Abstract
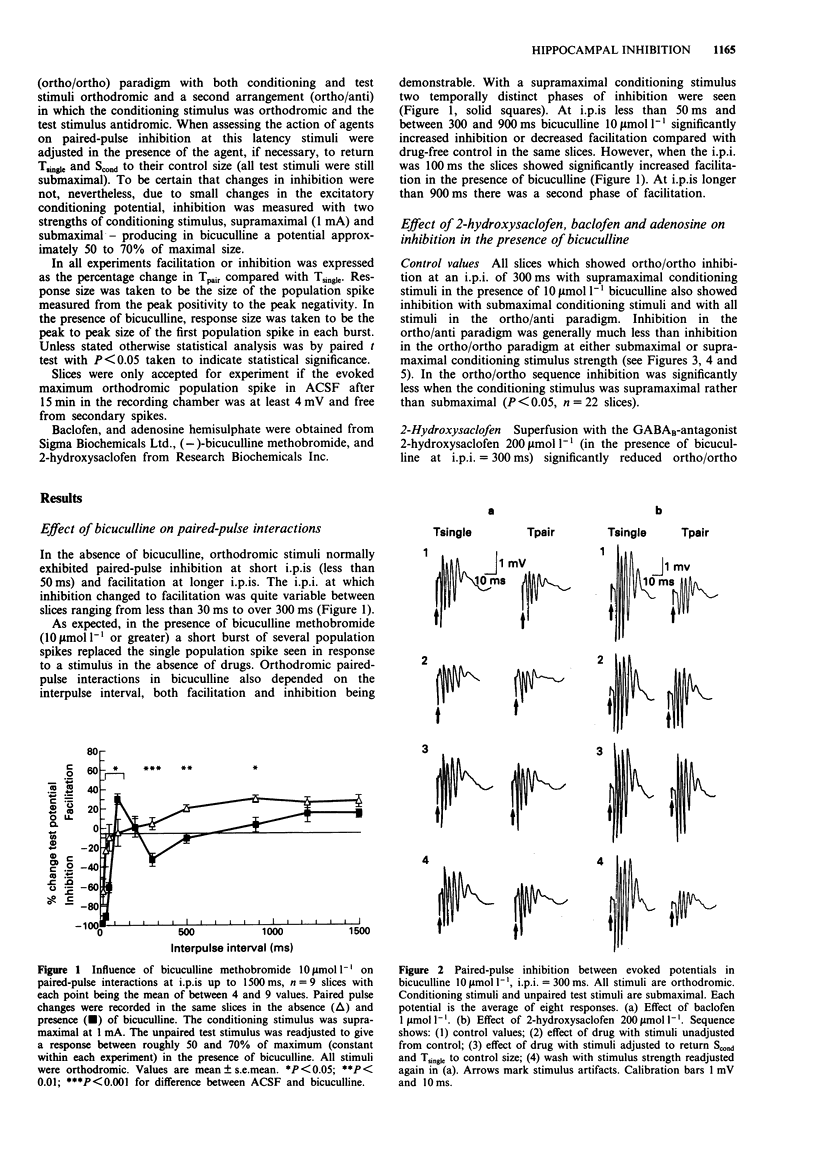
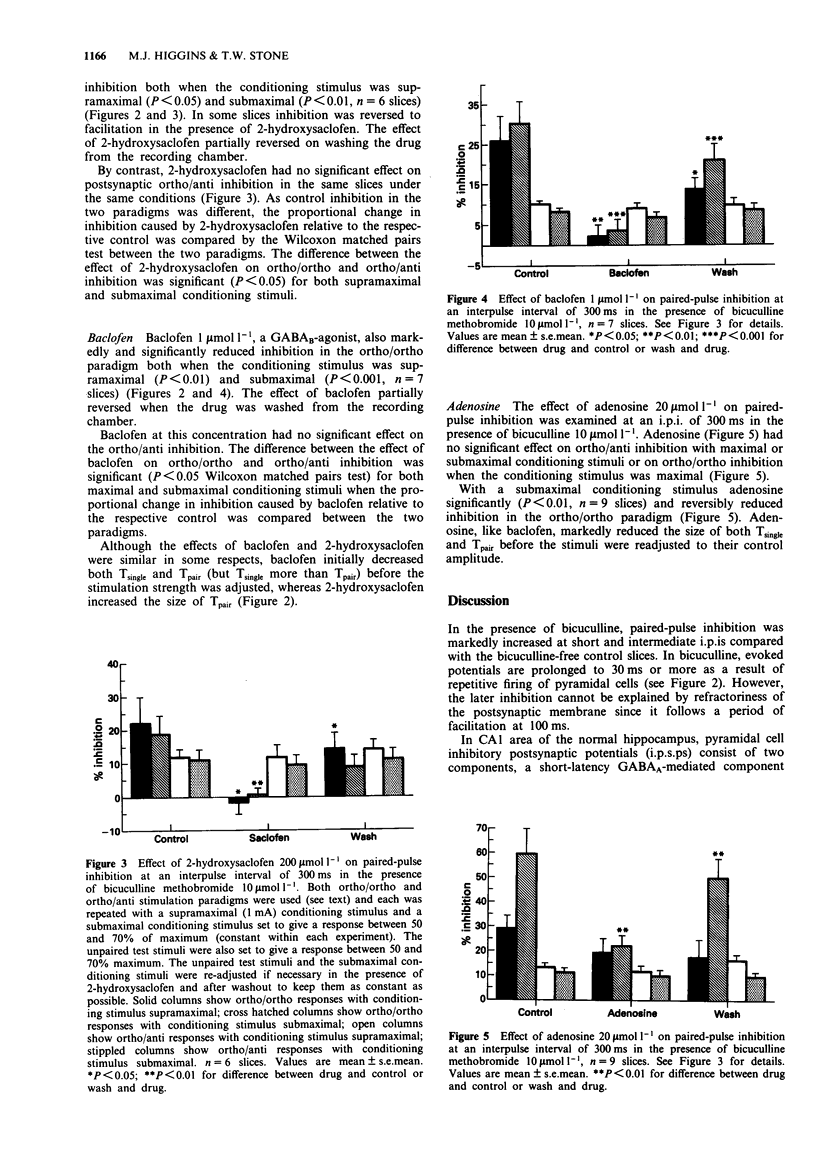
1. An initial observation that paired-pulse inhibition in hippocampal slices was increased rather than decreased by bicuculline prompted the present study to explore the mechanism underlying bicuculline-resistant inhibition. 2. In the presence of bicuculline, paired-pulse interactions were dependent on the interpulse interval (i.p.i.) but a medium-latency inhibition was consistently observed at an i.p.i. of 300 to 500 ms. 3. The medium-latency (300 ms) bicuculline-resistant inhibition produced by paired orthodromic stimuli was substantially reduced by 2-hydroxysaclofen and was probably largely mediated by GABAB-receptor activation. Paired-pulse inhibition produced by an orthodromic/antidromic stimulation sequence was not affected by 2-hydroxysaclofen suggesting the possibility that the GABAB-receptors involved in orthodromic inhibition may be located presynaptically on the Schaffer collateral terminals rather than on the postsynaptic surface. The medium latency inhibition was also reduced by baclofen and under some conditions, by adenosine. 4. In addition to the GABAB-component, a hydroxysaclofen-resistant depression of postsynaptic excitability contributed to bicuculline-resistant paired-pulse inhibition at the 300 ms latency.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alger B. E., Nicoll R. A. Feed-forward dendritic inhibition in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells studied in vitro. J Physiol. 1982 Jul;328:105–123. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alger B. E., Nicoll R. A. Pharmacological evidence for two kinds of GABA receptor on rat hippocampal pyramidal cells studied in vitro. J Physiol. 1982 Jul;328:125–141. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ault B., Nadler J. V. Anticonvulsant-like actions of baclofen in the rat hippocampal slice. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Apr;78(4):701–708. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb09423.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avoli M., Perreault P. A GABAergic depolarizing potential in the hippocampus disclosed by the convulsant 4-aminopyridine. Brain Res. 1987 Jan 1;400(1):191–195. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90671-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaxter T. J., Carlen P. L. Pre- and postsynaptic effects of baclofen in the rat hippocampal slice. Brain Res. 1985 Aug 19;341(1):195–199. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91489-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke S. P., Nadler J. V. Regulation of glutamate and aspartate release from slices of the hippocampal CA1 area: effects of adenosine and baclofen. J Neurochem. 1988 Nov;51(5):1541–1551. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb01123.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corradetti R., Lo Conte G., Moroni F., Passani M. B., Pepeu G. Adenosine decreases aspartate and glutamate release from rat hippocampal slices. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Sep 3;104(1-2):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90364-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creager R., Dunwiddie T., Lynch G. Paired-pulse and frequency facilitation in the CA1 region of the in vitro rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1980 Feb;299:409–424. