Abstract
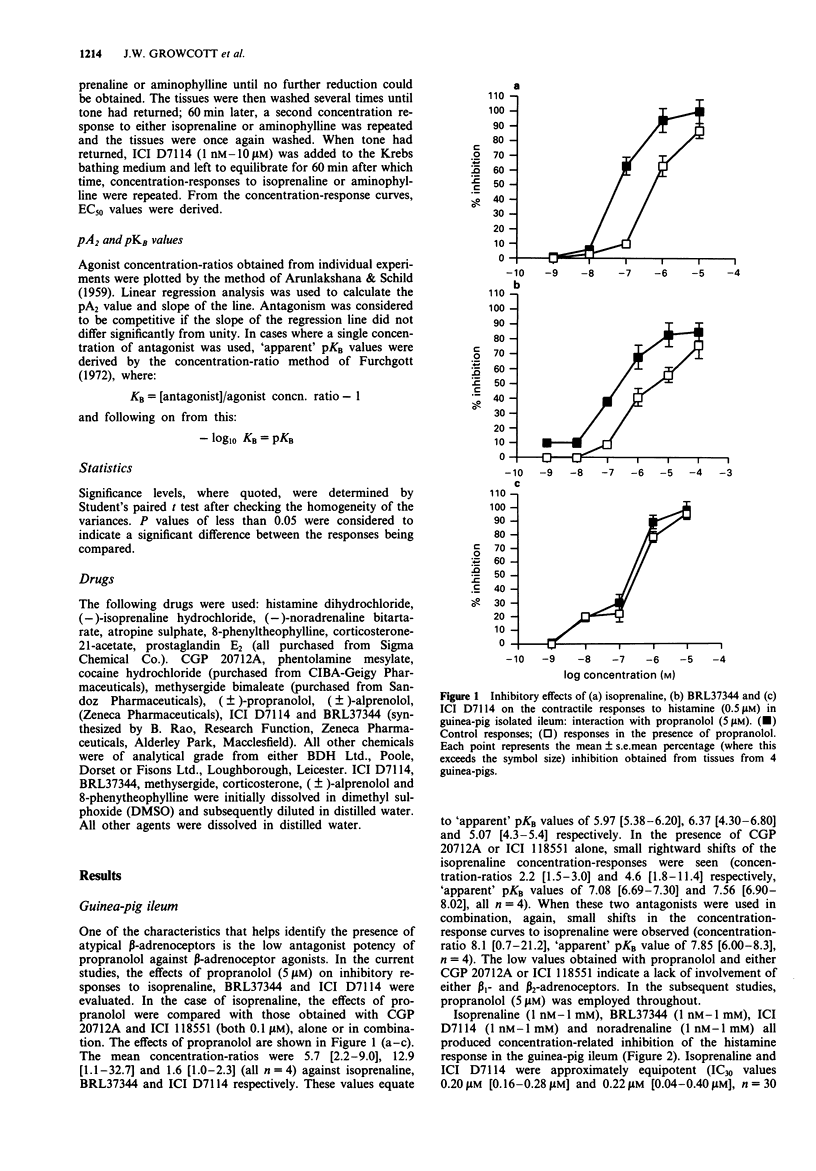
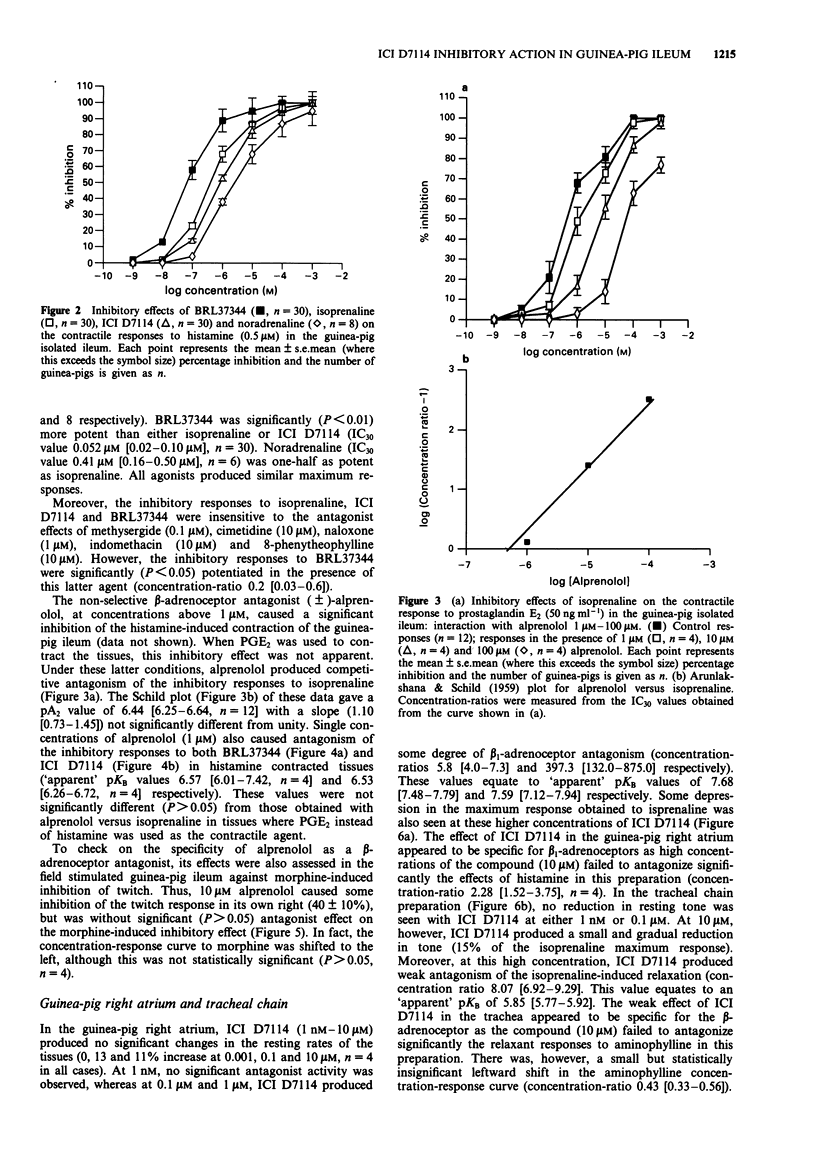
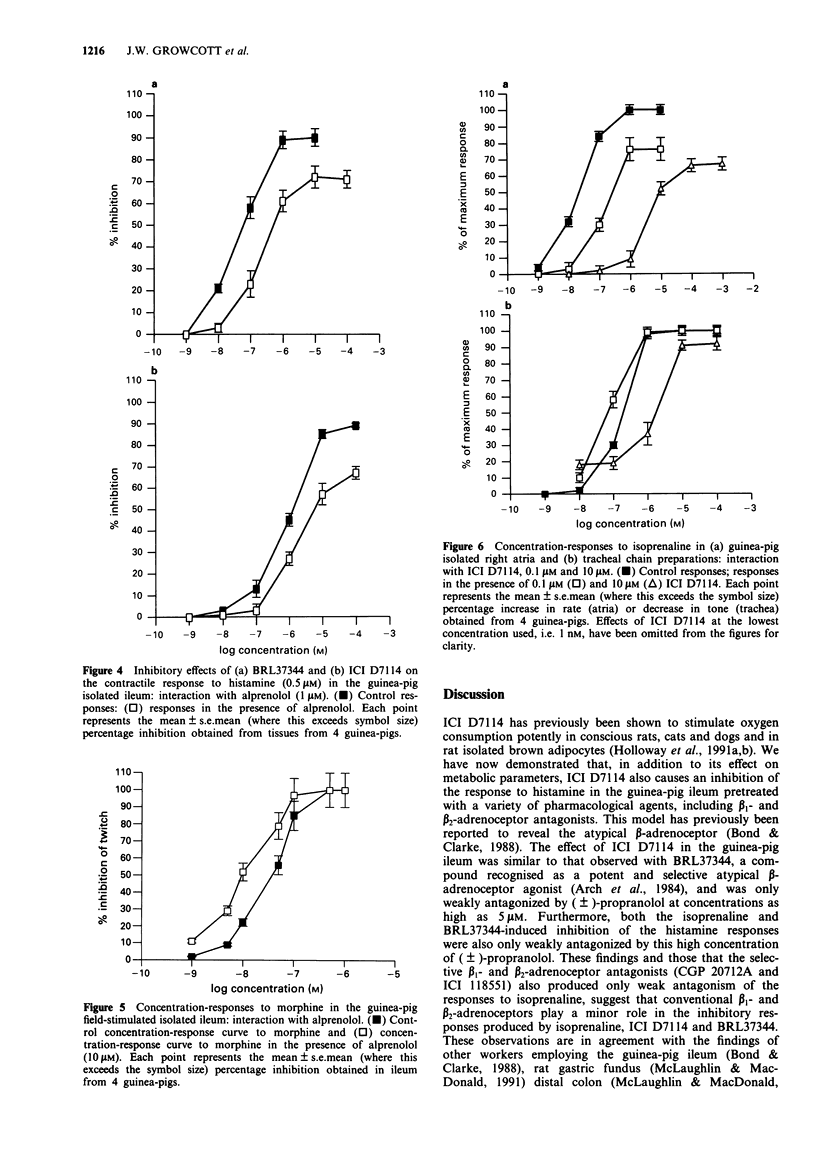
1. Experiments were performed to characterize the effects of the novel brown adipocyte stimulant, ICI D7114, in the guinea-pig isolated ileum, right atrium and tracheal chain. In the ileum, agonist-induced inhibition of the contractile response to either histamine or prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) was assessed, along with effects on resting rate in the atrium and resting tone in the tracheal chain. In the latter two preparations, antagonism of isoprenaline-induced responses by ICI D7114 was also assessed. 2. Inhibitory responses were obtained in the ileum to ICI D7114, isoprenaline, BRL37344, and noradrenaline. The responses to ICI D7114, isoprenaline and BRL37344 were resistant to blockade with propranolol (5 microM), naloxone (1 microM), methysergide (0.1 microM), cimetidine, indomethacin and 8-phenyltheophylline (all 10 microM). These responses to isoprenaline, in the presence of propranolol (5 microM), were competitively antagonized by alprenolol (1-100 microM) with a pA2 value of 6.44. The responses to ICI D7114 and BRL37344 were antagonized by single concentrations of alprenolol (1 microM) with apparent pKB values of 6.53 and 6.57 respectively. These data indicate an effect of ICI D7114 at the atypical beta-adrenoceptor in the guinea-pig ileum. 3. The order and relative potency of agonists at the atypical beta-adrenoceptor was BRL37344 (4) < isoprenaline (1) = ICI D7114 (1.1) > noradrenaline (0.5). 4. ICI D7114 (1 nM - 10 microM) caused no significant change in the rate of beating or the resting tone of the guinea-pig right atrium or tracheal chain respectively.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arch J. R., Ainsworth A. T., Cawthorne M. A., Piercy V., Sennitt M. V., Thody V. E., Wilson C., Wilson S. Atypical beta-adrenoceptor on brown adipocytes as target for anti-obesity drugs. Nature. 1984 May 10;309(5964):163–165. doi: 10.1038/309163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchetti A., Manara L. In vitro inhibition of intestinal motility by phenylethanolaminotetralines: evidence of atypical beta-adrenoceptors in rat colon. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;100(4):831–839. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14100.