. Rectal administration of diazepam in solution. A clinical study on sedation in paediatric dentistry. Swed Dent J. 1978;2(5):161–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren S., Rosenquist J. B. Comparison of sedation, amnesia, and patient comfort produced by intravenous and rectal diazepam. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1984 Oct;42(10):646–650. doi: 10.1016/0278-2391(84)90206-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattila M. A., Ruoppi M. K., Ahlström-Bengs E., Larni H. M., Pekkola P. O. Diazepam in rectal solution as premedication in children, with special reference to serum concentrations. Br J Anaesth. 1981 Dec;53(12):1269–1272. doi: 10.1093/bja/53.12.1269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meberg A., Langslet A., Bredesen J. E., Lunde P. K. Plasma concentration of diazepam and N-desmethyldiazepam in children after a single rectal or intramuscular dose of diazepam. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1978 Dec 1;14(4):273–276. doi: 10.1007/BF00560461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venham L., Quatrocelli S. The young child's response to repeated dental procedures. J Dent Res. 1977 Jul;56(7):734–738. doi: 10.1177/00220345770560070501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