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies C. H., Davies S. N., Collingridge G. L. Paired-pulse depression of monosynaptic GABA-mediated inhibitory postsynaptic responses in rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1990 May;424:513–531. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunwiddie T. V., Haas H. L. Adenosine increases synaptic facilitation in the in vitro rat hippocampus: evidence for a presynaptic site of action. J Physiol. 1985 Dec;369:365–377. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunwiddie T., Mueller A., Palmer M., Stewart J., Hoffer B. Electrophysiological interactions of enkephalins with neuronal circuitry in the rat hippocampus. I. Effects on pyramidal cell activity. Brain Res. 1980 Feb 24;184(2):311–330. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90801-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutar P., Nicoll R. A. A physiological role for GABAB receptors in the central nervous system. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):156–158. doi: 10.1038/332156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison N. L., Lovinger D. M., Lambert N. A., Teyler T. J., Prager R., Ong J., Kerr D. I. The actions of 2-hydroxy-saclofen at presynaptic GABAB receptors in the rat hippocampus. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Nov 13;119(2):272–276. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90851-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollins C., Stone T. W. Adenosine inhibition of gamma-aminobutyric acid release from slices of rat cerebral cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 May;69(1):107–112. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb10888.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacaille J. C. Postsynaptic potentials mediated by excitatory and inhibitory amino acids in interneurons of stratum pyramidale of the CA1 region of rat hippocampal slices in vitro. J Neurophysiol. 1991 Nov;66(5):1441–1454. doi: 10.1152/jn.1991.66.5.1441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert N. A., Borroni A. M., Grover L. M., Teyler T. J. Hyperpolarizing and depolarizing GABAA receptor-mediated dendritic inhibition in area CA1 of the rat hippocampus. J Neurophysiol. 1991 Nov;66(5):1538–1548. doi: 10.1152/jn.1991.66.5.1538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert N. A., Harrison N. L., Teyler T. J. Baclofen-induced disinhibition in area CA1 of rat hippocampus is resistant to extracellular Ba2+. Brain Res. 1991 May 3;547(2):349–352. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90985-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert N. A., Teyler T. J. Adenosine depresses excitatory but not fast inhibitory synaptic transmission in area CA1 of the rat hippocampus. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Jan 14;122(1):50–52. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90190-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch G. S., Jensen R. A., McGaugh J. L., Davila K., Oliver M. W. Effects of enkephalin, morphine, and naloxone on the electrical activity of the in vitro hippocampal slice preparation. Exp Neurol. 1981 Mar;71(3):527–540. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(81)90030-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison D. V., Nicoll R. A. Enkephalin hyperpolarizes interneurones in the rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1988 Apr;398:123–130. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misgeld U., Müller W., Brunner H. Effects of (-)baclofen on inhibitory neurons in the guinea pig hippocampal slice. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Jun;414(2):139–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00580955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan T., Lambert J. D. Depression of the fast IPSP underlies paired-pulse facilitation in area CA1 of the rat hippocampus. J Neurophysiol. 1991 Nov;66(5):1704–1715. doi: 10.1152/jn.1991.66.5.1704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newberry N. R., Nicoll R. A. A bicuculline-resistant inhibitory post-synaptic potential in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells in vitro. J Physiol. 1984 Mar;348:239–254. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newberry N. R., Nicoll R. A. Comparison of the action of baclofen with gamma-aminobutyric acid on rat hippocampal pyramidal cells in vitro. J Physiol. 1985 Mar;360:161–185. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman G. C., Qi H., Hospod F. E., Grundmann K. Preservation of hippocampal brain slices with in vivo or in vitro hypothermia. Brain Res. 1992 Mar 13;575(1):159–163. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90438-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Ozawa S. Inhibitory action of adenosine on synaptic transmission in the hippocampus of the guinea pig in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Dec 19;68(4):483–492. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90424-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peet M. J., McLennan H. Pre-and postsynaptic actions of baclofen: blockade of the late synaptically-evoked hyperpolarization of CA1 hippocampal neurones. Exp Brain Res. 1986;61(3):567–574. doi: 10.1007/BF00237582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzkroin P. A., Stafstrom C. E. Effects of EGTA on the calcium-activated afterhyperpolarization in hippocampal CA3 pyramidal cells. Science. 1980 Dec 5;210(4474):1125–1126. doi: 10.1126/science.6777871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M. Serotonin attenuates a slow inhibitory postsynaptic potential in rat hippocampal neurons. Neuroscience. 1990;36(3):631–641. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90006-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffensen S. C., Henriksen S. J. Effects of baclofen and bicuculline on inhibition in the fascia dentata and hippocampus regio superior. Brain Res. 1991 Jan 4;538(1):46–53. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90374-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. M., Gähwiler B. H. Comparison of the actions of baclofen at pre- and postsynaptic receptors in the rat hippocampus in vitro. J Physiol. 1992;451:329–345. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. M., Haas H. L., Gähwiler B. H. Comparison of the actions of adenosine at pre- and postsynaptic receptors in the rat hippocampus in vitro. J Physiol. 1992;451:347–363. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon K. W., Rothman S. M. Adenosine inhibits excitatory but not inhibitory synaptic transmission in the hippocampus. J Neurosci. 1991 May;11(5):1375–1380. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-05-01375.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


