Abstract
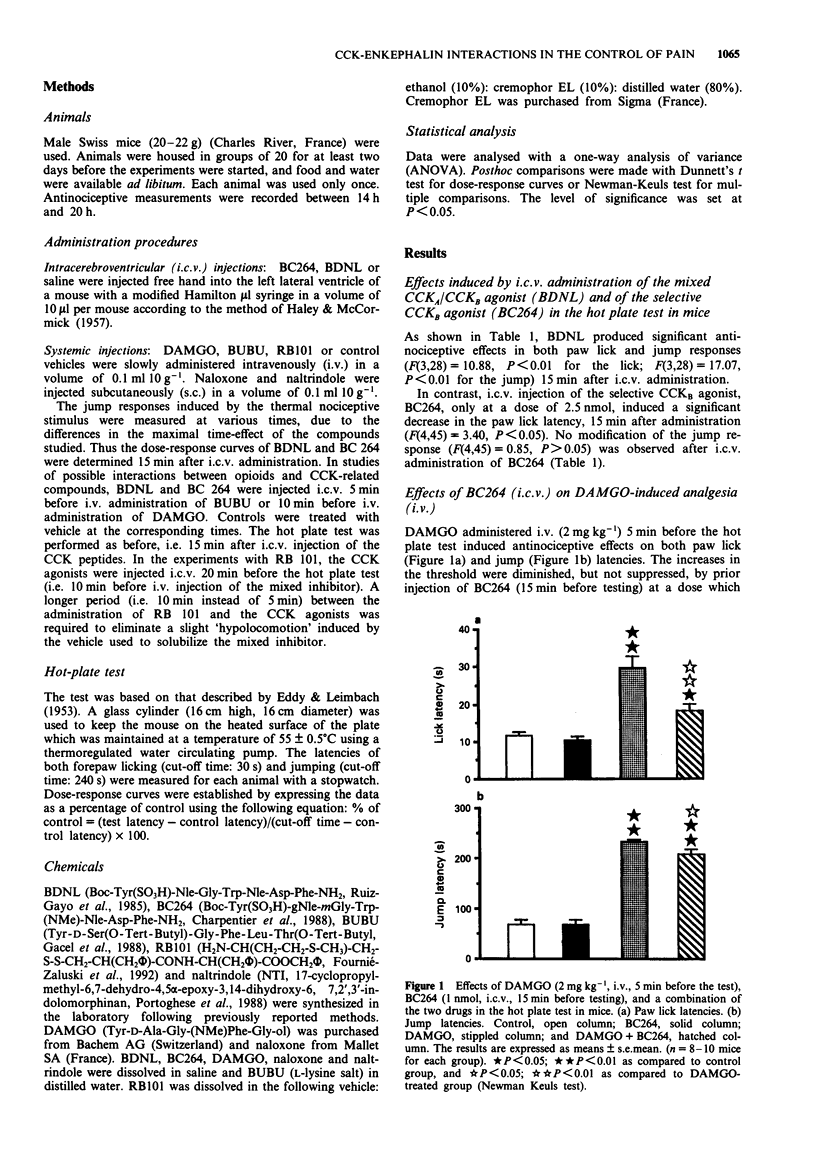
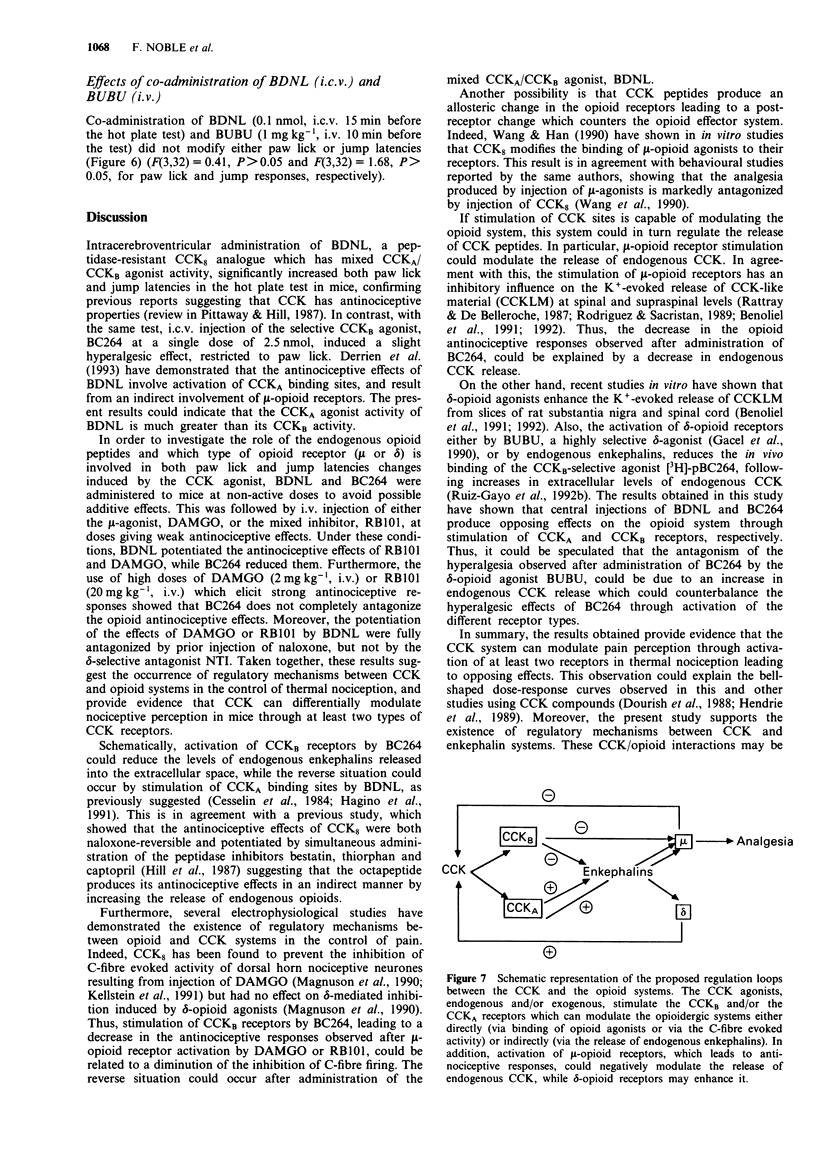
1. Much evidence in the literature supports the idea that cholecystokinin (CCK) interacts with opioids in pain mechanisms. In this work, we have investigated the supraspinal interactions between enkephalins and CCK, using the hot plate test in mice. 2. Intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) administration of BDNL (a mixed CCKA/CCKB agonist) induced dose-dependent antinociceptive responses on both paw lick and jump responses. In contrast, using the same test, the i.c.v. injection of BC 264 (a selective CCKB agonist) induced a hyperalgesic effect, which was restricted to paw licking and occurred only at a high dose of 2.5 nmol. 3. In addition, i.c.v. administration of BDNL potentiated the antinociceptive effects of the mixed inhibitor of enkephalin degrading enzymes, RB 101 and of the mu-agonist, DAMGO, while BC 264 reduced these effects. 4. Furthermore, at a dose where it interacts selectively with delta-opioid receptors, the opioid agonist BUBU reversed the hyperalgesic responses of BC 264 (2.5 nmol) but was unable to modify the effects induced by BDNL. 5. Taken together, these results suggest the existence of regulatory mechanisms between CCK and enkephalin systems in the control of pain. These regulatory loops could enhance the antinociceptive effects of morphine allowing the opiate doses used to be reduced and thus, possibly, the side-effects to be minimized.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baber N. S., Dourish C. T., Hill D. R. The role of CCK caerulein, and CCK antagonists in nociception. Pain. 1989 Dec;39(3):307–328. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(89)90045-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbaz B. S., Autry W. L., Ambrose F. G., Hall N. R., Liebman J. M. Antinociceptive profile of sulfated CCK-8. Comparison with CCK-4, unsulfated CCK-8 and other neuropeptides. Neuropharmacology. 1986 Aug;25(8):823–829. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(86)90005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoliel J. J., Bourgoin S., Mauborgne A., Legrand J. C., Hamon M., Cesselin F. Differential inhibitory/stimulatory modulation of spinal CCK release by mu and delta opioid agonists, and selective blockade of mu-dependent inhibition by kappa receptor stimulation. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Apr 1;124(2):204–207. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90094-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoliel J. J., Mauborgne A., Bourgoin S., Legrand J. C., Hamon M., Cesselin F. Opioid control of the in vitro release of cholecystokinin-like material from the rat substantia nigra. J Neurochem. 1992 Mar;58(3):916–922. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb09344.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cesselin F., Bourgoin S., Artaud F., Hamon M. Basic and regulatory mechanisms of in vitro release of Met-enkephalin from the dorsal zone of the rat spinal cord. J Neurochem. 1984 Sep;43(3):763–774. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb12798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charpentier B., Durieux C., Pelaprat D., Dor A., Reibaud M., Blanchard J. C., Roques B. P. Enzyme-resistant CCK analogs with high affinities for central receptors. Peptides. 1988 Jul-Aug;9(4):835–841. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(88)90130-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawley J. N. Comparative distribution of cholecystokinin and other neuropeptides. Why is this peptide different from all other peptides? Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;448:1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb29900.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dourish C. T., Hawley D., Iversen S. D. Enhancement of morphine analgesia and prevention of morphine tolerance in the rat by the cholecystokinin antagonist L-364,718. