Abstract
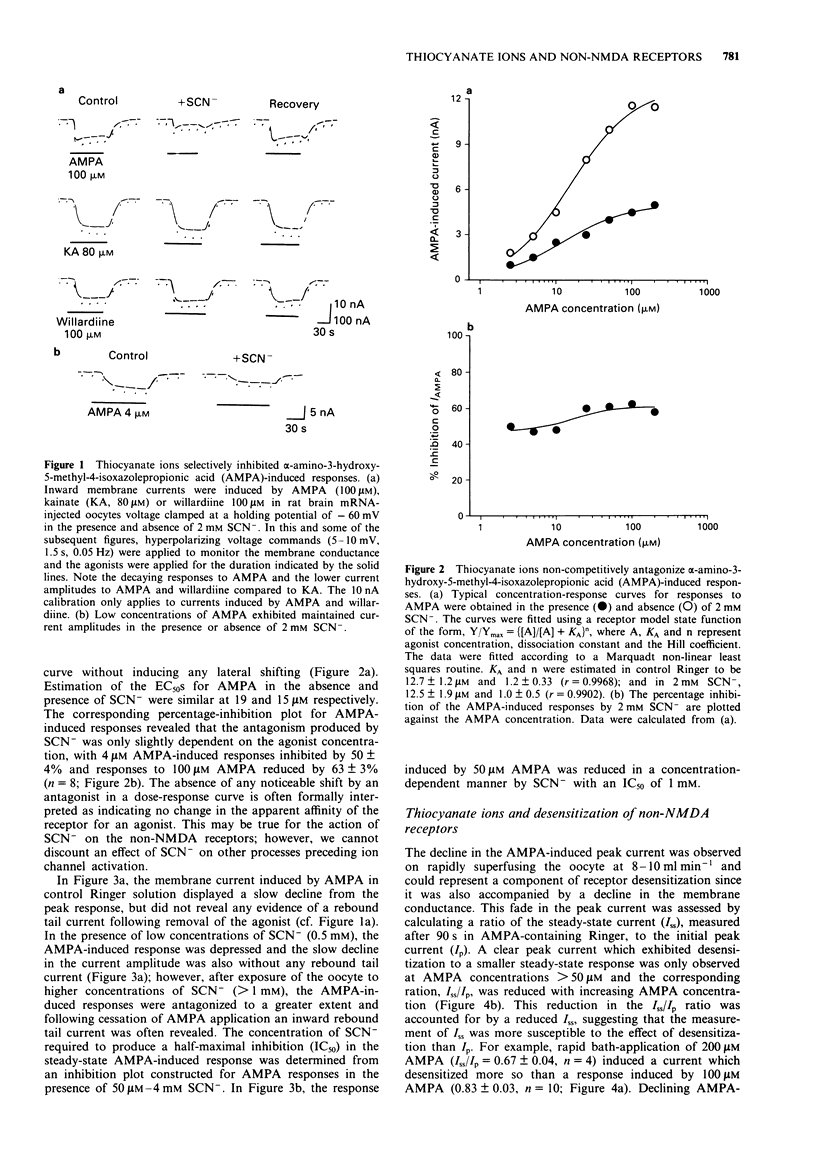
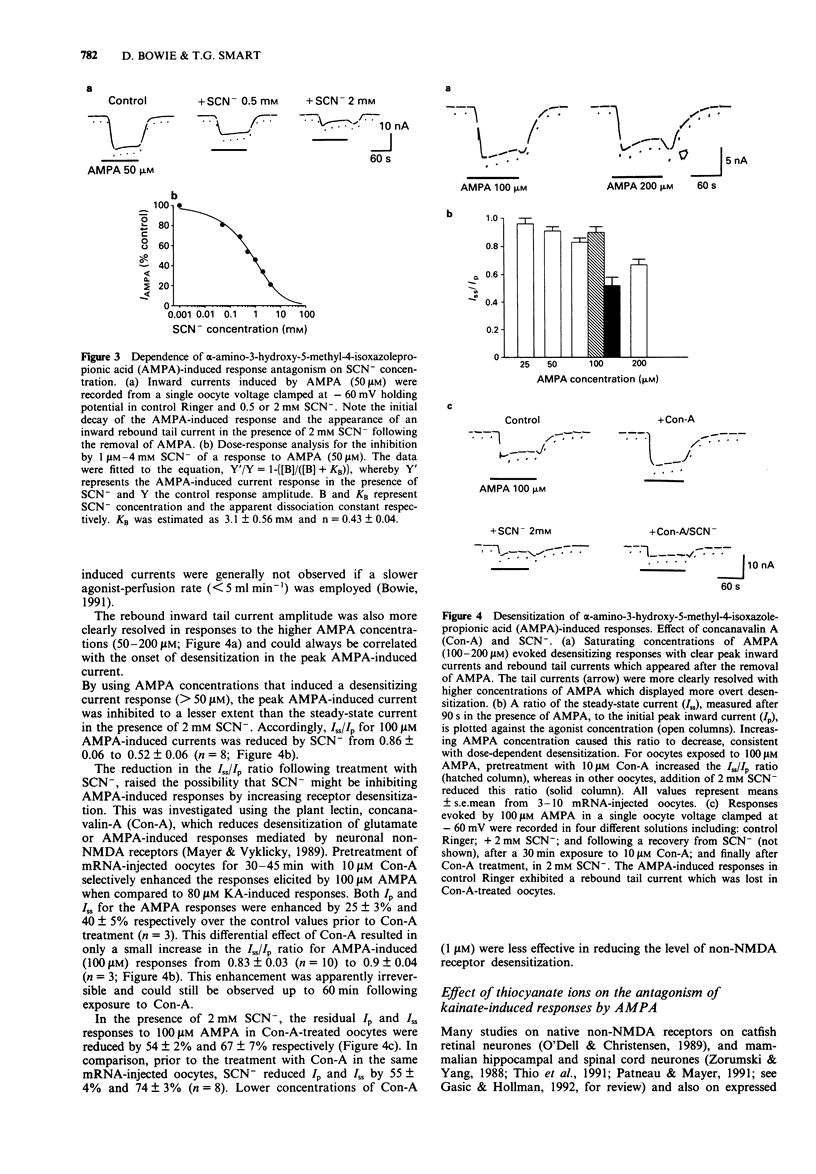
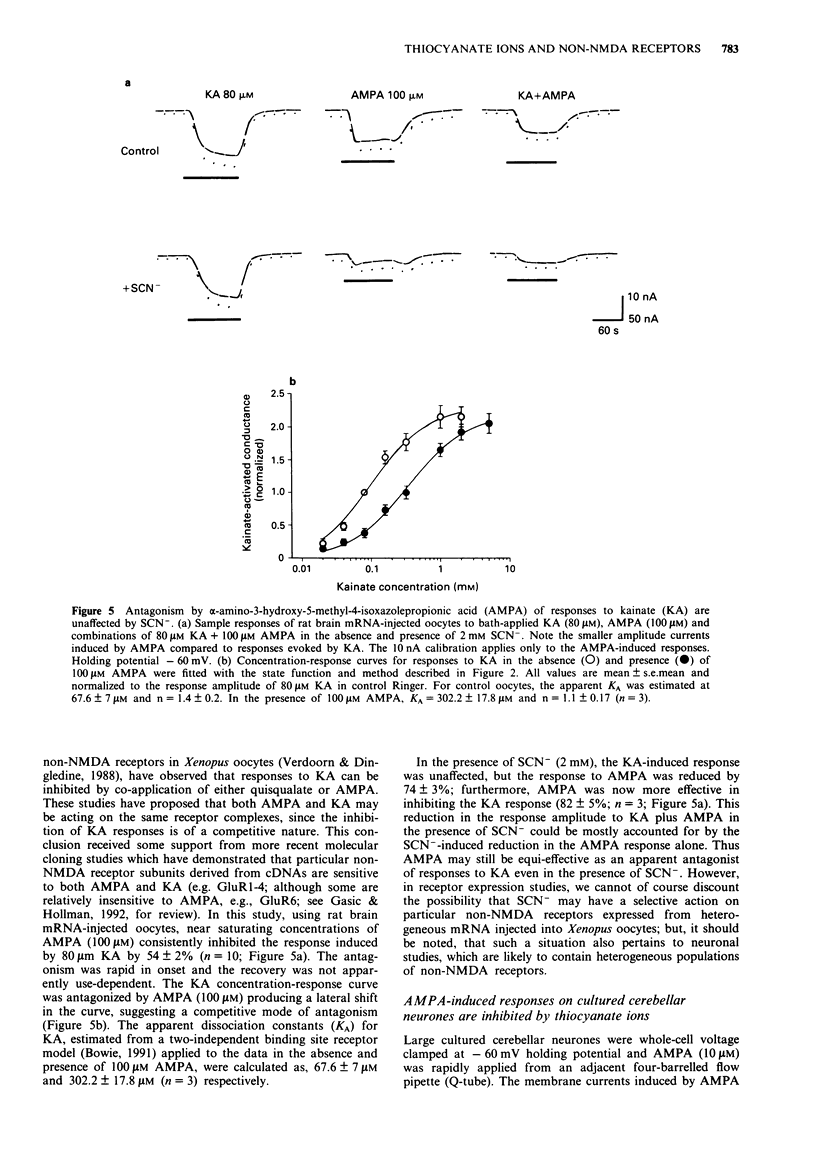
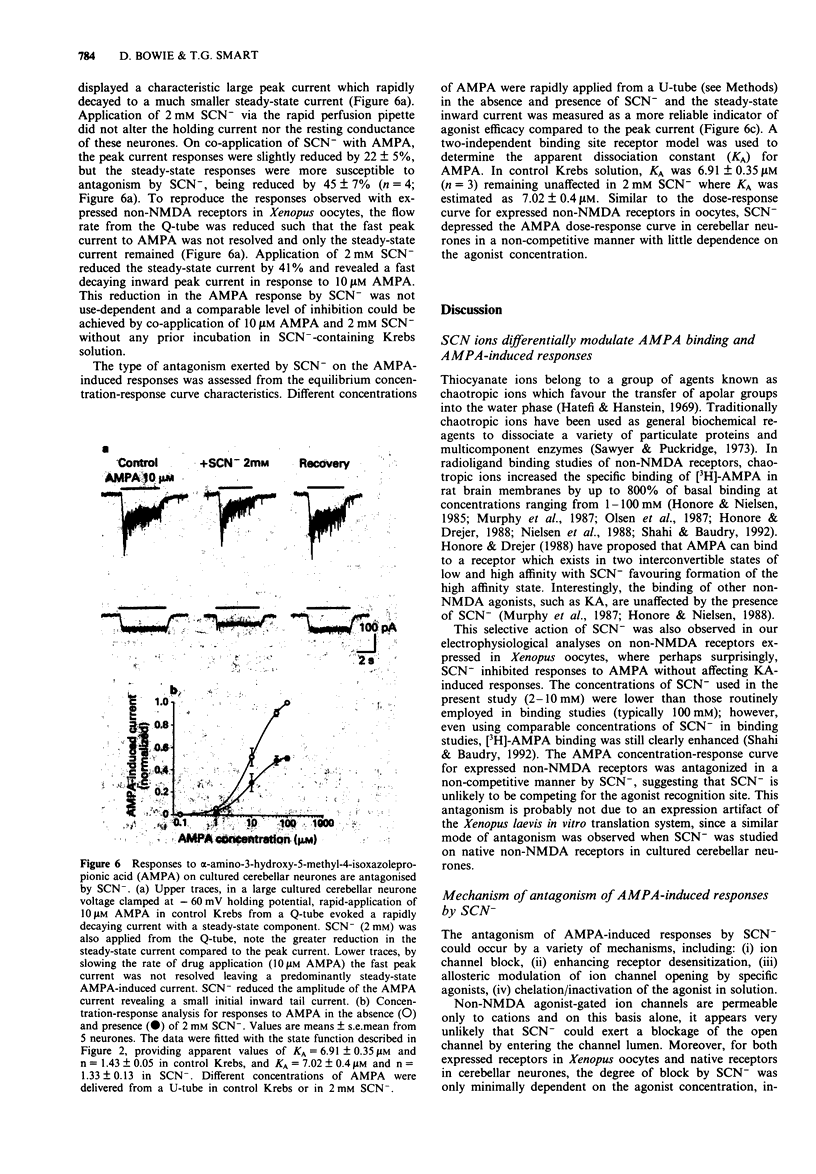
1 Responses to kainate (KA), willardiine and alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) were recorded from rat brain mRNA-injected Xenopus laevis oocytes by use of a two-electrode voltage clamp. 2 Thiocyanate (SCN-; 50 microM-4 mM) ions reversibly and selectively inhibited the membrane current responses to AMPA in a non-competitive manner without affecting KA or willardiine-induced responses. 3 The inhibition of AMPA-induced responses by SCN- was dependent on the SCN- concentration with an estimated IC50 of 1 mM. The antagonism was not dependent on the AMPA concentration. 4 The response to a high concentration of AMPA (100-200 microM) exhibited a peak inward current which declined to a steady-state. SCN- inhibited the steady-state current more than the peak response. The inhibition was unaffected by prior incubation with concanavalin-A (Con-A; 10 microM). 5 Responses to KA were antagonized by AMPA in a competitive manner, suggesting that both agonists may activate a common receptor-channel complex. This interaction between two non-NMDA agonists was not affected by the SCN(-)-induced inhibition of the AMPA response. 6 AMPA-induced responses recorded from large cultured cerebellar neurones by whole-cell recording were also inhibited by SCN- in a non-competitive manner. The AMPA-induced peak current was less affected than the steady-state response. 7 We conclude that SCN- can inhibit the response to AMPA in expressed non-NMDA receptors in Xenopus oocytes and also in native receptors in cultured cerebellar neurones.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R. A study of desensitization using voltage clamp. Pflugers Arch. 1975 Oct 28;360(2):135–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00580536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ascher P., Nowak L. Quisqualate- and kainate-activated channels in mouse central neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1988 May;399:227–245. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnard E. A., Henley J. M. The non-NMDA receptors: types, protein structure and molecular biology. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Dec;11(12):500–507. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90051-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulter J., Hollmann M., O'Shea-Greenfield A., Hartley M., Deneris E., Maron C., Heinemann S. Molecular cloning and functional expression of glutamate receptor subunit genes. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1033–1037. doi: 10.1126/science.2168579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen B. N., Hida E. Protonation of histidine groups inhibits gating of the quisqualate/kainate channel protein in isolated catfish cone horizontal cells. Neuron. 1990 Oct;5(4):471–478. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90086-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Usowicz M. M. Multiple-conductance channels activated by excitatory amino acids in cerebellar neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):525–528. doi: 10.1038/325525a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont J. N. Oogenesis in Xenopus laevis (Daudin). I. Stages of oocyte development in laboratory maintained animals. J Morphol. 1972 Feb;136(2):153–179. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051360203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enomoto R., Ogita K., Han D., Yoneda Y. Differential modulation by divalent cations of [3H]MK-801 binding in brain synaptic membranes. J Neurochem. 1992 Aug;59(2):473–481. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb09394.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick E. M., Marty A., Neher E. A patch-clamp study of bovine chromaffin cells and of their sensitivity to acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:577–597. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsythe I. D., Westbrook G. L., Mayer M. L. Modulation of excitatory synaptic transmission by glycine and zinc in cultures of mouse hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci. 1988 Oct;8(10):3733–3741. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-10-03733.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasic G. P., Hollmann M. Molecular neurobiology of glutamate receptors. Annu Rev Physiol. 1992;54:507–536. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.54.030192.002451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geoffroy M., Lambolez B., Audinat E., Hamon B., Crepel F., Rossier J., Kado R. T. Reduction of desensitization of a glutamate ionotropic receptor by antagonists. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 May;39(5):587–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu Y. P., Huang L. Y. Block of kainate receptor channels by Ca2+ in isolated spinal trigeminal neurons of rat. Neuron. 1991 May;6(5):777–784. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90174-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatefi Y., Hanstein W. G. Solubilization of particulate proteins and nonelectrolytes by chaotropic agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1129–1136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honoré T., Drejer J. Chaotropic ions affect the conformation of quisqualate receptors in rat cortical membranes. J Neurochem. 1988 Aug;51(2):457–461. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb01060.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honoré T., Drejer J., Nielsen M. Calcium discriminates two [3H]kainate binding sites with different molecular target sizes in rat cortex. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Mar 28;65(1):47–52. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90118-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honoré T., Nielsen M. Complex structure of quisqualate-sensitive glutamate receptors in rat cortex. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Feb 28;54(1):27–32. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3940(85)80113-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahr C. E., Stevens C. F. Glutamate activates multiple single channel conductances in hippocampal neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):522–525. doi: 10.1038/325522a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. W., Ascher P. Glycine potentiates the NMDA response in cultured mouse brain neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):529–531. doi: 10.1038/325529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keinänen K., Wisden W., Sommer B., Werner P., Herb A., Verdoorn T. A., Sakmann B., Seeburg P. H. A family of AMPA-selective glutamate receptors. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):556–560. doi: 10.1126/science.2166337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiskin N. I., Krishtal O. A., Tsyndrenko AYa, Akaike N. Are sulfhydryl groups essential for function of the glutamate-operated receptor-ionophore complex? Neurosci Lett. 1986 May 23;66(3):305–310. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishtal O. A., Pidoplichko V. I. A receptor for protons in the nerve cell membrane. Neuroscience. 1980;5(12):2325–2327. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90149-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambolez B., Audinat E., Bochet P., Crépel F., Rossier J. AMPA receptor subunits expressed by single Purkinje cells. Neuron. 1992 Aug;9(2):247–258. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90164-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Vyklicky L., Jr Concanavalin A selectively reduces desensitization of mammalian neuronal quisqualate receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1411–1415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Vyklicky L., Jr, Westbrook G. L. Modulation of excitatory amino acid receptors by group IIB metal cations in cultured mouse hippocampal neurones. J Physiol. 1989 Aug;415:329–350. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L., Guthrie P. B. Voltage-dependent block by Mg2+ of NMDA responses in spinal cord neurones. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):261–263. doi: 10.1038/309261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L., Vyklický L., Jr Sites of antagonist action on N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptors studied using fluctuation analysis and a rapid perfusion technique. J Neurophysiol. 