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blue D. R., Bond R. A., Adham N., Delmendo R., Michel A. D., Eglen R. M., Whiting R. L., Clarke D. E. Antagonist characterization of atypical beta adrenoceptors in guinea pig ileum: blockade by alprenolol and dihydroalprenolol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Mar;252(3):1034–1042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond R. A., Clarke D. E. A response to isoprenaline unrelated to alpha- and beta-adrenoceptor agonism. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Jul;91(3):683–686. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11262.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond R. A., Clarke D. E. Agonist and antagonist characterization of a putative adrenoceptor with distinct pharmacological properties from the alpha- and beta-subtypes. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Nov;95(3):723–734. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11698.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emorine L. J., Marullo S., Briend-Sutren M. M., Patey G., Tate K., Delavier-Klutchko C., Strosberg A. D. Molecular characterization of the human beta 3-adrenergic receptor. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1118–1121. doi: 10.1126/science.2570461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel G., Hoyer D., Berthold R., Wagner H. (+/-)[125Iodo] cyanopindolol, a new ligand for beta-adrenoceptors: identification and quantitation of subclasses of beta-adrenoceptors in guinea pig. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1981;317(4):277–285. doi: 10.1007/BF00501307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoefle M. L., Hastings S. G., Meyer R. F., Corey R. M., Holmes A., Stratton C. D. Cardioselective beta-adrenergic blocking agents. 1. 1-((3,4-Dimethoxyphenethyl)amino)-3-aryloxy-2-propanols. J Med Chem. 1975 Feb;18(2):148–152. doi: 10.1021/jm00236a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenga C., Haas M., Deinum J. T., Zaagsma J. Discrepancies in lipolytic activities induced by beta-adrenoceptor agonists in human and rat adipocytes. Horm Metab Res. 1990 Jan;22(1):17–21. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1004839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. R., Howe R., Rao B. S., Stribling D., Mayers R. M., Briscoe M. G., Jackson J. M. ICI D7114 a novel selective beta-adrenoceptor agonist selectively stimulates brown fat and increases whole-body oxygen consumption. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Sep;104(1):97–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12391.