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Mar 15;147(3):469–472. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90183-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dourish C. T., O'Neill M. F., Coughlan J., Kitchener S. J., Hawley D., Iversen S. D. The selective CCK-B receptor antagonist L-365,260 enhances morphine analgesia and prevents morphine tolerance in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Jan 25;176(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90129-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durieux C., Pélaprat D., Charpentier B., Morgat J. L., Roques B. P. Characterization of [3H] CCK4 binding sites in mouse and rat brain. Neuropeptides. 1988 Oct;12(3):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(88)90045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDDY N. B., LEIMBACH D. Synthetic analgesics. II. Dithienylbutenyl- and dithienylbutylamines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1953 Mar;107(3):385–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faris P. L., Komisaruk B. R., Watkins L. R., Mayer D. J. Evidence for the neuropeptide cholecystokinin as an antagonist of opiate analgesia. Science. 1983 Jan 21;219(4582):310–312. doi: 10.1126/science.6294831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournié-Zaluski M. C., Coric P., Turcaud S., Lucas E., Noble F., Maldonado R., Roques B. P. "Mixed inhibitor-prodrug" as a new approach toward systemically active inhibitors of enkephalin-degrading enzymes. J Med Chem. 1992 Jun 26;35(13):2473–2481. doi: 10.1021/jm00091a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gacel G. A., Fellion E., Baamonde A., Dauge V., Roques B. P. Synthesis, biochemical and pharmacological properties of BUBUC, a highly selective and systemically active agonist for in vivo studies of delta-opioid receptors. Peptides. 1990 Sep-Oct;11(5):983–988. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(90)90021-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gacel G., Daugé V., Breuzé P., Delay-Goyet P., Roques B. P. Development of conformationally constrained linear peptides exhibiting a high affinity and pronounced selectivity for delta opioid receptors. J Med Chem. 1988 Oct;31(10):1891–1897. doi: 10.1021/jm00118a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall C., Lauterborn J., Burks D., Seroogy K. Co-localization of enkephalin and cholecystokinin in discrete areas of rat brain. Brain Res. 1987 Feb 17;403(2):403–408. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90085-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudreau P., Quirion R., St-Pierre S., Pert C. B. Characterization and visualization of cholecystokinin receptors in rat brain using [3H]pentagastrin. Peptides. 1983 Sep-Oct;4(5):755–762. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(83)90032-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALEY T. J., MCCORMICK W. G. Pharmacological effects produced by intracerebral injection of drugs in the conscious mouse. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1957 Mar;12(1):12–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1957.tb01354.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagino Y., Okuwa M., Moroji T. Effects of ceruletide and haloperidol on the hypothalamo-pituitary beta-endorphin system and brain beta-endorphin contents in the rat: with special reference to effects of ceruletide in chronically haloperidol-treated rats. Neuropeptides. 1991 Jan;18(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(91)90157-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward N. J., Harding M., Lloyd S. A., McKnight A. T., Hughes J., Woodruff G. N. The effect of CCKB/gastrin antagonists on stimulated gastric acid secretion in the anaesthetized rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Dec;104(4):973–977. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12535.