Abstract
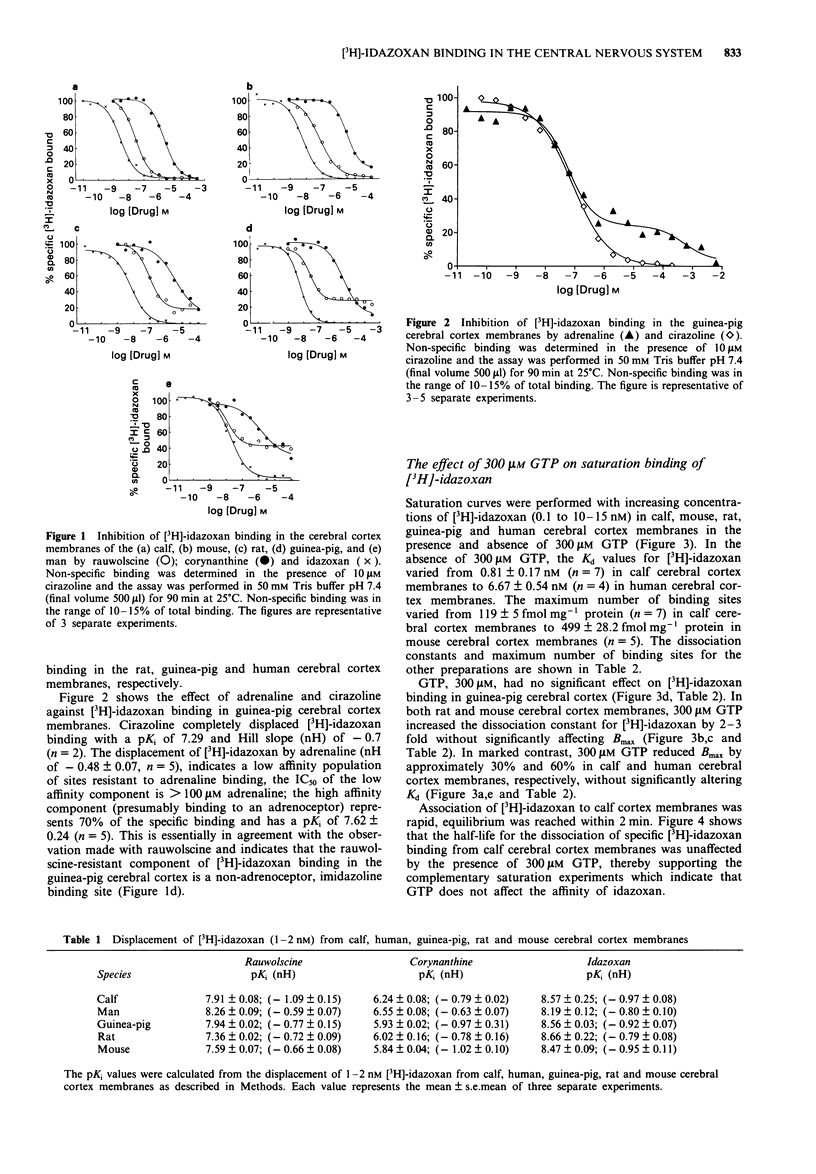
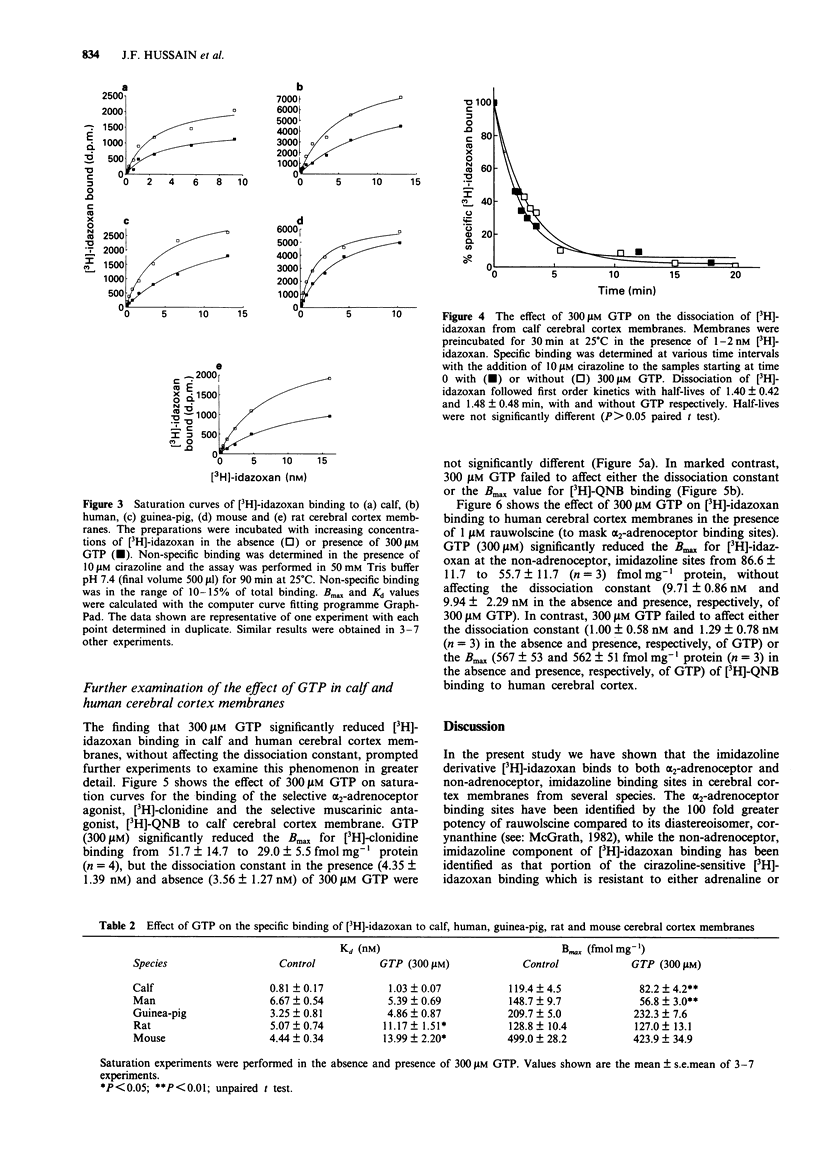
1. We have used the imidazoline derivative [3H]-idazoxan to define alpha 2-adrenoceptors and non-adrenoceptor, imidazoline binding sites in cerebral cortex membranes of calf, mouse, rat, guinea-pig and man. 2. Competition experiments using the selective alpha-adrenoceptor drugs, rauwolscine and corynanthine, indicated that [3H]-idazoxan bound to a single population of sites in the calf and mouse membranes. However, [3H]-idazoxan also labelled non-adrenoceptor, imidazoline binding sites in the rat (15%), guinea-pig (30%) and human (40%) cerebral cortex membranes. 3. Competition experiments with adrenaline and cirazoline in the guinea-pig cortex, verified [3H]-idazoxan binding to both alpha 2-adrenoceptors and to non-adrenoceptor, imidazoline binding sites. 4. It has been postulated by several groups that [3H]-idazoxan may possess partial agonist activity. To investigate this further, saturation experiments were performed in the cerebral cortex membranes of all five species in the absence and presence of 300 microM guanosine triphosphate (GTP). GTP had no effect on [3H]-idazoxan binding in guinea-pig cerebral cortex; in both rat and mouse membranes 300 microM GTP increased the dissociation constant for [3H]-idazoxan by 2-3 fold without significantly affecting the Bmax. GTP reduced the Bmax by approximately 30% and 60% in calf and human cerebral cortex membranes, respectively, without significantly altering the Kd. 5. Saturation experiments were performed in the calf cerebral cortex membranes in the absence and presence of 300 microM GTP with the selective alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist [3H]-clonidine and the selective muscarinic antagonist [3H]-quinuclidinyl benzilate (QNB).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge T. L., Gadie B., Roach A. G., Tulloch I. F. alpha 2-Adrenoceptor agonists induced mydriasis in the rat by an action within the central nervous system. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Mar;78(3):507–515. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb08810.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. M., MacKinnon A. C., McGrath J. C., Spedding M., Kilpatrick A. T. Alpha 2-adrenoceptor subtypes and imidazoline-like binding sites in the rat brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Apr;99(4):803–809. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb13010.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly C. J., McGrath J. C., Wilson V. G. An examination of the postjunctional alpha-adrenoceptor subtypes for (-)-noradrenaline in several isolated blood vessels from the rabbit. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Oct;95(2):473–484. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11668.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doxey J. C., Roach A. G., Smith C. F. Studies on RX 781094: a selective, potent and specific antagonist of alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Mar;78(3):489–505. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb08809.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doxey J. C., Roach A. G., Strachan D. A., Virdee N. K. Selectivity and potency of 2-alkyl analogues of the alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonist idazoxan (RX 781094) in peripheral systems. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Nov;83(3):713–722. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16225.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhardt M. A., Wade S. M., Neubig R. R. p-[125I]iodoclonidine is a partial agonist at the alpha 2-adrenergic receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;38(2):214–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göthert M., Molderings G. J. Involvement of presynaptic imidazoline receptors in the alpha 2-adrenoceptor-independent inhibition of noradrenaline release by imidazoline derivatives. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;343(3):271–282. doi: 10.1007/BF00251126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannah J. A., Hamilton C. A., Reid J. L. RX781094, a new potent alpha 2 adrenoceptor antagonist. In vivo and in vitro studies in the rabbit. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1983 Apr;322(3):221–227. doi: 10.1007/BF00500769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington M. A., Peroutka S. J. Modulation of 5-hydroxytryptamine1A receptor density by nonhydrolyzable GTP analogues. J Neurochem. 1990 Jan;54(1):294–299. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb13314.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman B. B., Mullikin-Kilpatrick D., Lefkowitz R. J. Heterogeneity of radioligand binding to alpha-adrenergic receptors. Analysis of guanine nucleotide regulation of agonist binding in relation to receptor subtypes. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4645–4652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulich L., Jurcovicová J., Le T. Prolactin (PRL) release-inhibiting properties of the alpha 2 adrenergic receptor antagonist idazoxan: comparison with yohimbine. Life Sci. 1989;44(12):809–818. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(89)90378-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachaud-Pettiti V., Podevin R. A., Chrétien Y., Parini A. Imidazoline-guanidinium and alpha 2-adrenergic binding sites in basolateral membranes from human kidney. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Jan 25;206(1):23–31. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(91)90142-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachaud V., Coupry I., Podevin R. A., Dausse J. P., Koenig E., Parini A. Interaction of clonidine and rilmenidine with imidazoline-preferring receptors. J Hypertens Suppl. 1988 Dec;6(4):S511–S513. doi: 10.1097/00004872-198812040-00161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langin D., Paris H., Lafontan M. Binding of [3H]idazoxan and of its methoxy derivative [3H] RX821002 in human fat cells: [3H]idazoxan but not [3H] RX821002 labels additional non-alpha 2-adrenergic binding sites. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Jun;37(6):876–885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon A. C., Brown C. M., Spedding M., Kilpatrick A. T. [3H]-idazoxan binds with high affinity to two sites on hamster adipocytes: an alpha 2-adrenoceptor and a non-adrenoceptor site. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;98(4):1143–1150. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12658.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallat M., Hamon M. Ca2+-guanine nucleotide interactions in brain membranes. I. Modulation of central 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors in the rat. J Neurochem. 1982 Jan;38(1):151–161. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb10866.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. C. Evidence for more than one type of post-junctional alpha-adrenoceptor. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Feb 15;31(4):467–484. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. C., Brodde O. E., Schnepel B., Behrendt J., Tschada R., Motulsky H. J., Insel P. A. [3H]idazoxan and some other alpha 2-adrenergic drugs also bind with high affinity to a nonadrenergic site. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Mar;35(3):324–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofri D., Ritter A. M., Liu Y. F., Gioannini T. L., Hiller J. M., Simon E. J. Characterization of solubilized opioid receptors: reconstitution and uncoupling of guanine nucleotide-sensitive agonist binding. J Neurochem. 