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J., Macdonald A. Relaxant effects of alpha-adrenoceptor agonists in the rat isolated gastric fundus. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1990 Jan;42(1):30–34. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1990.tb05344.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenakin T. P., Beek D. Is prenalterol (H133/80) really a selective beta 1 adrenoceptor agonist? Tissue selectivity resulting from differences in stimulus-response relationships. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 May;213(2):406–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin D. P., MacDonald A. Characterization of catecholamine-mediated relaxations in rat isolated gastric fundus: evidence for an atypical beta-adrenoceptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jun;103(2):1351–1356. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb09792.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin D. P., MacDonald A. Evidence for the existence of 'atypical' beta-adrenoceptors (beta 3-adrenoceptors) mediating relaxation in the rat distal colon in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):569–574. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14122.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellor P. M. A precision isotonic measuring system for isolated tissues. J Pharmacol Methods. 1984 Dec;12(4):259–264. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(84)90012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman B. J., Leathard H. L. Evidence that an atypical beta-adrenoceptor mediates the inhibition of spontaneous rhythmical contractions of rabbit isolated jejunum induced by ritodrine and salbutamol. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Sep;101(1):27–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12083.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taneja D. T., Clarke D. E. Evidence for a noradrenergic innervation to "atypical" beta adrenoceptors (or putative beta-3 adrenoceptors) in the ileum of guinea pig. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Jan;260(1):192–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Vliet A., Rademaker B., Bast A. A beta adrenoceptor with atypical characteristics is involved in the relaxation of the rat small intestine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Oct;255(1):218–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


