Abstract
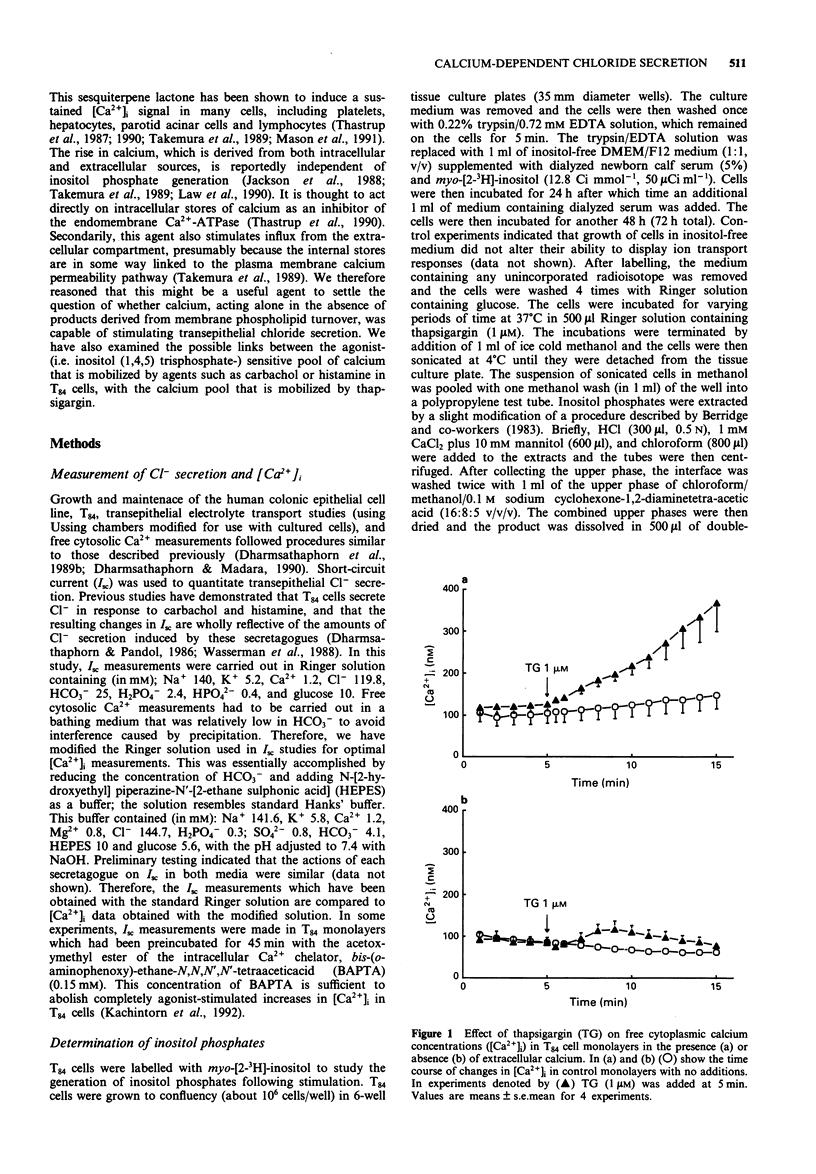
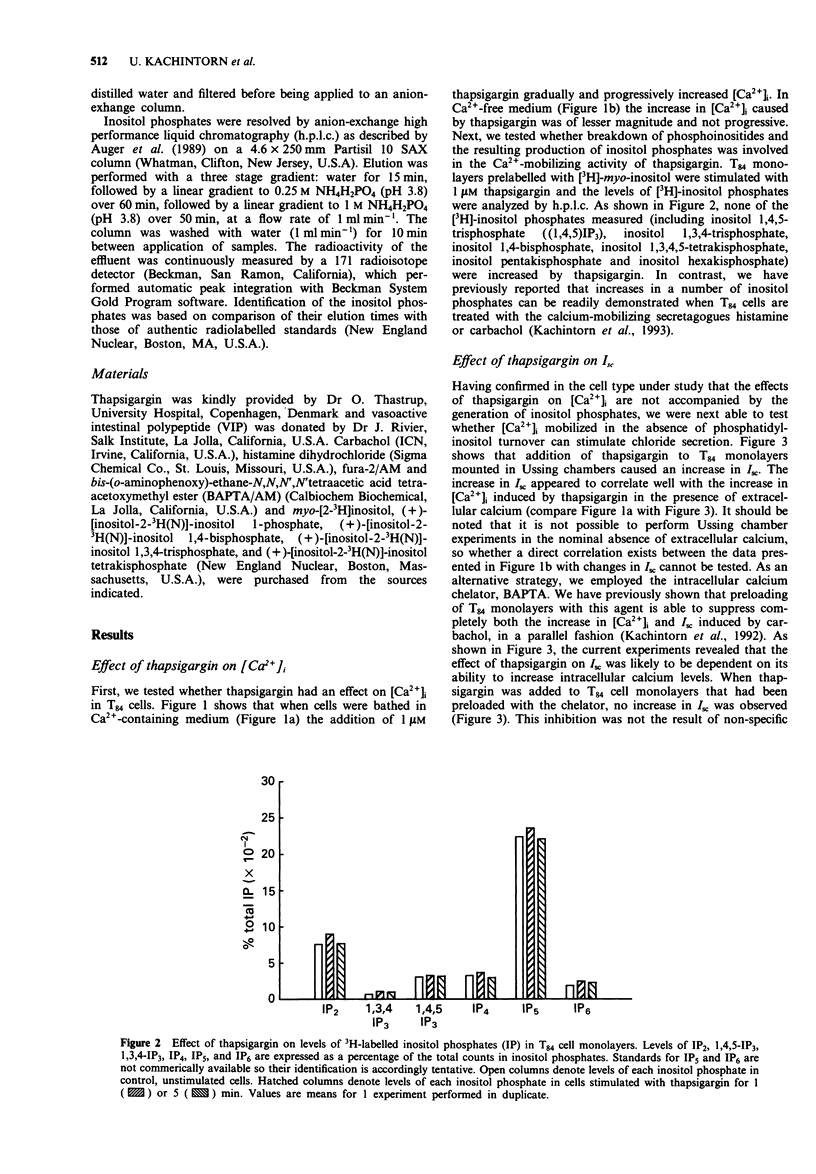
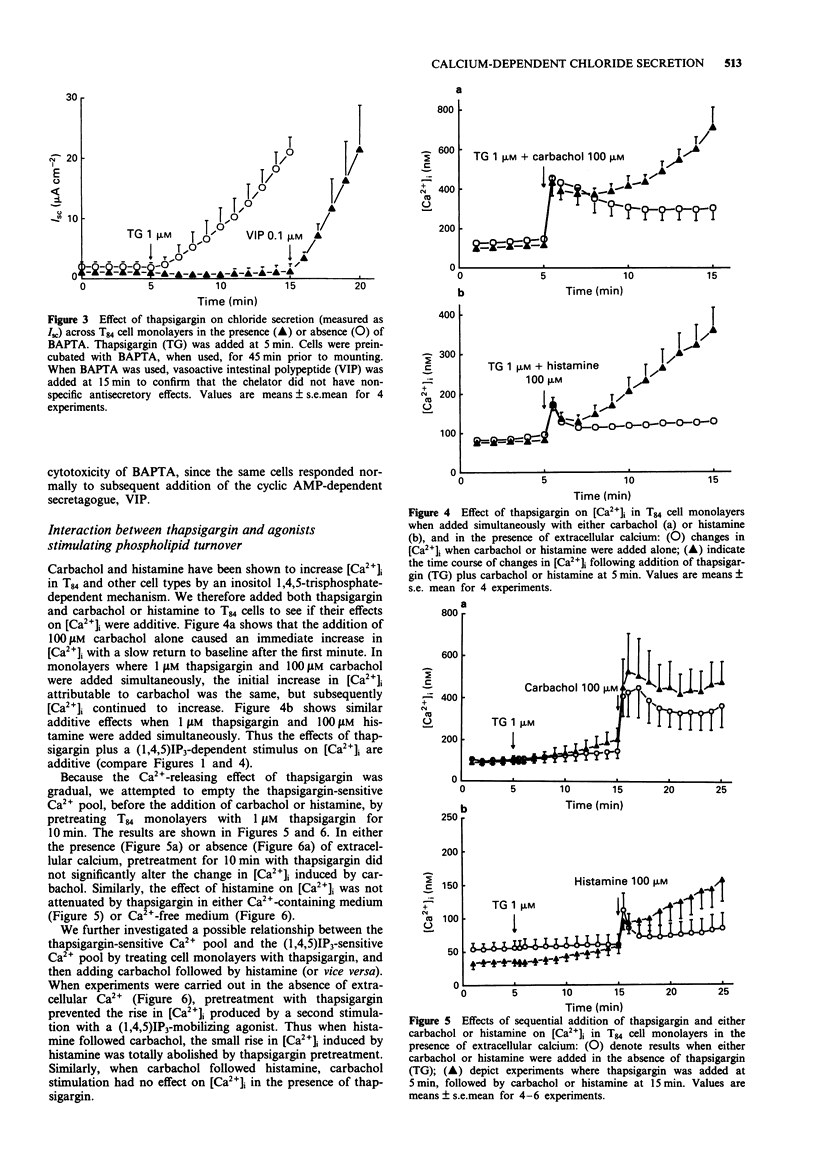
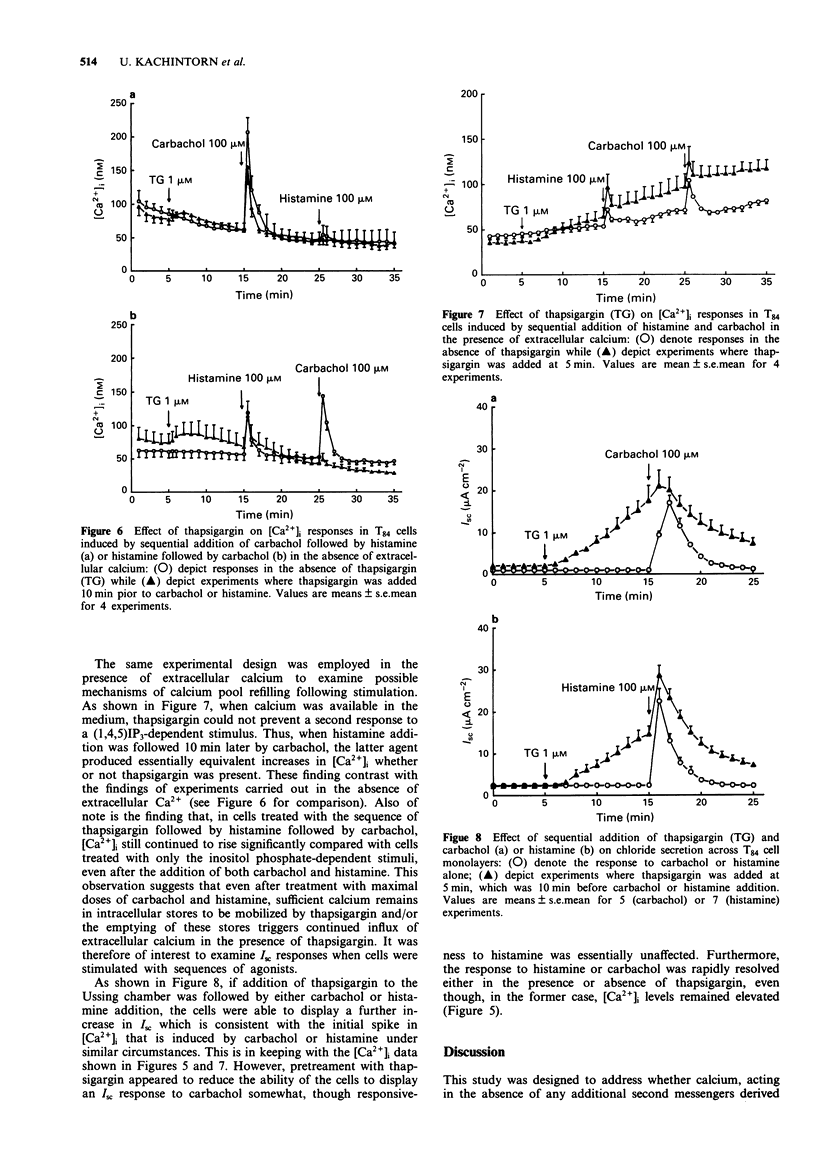
1. The goal of this study was to determine if an increase in cytoplasmic calcium concentration ([Ca2+]i), in the absence of additional second messengers derived from membrane phospholipid turnover, is a sufficient signal to induce chloride secretion across monolayers of the human colonic epithelial line, T84. 2. Thapsigargin was used to increase [Ca2+]i by inhibiting the endomembrane Ca(2+)-ATPase. [Ca2+]i was monitored in monolayers by fura-2 fluorescence spectroscopy, chloride secretion by measuring changes in short circuit current (Isc) in modified Ussing chambers, and inositol phosphates were measured by radio-h.p.l.c. of extracts of cells prelabelled with [3H]-inositol. 3. Thapsigargin increased [Ca2+]i and Isc in parallel, without increasing any inositol phosphates. The effect of thapsigargin on Isc was abolished by the intracellular calcium chelator, bis-(o-aminophenoxy)-ethane-N,N,N',N"-tetraacetic acid (BAPTA). 4. Increasing [Ca2+]i with thapsigargin did not prevent a subsequent calcium response to carbachol or histamine if extracellular calcium was available. In the absence of extracellular calcium, only one such release of calcium to hormonal stimulation occurred when cells were pretreated with thapsigargin, and a second response to either carbachol histamine was essentially abolished. 5. Addition of carbachol or histamine to thapsigargin-treated cells mounted in Ussing chambers caused a transient further increase in Isc followed by termination of the response, even though [Ca2+]i continued to rise. 6. We conclude that an elevation in [Ca2+]i is a sufficient signal to induce chloride secretion in T84 cells. Rather than being required to stimulate secretory responses, additional second messengers induced by hormonal secretagogues (such as inositol phosphates) may in fact serve to limit the secretory response.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auger K. R., Serunian L. A., Soltoff S. P., Libby P., Cantley L. C. PDGF-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation stimulates production of novel polyphosphoinositides in intact cells. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):167–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90182-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton H. P., Jackson T. R., Hanley M. R. Identification of a novel inflammatory stimulant of chondrocytes. Early events in cell activation by bradykinin receptors on pig articular chondrocytes. Biochem J. 1989 Mar 15;258(3):861–867. doi: 10.1042/bj2580861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Dawson R. M., Downes C. P., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F. Changes in the levels of inositol phosphates after agonist-dependent hydrolysis of membrane phosphoinositides. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):473–482. doi: 10.1042/bj2120473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton J. E., Field M. Ca ionophore-stimulated ion secretion in rabbit ileal mucosa: relation to actions of cyclic 3',5'-AMP and carbamylcholine. J Membr Biol. 1977 Jun 30;35(2):159–173. doi: 10.1007/BF01869947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brayden D. J., Hanley M. R., Thastrup O., Cuthbert A. W. Thapsigargin, a new calcium-dependent epithelial anion secretagogue. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;98(3):809–816. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb14609.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright C. A., McRoberts J. A., Mandel K. G., Dharmsathaphorn K. Synergistic action of cyclic adenosine monophosphate- and calcium-mediated chloride secretion in a colonic epithelial cell line. J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):1837–1842. doi: 10.1172/JCI112176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase H. S., Jr Does calcium couple the apical and basolateral membrane permeabilities in epithelia? Am J Physiol. 1984 Dec;247(6 Pt 2):F869–F876. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.6.F869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn J. A. Protein kinase C mediates cholinergically regulated protein phosphorylation in a Cl(-)-secreting epithelium. Am J Physiol. 1990 Feb;258(2 Pt 1):C227–C233. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.2.C227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharmsathaphorn K., Cohn J., Beuerlein G. Multiple calcium-mediated effector mechanisms regulate chloride secretory responses in T84-cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jun;256(6 Pt 1):C1224–C1230. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.6.C1224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharmsathaphorn K., Huott P. A., Vongkovit P., Beuerlein G., Pandol S. J., Ammon H. V. Cl- secretion induced by bile salts. A study of the mechanism of action based on a cultured colonic epithelial cell line. J Clin Invest. 1989 Sep;84(3):945–953. doi: 10.1172/JCI114257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharmsathaphorn K., Madara J. L. Established intestinal cell lines as model systems for electrolyte transport studies. Methods Enzymol. 