1992 Feb;58(2):628–635. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb09764.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmos G., Miralles A., Barturen F., Garcia-Sevilla J. A. Characterization of brain imidazoline receptors in normotensive and hypertensive rats: differential regulation by chronic imidazoline drug treatment. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Mar;260(3):1000–1007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmos G., Miralles A., Barturen F., García-Sevilla J. A. Repeated idazoxan increases brain imidazoline receptors in normotensive (WKY) but not in hypertensive (SHR) rats. J Neurochem. 1991 Nov;57(5):1811–1813. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb06386.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paciorek P. M., Shepperson N. B. alpha 1-Adrenoceptor agonist activity of alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonists in the pithed rat preparation. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 May;79(1):12–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10488.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pimoule C., Scatton B., Langer S. Z. [3H]RX 781094: a new antagonist ligand labels alpha 2-adrenoceptors in the rat brain cortex. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Nov 11;95(1-2):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90269-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schloos J., Wellstein A., Palm D. Agonist binding at alpha 2-adrenoceptors of human platelets using 3H-UK-14,304: regulation by Gpp(NH)p and cations. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1987 Jul;336(1):48–59. doi: 10.1007/BF00177750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- U'Prichard D. C., Greenberg D. A., Snyder S. H. Binding characteristics of a radiolabeled agonist and antagonist at central nervous system alpha noradrenergic receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1977 May;13(3):454–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikberg J. E., Uhlén S. Further characterization of the guinea pig cerebral cortex idazoxan receptor: solubilization, distinction from the imidazole site, and demonstration of cirazoline as an idazoxan receptor-selective drug. J Neurochem. 1990 Jul;55(1):192–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb08838.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yablonsky F., Riffaud J. P., Lacolle J. Y., Dausse J. P. Evidence for non-adrenergic binding sites for [3H]idazoxan in the smooth muscle of rabbit urethra. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Sep 13;154(2):209–212. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90100-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yakubu M. A., Deighton N. M., Hamilton C. A., Reid J. L. Differences in the regulation of [3H]idazoxan and [3H]yohimbine binding sites in the rabbit. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Feb 13;176(3):305–311. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90024-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zonnenchein R., Diamant S., Atlas D. Imidazoline receptors in rat liver cells: a novel receptor or a subtype of alpha 2-adrenoceptors? Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov 6;190(1-2):203–215. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)94127-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- limberger N., Starke K. Partial agonist effect of 2-[2-(1,4-benzodioxanyl)]-2-imidazoline (RX 781 094) at presynaptic alpha 2-adrenoceptors in rabbit ear artery. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1983 Sep;324(1):75–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00647842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