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrie C. A., Shepherd J. K., Rodgers R. J. Differential effects of the CCK antagonist, MK-329, on analgesia induced by morphine, social conflict (opioid) and defeat experience (non-opioid) in male mice. Neuropharmacology. 1989 Oct;28(10):1025–1032. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(89)90113-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. G., Hughes J., Pittaway K. M. Antinociceptive action of cholecystokinin octapeptide (CCK 8) and related peptides in rats and mice: effects of naloxone and peptidase inhibitors. Neuropharmacology. 1987 Apr;26(4):289–300. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(87)90180-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong E. K., Takemori A. E. Indirect involvement of delta opioid receptors in cholecystokinin octapeptide-induced analgesia in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Nov;251(2):594–598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innis R. B., Snyder S. H. Distinct cholecystokinin receptors in brain and pancreas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6917–6921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh S., Katsuura G., Maeda Y. Caerulein and cholecystokinin suppress beta-endorphin-induced analgesia in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Jun 4;80(4):421–425. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90089-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellstein D. E., Price D. D., Mayer D. J. Cholecystokinin and its antagonist lorglumide respectively attenuate and facilitate morphine-induced inhibition of C-fiber evoked discharges of dorsal horn nociceptive neurons. Brain Res. 1991 Feb 1;540(1-2):302–306. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90524-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavigne G. J., Millington W. R., Mueller G. P. The CCK-A and CCK-B receptor antagonists, devazepide and L-365,260, enhance morphine antinociception only in non-acclimated rats exposed to a novel environment. Neuropeptides. 1992 Feb;21(2):119–129. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(92)90522-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnuson D. S., Sullivan A. F., Simonnet G., Roques B. P., Dickenson A. H. Differential interactions of cholecystokinin and FLFQPQRF-NH2 with mu and delta opioid antinociception in the rat spinal cord. Neuropeptides. 1990 Aug;16(4):213–218. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(90)90065-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran T. H., Robinson P. H., Goldrich M. S., McHugh P. R. Two brain cholecystokinin receptors: implications for behavioral actions. Brain Res. 1986 Jan 1;362(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91413-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittaway K. M., Rodriguez R. E., Hughes J., Hill R. G. CCK 8 analgesia and hyperalgesia after intrathecal administration in the rat: comparison with CCK-related peptides. Neuropeptides. 1987 Jul;10(1):87–108. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(87)90092-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl M., Benoliel J. J., Bourgoin S., Lombard M. C., Mauborgne A., Taquet H., Carayon A., Besson J. M., Cesselin F., Hamon M. Regional distribution of calcitonin gene-related peptide-, substance P-, cholecystokinin-, Met5-enkephalin-, and dynorphin A (1-8)-like materials in the spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia of adult rats: effects of dorsal rhizotomy and neonatal capsaicin. J Neurochem. 1990 Oct;55(4):1122–1130. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb03114.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portoghese P. S., Sultana M., Takemori A. E. Naltrindole, a highly selective and potent non-peptide delta opioid receptor antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Jan 27;146(1):185–186. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90502-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rattray M., Jordan C. C., De Belleroche J. The novel CCK antagonist L364,718 abolished caerulein- but potentiates morphine-induced antinociception. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Jul 26;152(1-2):163–166. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90849-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rattray M., de Belleroche J. Morphine action on cholecystokinin octapeptide release from rat periaqueductal grey slices: sensitisation by naloxone. Neuropeptides. 1987 Aug-Sep;10(2):189–200. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(87)90021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez R. E., Sacristán M. P. In vivo release of CCK-8 from the dorsal horn of the rat: inhibition by DAGOL. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 3;250(2):215–217. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80723-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Gayo M., Baamonde A., Turcaud S., Fournie-Zaluski M. C., Roques B. P. In vivo occupation of mouse brain opioid receptors by endogenous enkephalins: blockade of enkephalin degrading enzymes by RB 101 inhibits [3H]diprenorphine binding. Brain Res. 1992 Feb 7;571(2):306–312. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90669-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Gayo M., Daugé V., Menant I., Bégué D., Gacel G., Roques B. P. Synthesis and biological activity of Boc [Nle28, Nle31]CCK27-33, a highly potent CCK8 analogue. Peptides. 1985 May-Jun;6(3):415–420. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(85)90106-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Gayo M., Durieux C., Fournié-Zaluski M. C., Roques B. P. Stimulation of delta-opioid receptors reduces the in vivo binding of the cholecystokinin (CCK)-B-selective agonist [3H]pBC 264: evidence for a physiological regulation of CCKergic systems by endogenous enkephalins. J Neurochem. 1992 Nov;59(5):1805–1811. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb11013.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmauss C., Yaksh T. L. In vivo studies on spinal opiate receptor systems mediating antinociception. II. Pharmacological profiles suggesting a differential association of mu, delta and kappa receptors with visceral chemical and cutaneous thermal stimuli in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Jan;228(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderhaeghen J. J., Signeau J. C., Gepts W. New peptide in the vertebrate CNS reacting with antigastrin antibodies. Nature. 1975 Oct 16;257(5527):604–605. doi: 10.1038/257604a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X. J., Han J. S. Modification by cholecystokinin octapeptide of the binding of mu-, delta-, and kappa-opioid receptors. J Neurochem. 1990 Oct;55(4):1379–1382. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb03149.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X. J., Wang X. H., Han J. S. Cholecystokinin octapeptide antagonized opioid analgesia mediated by mu- and kappa- but not delta-receptors in the spinal cord of the rat. Brain Res. 1990 Jul 16;523(1):5–10. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91629-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins L. R., Kinscheck I. B., Mayer D. J. Potentiation of morphine analgesia by the cholecystokinin antagonist proglumide. Brain Res. 1985 Feb 18;327(1-2):169–180. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91511-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z., Xu X. J., Hughes J., Horwell D. C., Hökfelt T. PD134308, a selective antagonist of cholecystokinin type B receptor, enhances the analgesic effect of morphine and synergistically interacts with intrathecal galanin to depress spinal nociceptive reflexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7105–7109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zetler G. Analgesia and ptosis caused by caerulein and cholecystokinin octapeptide (CCK-8). Neuropharmacology. 1980 May;19(5):415–422. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(80)90047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


