Abstract
1. The role of bradykinin B1 receptors in the thermal hyperalgesia following unilateral ultra-violet (u.v.) irradiation of the hindpaw of rats has been investigated. 2. In non-irradiated (naive) animals the B1 receptor agonist des-Arg9-bradykinin and bradykinin (BK) (up to 1 mumol kg-1 i.v.) had no effect on withdrawal latency to a noxious heat stimulus when administered 60 min before testing. 3. Following exposure of one hindpaw to strong u.v. irradiation the withdrawal latency of the u.v.-treated paw to radiant noxious heat fell by a maximum of 50% after 48 h. There was no reduction in latency in the contralateral paw. 4. des-Arg9-BK (1-100 nmol kg-1 i.v.) administered 24 h after u.v. exposure caused a further dose-dependent fall (50 +/- 4% reduction from saline injected animals at 100 nmol kg-1 i.v.) in withdrawal latency in the u.v.-treated paw when measured 60 min after injection. The withdrawal latency of the contralateral paw was also reduced but to a lesser extent following des-Arg9-BK (100 nmol kg-1 i.v.) with a maximum reduction of 19 +/- 3%. 5. Bradykinin also induced a further reduction in withdrawal latency (33 +/- 5% reduction at 1 mumol kg-1) although it was not as effective as des-Arg9-BK. Bradykinin did not reduce the withdrawal latency in the contralateral paw.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF
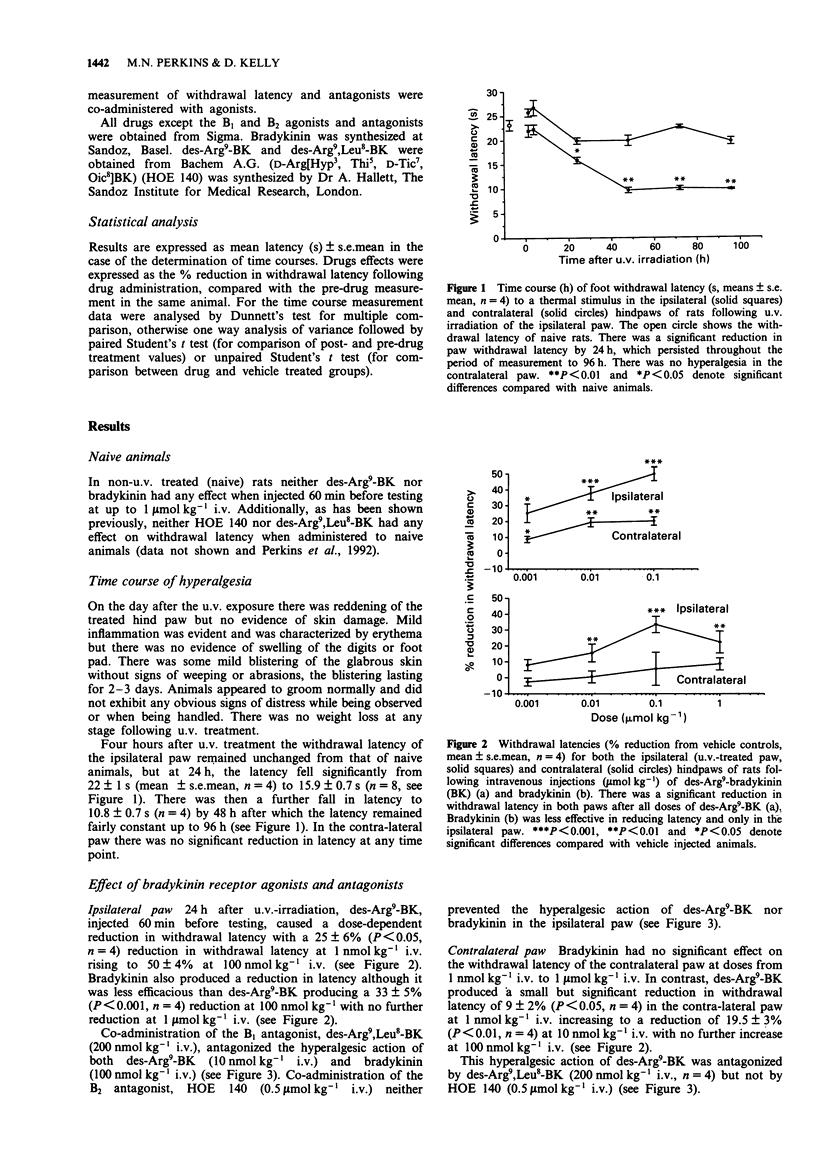
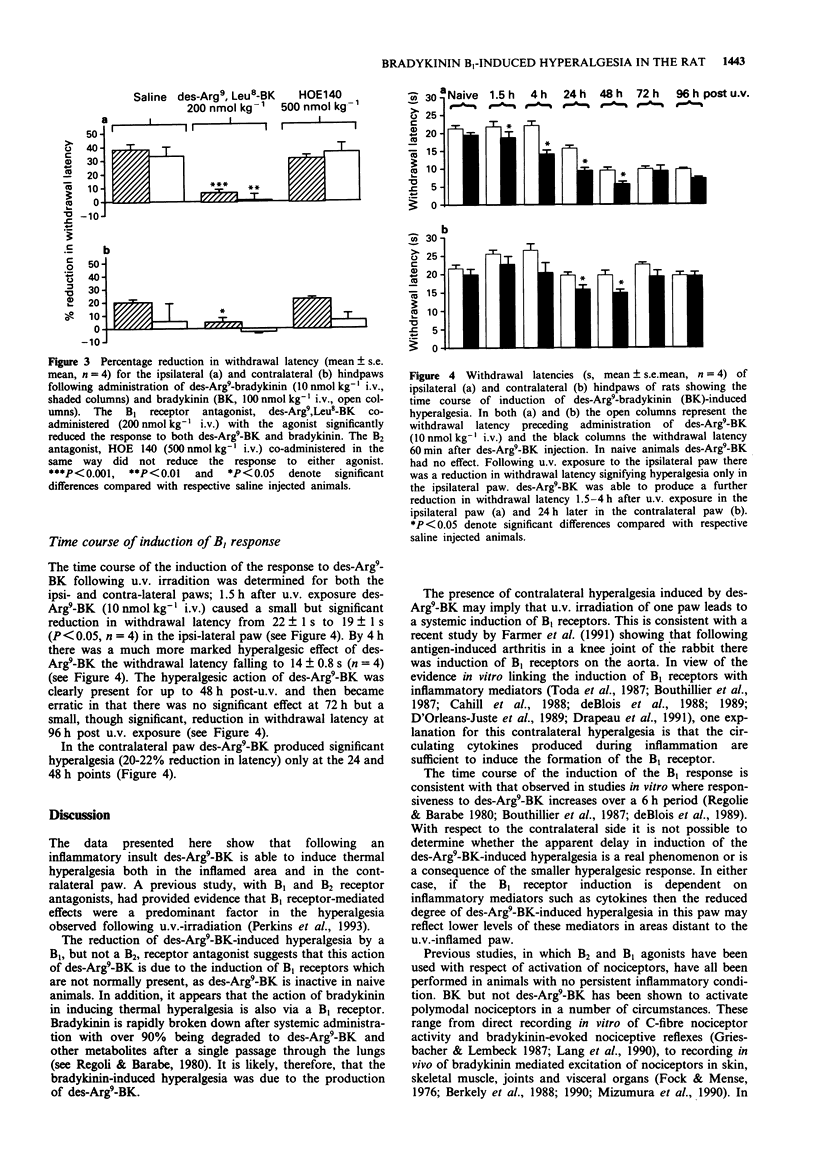

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berkley K. J., Hotta H., Robbins A., Sato Y. Functional properties of afferent fibers supplying reproductive and other pelvic organs in pelvic nerve of female rat. J Neurophysiol. 1990 Feb;63(2):256–272. doi: 10.1152/jn.1990.63.2.256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkley K. J., Robbins A., Sato Y. Afferent fibers supplying the uterus in the rat. J Neurophysiol. 1988 Jan;59(1):142–163. doi: 10.1152/jn.1988.59.1.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouthillier J., Deblois D., Marceau F. Studies on the induction of pharmacological responses to des-Arg9-bradykinin in vitro and in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Oct;92(2):257–264. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11319.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch R. M., Connor J. R., Tiffany C. W. The kallikrein-kininogen-kinin system in chronic inflammation. Agents Actions. 1989 Jun;27(3-4):258–260. doi: 10.1007/BF01972790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill M., Fishman J. B., Polgar P. Effect of des arginine9-bradykinin and other bradykinin fragments on the synthesis of prostacyclin and the binding of bradykinin by vascular cells in culture. Agents Actions. 1988 Jul;24(3-4):224–231. doi: 10.1007/BF02028275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Orléans-Juste P., de Nucci G., Vane J. R. Kinins act on B1 or B2 receptors to release conjointly endothelium-derived relaxing factor and prostacyclin from bovine aortic endothelial cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Apr;96(4):920–926. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11903.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deblois D., Bouthillier J., Marceau F. Effect of glucocorticoids, monokines and growth factors on the spontaneously developing responses of the rabbit isolated aorta to des-Arg9-bradykinin. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Apr;93(4):969–977. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11487.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapeau G., deBlois D., Marceau F. Hypotensive effects of Lys-des-Arg9-bradykinin and metabolically protected agonists of B1 receptors for kinins. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Dec;259(3):997–1003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dray A., Bettaney J., Forster P., Perkins M. N. Activation of a bradykinin receptor in peripheral nerve and spinal cord in the neonatal rat in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;95(4):1008–1010. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11732.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. G., McMillan B. A., