Abstract
The effects of variations in growth conditions on the penicillin response of Streptococcus faecium ATCC 9790 were studied. Changes in the growth temperature and medium composition were found to cause striking changes in the bacterial generation time, cellular penicillin sensitivity (minimum inhibitory concentration), sensitivity of peptidoglycan synthesis to inhibition by penicillin, rate of autolysis, and labeling pattern of penicillin-binding proteins. However, no constant relationship between these parameters and the minimum inhibitory concentration could be observed. Similar electrophoretic patterns for penicillin-binding proteins were observed in cells grown in different media at the optimal growth temperature. Inhibition of cell division by penicillin in cells grown at this temperature (but not at higher or lower temperatures) caused filamentation of the bacteria. In cells grown in a chemically defined medium at the optimal temperature (but not at temperatures above or below), complete inhibition of cell division was associated with only partial inhibition (34% after 150 min) of peptidoglycan synthesis. It is suggested that the status and physiological importance of individual penicillin-binding proteins in S. faecium are heavily influenced by growth conditions. Depending on the growth conditions, different penicillin-binding proteins may perform the cellular function, indispensible for bacterial growth.
Full text
PDF


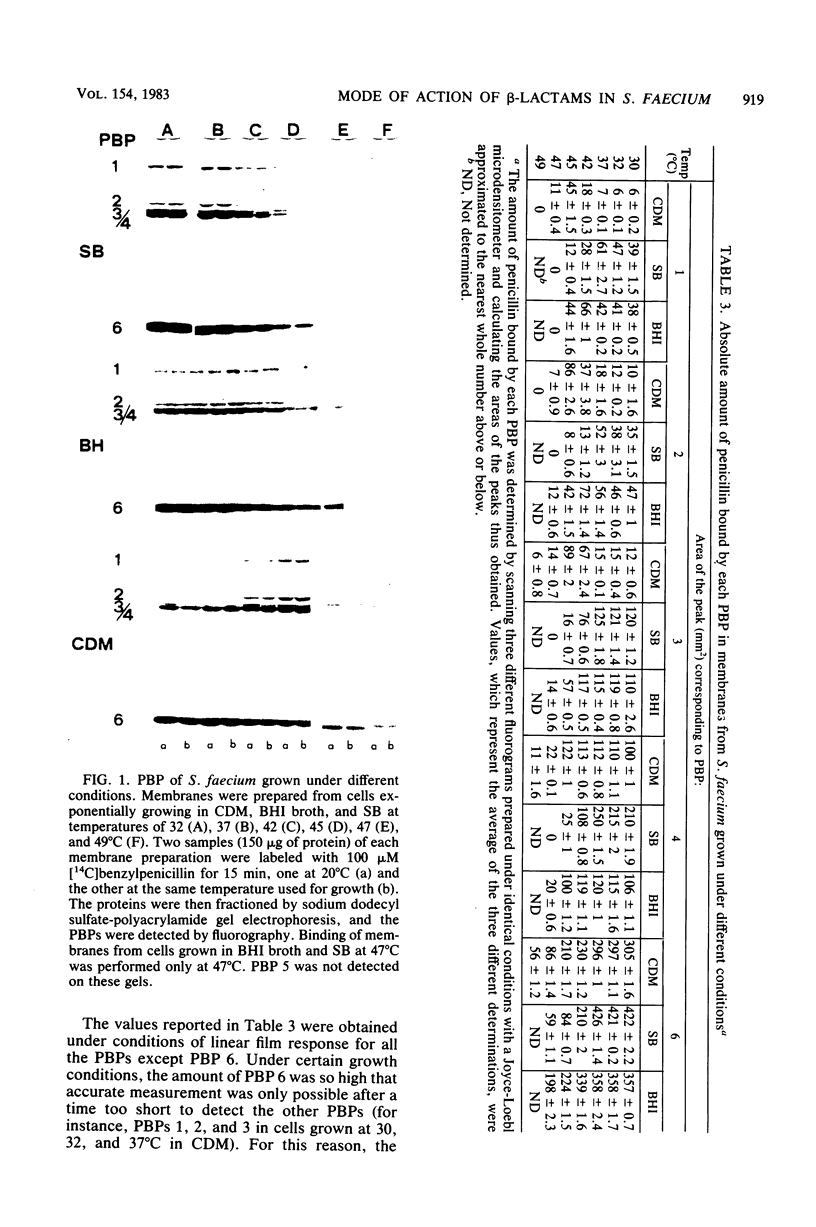

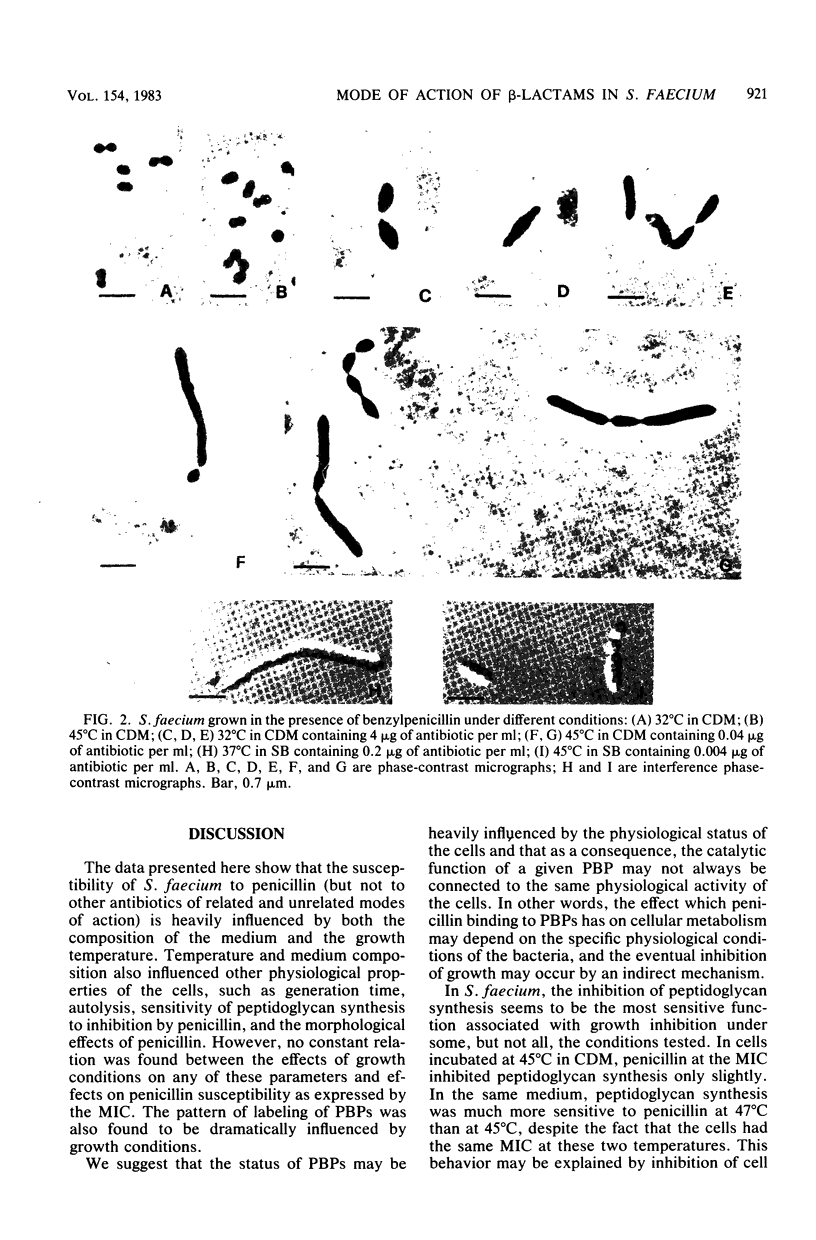
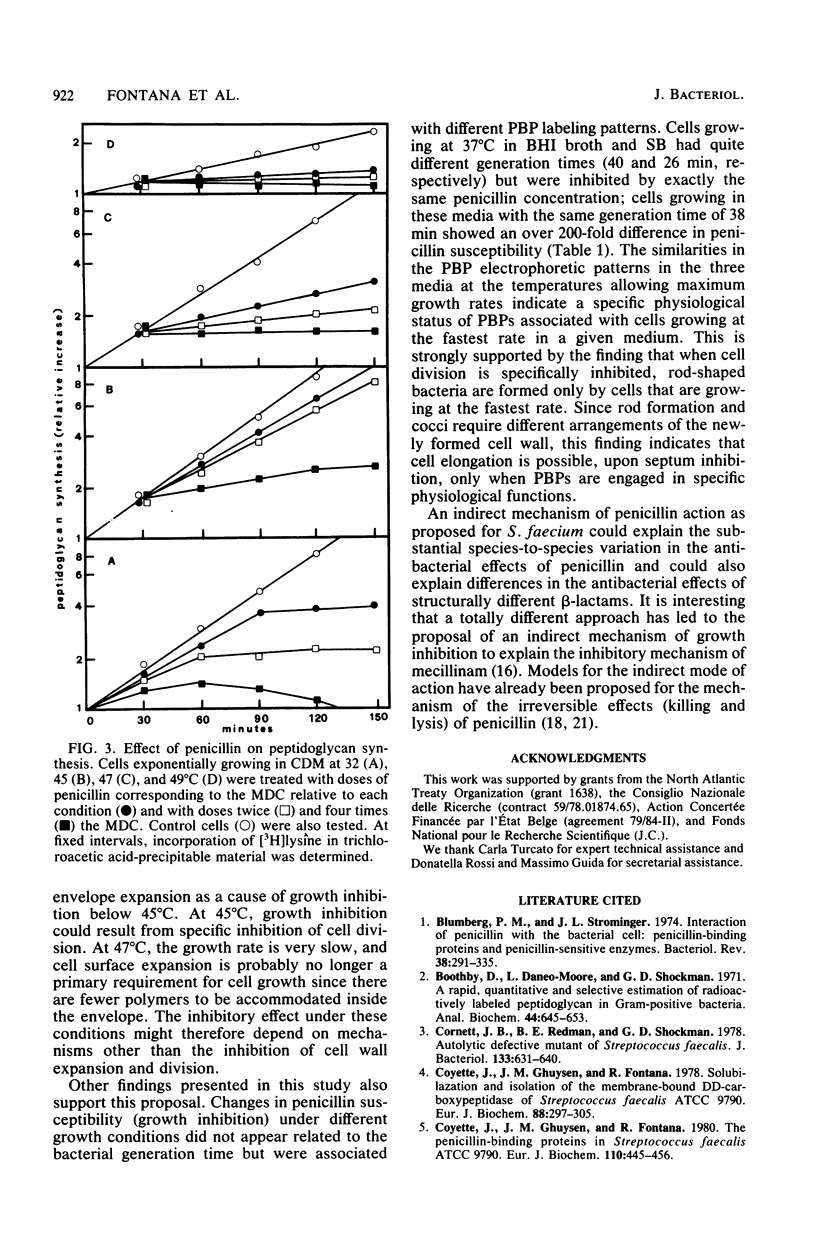

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blumberg P. M., Strominger J. L. Interaction of penicillin with the bacterial cell: penicillin-binding proteins and penicillin-sensitive enzymes. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Sep;38(3):291–335. doi: 10.1128/br.38.3.291-335.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boothby D., Daneo-Moore L., Shockman G. D. A rapid, guantitative, and selective estimation of radioactively labeled peptidoglycan in gram-positive bacteria. Anal Biochem. 1971 Dec;44(2):645–653. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90255-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornett J. B., Redman B. E., Shockman G. D. Autolytic defective mutant of Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):631–640. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.631-640.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyette J., Ghuysen J. M., Fontana R. Solubilization and isolation of the membrane-bound DD-carboxypeptidase of Streptococcus faecalis ATCC9790. Properties of the purified enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jul 17;88(1):297–305. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12450.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyette J., Ghuysen J. M., Fontana R. The penicillin-binding proteins in Streptococcus faecalis ATCC 9790. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Sep;110(2):445–456. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04886.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana R., Canepari P., Satta G., Coyette J. Identification of the lethal target of benzylpenicillin in Streptococcus faecalis by in vivo penicillin binding studies. Nature. 1980 Sep 4;287(5777):70–72. doi: 10.1038/287070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammes W. P. Biosynthesis of peptidoglycan in Gaffkya homari. The mode of action of penicillin G and mecillinam. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Nov 1;70(1):107–113. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10961.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins M. L., McDowell T. D., Sleytr U. B., Mychajlonka M., Shockman G. D. Effects of penicillin on macromolecular synthesis and surface growth of a tolerant streptococcus as studied by computer reconstruction methods. J Bacteriol. 1980 Dec;144(3):1168–1173. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.3.1168-1173.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne D., Tomasz A. Tolerant response of Streptococcus sanguis to beta-lactams and other cell wall inhibitors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 May;11(5):888–896. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.5.888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida K., Hirata S., Nakamuta S., Koike M. Inhibition of cell division of Escherichia coli by a new synthetic penicillin, piperacillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Aug;14(2):257–266. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.2.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D., Nuchamowitz Y. Biosynthesis of peptidoglycan in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. 2. Mode of action of beta-lactam antibiotics. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Mar;94(2):549–556. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12924.