1990;192:354–389. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)92082-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharmsathaphorn K., Pandol S. J. Mechanism of chloride secretion induced by carbachol in a colonic epithelial cell line. J Clin Invest. 1986 Feb;77(2):348–354. doi: 10.1172/JCI112311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donowitz M., Welsh M. J. Ca2+ and cyclic AMP in regulation of intestinal Na, K, and Cl transport. Annu Rev Physiol. 1986;48:135–150. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.48.030186.001031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foder B., Scharff O., Thastrup O. Ca2+ transients and Mn2+ entry in human neutrophils induced by thapsigargin. Cell Calcium. 1989 Oct;10(7):477–490. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(89)90025-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frizzell R. A. Active chloride secretion by rabbit colon: calcium-dependent stimulation by ionophore A23187. J Membr Biol. 1977 Jun 30;35(2):175–187. doi: 10.1007/BF01869948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen C. A., Yang L. J., Williamson J. R. Mechanisms of receptor-mediated Ca2+ signaling in rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):18573–18579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson T. R., Patterson S. I., Thastrup O., Hanley M. R. A novel tumour promoter, thapsigargin, transiently increases cytoplasmic free Ca2+ without generation of inositol phosphates in NG115-401L neuronal cells. Biochem J. 1988 Jul 1;253(1):81–86. doi: 10.1042/bj2530081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kachintorn U., Vongkovit P., Vajanaphanich M., Dinh S., Barrett K. E., Dharmsathaphorn K. Dual effects of a phorbol ester on calcium-dependent chloride secretion by T84 epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jan;262(1 Pt 1):C15–C22. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.1.C15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwan C. Y., Takemura H., Obie J. F., Thastrup O., Putney J. W., Jr Effects of MeCh, thapsigargin, and La3+ on plasmalemmal and intracellular Ca2+ transport in lacrimal acinar cells. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jun;258(6 Pt 1):C1006–C1015. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.6.C1006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law G. J., Pachter J. A., Thastrup O., Hanley M. R., Dannies P. S. Thapsigargin, but not caffeine, blocks the ability of thyrotropin-releasing hormone to release Ca2+ from an intracellular store in GH4C1 pituitary cells. Biochem J. 1990 Apr 15;267(2):359–364. doi: 10.1042/bj2670359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lückhoff A., Clapham D. E. Inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate activates an endothelial Ca(2+)-permeable channel. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):356–358. doi: 10.1038/355356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel K. G., McRoberts J. A., Beuerlein G., Foster E. S., Dharmsathaphorn K. Ba2+ inhibition of VIP- and A23187-stimulated Cl- secretion by T84 cell monolayers. Am J Physiol. 1986 Mar;250(3 Pt 1):C486–C494. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.250.3.C486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason M. J., Garcia-Rodriguez C., Grinstein S. Coupling between intracellular Ca2+ stores and the Ca2+ permeability of the plasma membrane. Comparison of the effects of thapsigargin, 2,5-di-(tert-butyl)-1,4-hydroquinone, and cyclopiazonic acid in rat thymic lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):20856–20862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann J. D., Welsh M. J. Regulation of Cl- and K+ channels in airway epithelium. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:115–135. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.000555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohuchi K., Sugawara T., Watanabe M., Hirasawa N., Tsurufuji S., Fujiki H., Christensen S. B., Sugimura T. Analysis of the stimulative effect of thapsigargin, a non-TPA-type tumour promoter, on arachidonic acid metabolism in rat peritoneal macrophages. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jul;94(3):917–923. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11604.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickles R. J., Cuthbert A. W. Failure of thapsigargin to alter ion transport in human sweat gland epithelia while intracellular Ca2+ concentration is raised. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):14818–14825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharff O., Foder B., Thastrup O., Hofmann B., Møller J., Ryder L. P., Jacobsen K. D., Langhoff E., Dickmeiss E., Christensen S. B. Effect of thapsigargin on cytoplasmic Ca2+ and proliferation of human lymphocytes in relation to AIDS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Dec 9;972(3):257–264. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(88)90200-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemura H., Hughes A. R., Thastrup O., Putney J. W., Jr Activation of calcium entry by the tumor promoter thapsigargin in parotid acinar cells. Evidence that an intracellular calcium pool and not an inositol phosphate regulates calcium fluxes at the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12266–12271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemura H., Thastrup O., Putney J. W., Jr Calcium efflux across the plasma membrane of rat parotid acinar cells is unaffected by receptor activation or by the microsomal calcium ATPase inhibitor, thapsigargin. Cell Calcium. 1990 Jan;11(1):11–17. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(90)90044-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thastrup O., Cullen P. J., Drøbak B. K., Hanley M. R., Dawson A. P. Thapsigargin, a tumor promoter, discharges intracellular Ca2+ stores by specific inhibition of the endoplasmic reticulum Ca2(+)-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2466–2470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thastrup O., Foder B., Scharff O. The calcium mobilizing tumor promoting agent, thapsigargin elevates the platelet cytoplasmic free calcium concentration to a higher steady state level. A possible mechanism of action for the tumor promotion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Feb 13;142(3):654–660. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91464-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thastrup O. Role of Ca2(+)-ATPases in regulation of cellular Ca2+ signalling, as studied with the selective microsomal Ca2(+)-ATPase inhibitor, thapsigargin. Agents Actions. 1990 Jan;29(1-2):8–15. doi: 10.1007/BF01964706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman S. I., Barrett K. E., Huott P. A., Beuerlein G., Kagnoff M. F., Dharmsathaphorn K. Immune-related intestinal Cl- secretion. I. Effect of histamine on the T84 cell line. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jan;254(1 Pt 1):C53–C62. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.254.1.C53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M. J. Effect of phorbol ester and calcium ionophore on chloride secretion in canine tracheal epithelium. Am J Physiol. 1987 Dec;253(6 Pt 1):C828–C834. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.6.C828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S. M., Lindeman R. P., Parangi S., Chase H. S., Jr Role of calcium in mediating action of carbachol in T84 cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Nov;257(5 Pt 1):C976–C985. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.257.5.C976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