1988 Aug;60(2):645–663. doi: 10.1152/jn.1988.60.2.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. W., Johnston M. V. Physiological and pathophysiological roles of excitatory amino acids during central nervous system development. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1990 Jan-Apr;15(1):41–70. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(90)90011-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaghan D. T., Nguyen L., Cotman C. W. The distribution of [3H]kainate binding sites in primate hippocampus is similar to the distribution of both Ca2+-sensitive and Ca2+-insensitive [3H]kainate binding sites in rat hippocampus. Neurochem Res. 1986 Jul;11(7):1073–1082. doi: 10.1007/BF00965595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D. E., Snowhill E. W., Williams M. Characterization of quisqualate recognition sites in rat brain tissue using DL-[3H]alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid (AMPA) and a filtration assay. Neurochem Res. 1987 Sep;12(9):775–781. doi: 10.1007/BF00971514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen E. O., Cha J. H., Honoré T., Penney J. B., Young A. B. Thiocyanate stabilizes AMPA binding to the quisqualate receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Nov 22;157(2-3):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90383-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak L., Bregestovski P., Ascher P., Herbet A., Prochiantz A. Magnesium gates glutamate-activated channels in mouse central neurones. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):462–465. doi: 10.1038/307462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dell T. J., Christensen B. N. Horizontal cells isolated from catfish retina contain two types of excitatory amino acid receptors. J Neurophysiol. 1989 Jun;61(6):1097–1109. doi: 10.1152/jn.1989.61.6.1097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. W., Szamraj O., Houser C. R. [3H]AMPA binding to glutamate receptor subpopulations in rat brain. Brain Res. 1987 Feb 3;402(2):243–254. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90030-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patneau D. K., Mayer M. L. Kinetic analysis of interactions between kainate and AMPA: evidence for activation of a single receptor in mouse hippocampal neurons. Neuron. 1991 May;6(5):785–798. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90175-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patneau D. K., Mayer M. L. Structure-activity relationships for amino acid transmitter candidates acting at N-methyl-D-aspartate and quisqualate receptors. J Neurosci. 1990 Jul;10(7):2385–2399. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-07-02385.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perouansky M., Grantyn R. Separation of quisqualate- and kainate-selective glutamate receptors in cultured neurons from the rat superior colliculus. J Neurosci. 1989 Jan;9(1):70–80. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-01-00070.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters S., Koh J., Choi D. W. Zinc selectively blocks the action of N-methyl-D-aspartate on cortical neurons. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):589–593. doi: 10.1126/science.2883728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randle J. C., Vernier P., Garrigues A. M., Brault E. Properties of the kainate channel in rat brain mRNA injected Xenopus oocytes: ionic selectivity and blockage. Mol Cell Biochem. 1988 Mar-Apr;80(1-2):121–132. doi: 10.1007/BF00231010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rassendren F. A., Lory P., Pin J. P., Nargeot J. Zinc has opposite effects on NMDA and non-NMDA receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Neuron. 1990 May;4(5):733–740. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90199-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer W. H., Puckridge J. The dissociation of proteins by chaotropic salts. J Biol Chem. 1973 Dec 25;248(24):8429–8433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahi K., Baudry M. Increasing binding affinity of agonists to glutamate receptors increases synaptic responses at glutamatergic synapses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6881–6885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smart T. G. A novel modulatory binding site for zinc on the GABAA receptor complex in cultured rat neurones. J Physiol. 1992 Feb;447:587–625. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smart T. G., Constanti A. A novel effect of zinc on the lobster muscle GABA receptor. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Jun 22;215(1200):327–341. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1982.0045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer B., Keinänen K., Verdoorn T. A., Wisden W., Burnashev N., Herb A., Köhler M., Takagi T., Sakmann B., Seeburg P. H. Flip and flop: a cell-specific functional switch in glutamate-operated channels of the CNS. Science. 1990 Sep 28;249(4976):1580–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.1699275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang C. M., Dichter M., Morad M. Modulation of the N-methyl-D-aspartate channel by extracellular H+. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6445–6449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang C. M., Dichter M., Morad M. Quisqualate activates a rapidly inactivating high conductance ionic channel in hippocampal neurons. Science. 1989 Mar 17;243(4897):1474–1477. doi: 10.1126/science.2467378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thio L. L., Clifford D. B., Zorumski C. F. Characterization of quisqualate receptor desensitization in cultured postnatal rat hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci. 1991 Nov;11(11):3430–3441. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-11-03430.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traynelis S. F., Cull-Candy S. G. Pharmacological properties and H+ sensitivity of excitatory amino acid receptor channels in rat cerebellar granule neurones. J Physiol. 1991 Feb;433:727–763. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traynelis S. F., Cull-Candy S. G. Proton inhibition of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in cerebellar neurons. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):347–350. doi: 10.1038/345347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trussell L. O., Thio L. L., Zorumski C. F., Fischbach G. D. Rapid desensitization of glutamate receptors in vertebrate central neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2834–2838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umbach J. A., Gundersen C. B. Mercuric ions are potent noncompetitive antagonists of human brain kainate receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Oct;36(4):582–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdoorn T. A., Dingledine R. Excitatory amino acid receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes: agonist pharmacology. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Sep;34(3):298–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlachová V., Vyklický L., Vyklický L., Jr, Vyskocil F. The action of excitatory amino acids on chick spinal cord neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1987 May;386:425–438. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyklický L., Jr, Vlachová V., Krůsek J. The effect of external pH changes on responses to excitatory amino acids in mouse hippocampal neurones. J Physiol. 1990 Nov;430:497–517. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyklický L., Vyklický L., Jr, Vyskocil F., Vlachová V., Ujec E., Michl J. Evidence that excitatory amino acids not only activate the receptor channel complex but also lead to use-dependent block. Brain Res. 1986 Jan 15;363(1):148–151. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90668-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westbrook G. L., Mayer M. L. Micromolar concentrations of Zn2+ antagonize NMDA and GABA responses of hippocampal neurons. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):640–643. doi: 10.1038/328640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorumski C. F., Yang J. AMPA, kainate, and quisqualate activate a common receptor-channel complex on embryonic chick motoneurons. J Neurosci. 1988 Nov;8(11):4277–4286. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-11-04277.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