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mychajlonka M., McDowell T. D., Shockman G. D. Inhibition of peptidoglycan, ribonucleic acid, and protein synthesis in tolerant strains of Streptococcus mutans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Apr;17(4):572–582. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.4.572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park J. T., Burman L. FL-1060: a new penicillin with a unique mode of action. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Apr 16;51(4):863–868. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pooley H. M., Shockman G. D. Relationship between the latent form and the active form of the autolytic enzyme of Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):617–624. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.617-624.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satta G., Canepari P., Botta G., Fontana R. Control of cell septation by lateral wall extension in a pH-conditional morphology mutant of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1980 Apr;142(1):43–51. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.1.43-51.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shockman G. D., Daneo-Moore L., Cornett J. B., Mychajlonka M. Does penicillin kill bacteria?. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 Sep-Oct;1(5):787–796. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.5.787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Distinct penicillin binding proteins involved in the division, elongation, and shape of Escherichia coli K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2999–3003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipper D. J., Strominger J. L. Mechanism of action of penicillins: a proposal based on their structural similarity to acyl-D-alanyl-D-alanine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Oct;54(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.4.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. The mechanism of the irreversible antimicrobial effects of penicillins: how the beta-lactam antibiotics kill and lyse bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1979;33:113–137. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.33.100179.000553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise E. M., Jr, Park J. T. Penicillin: its basic site of action as an inhibitor of a peptide cross-linking reaction in cell wall mucopeptide synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jul;54(1):75–81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]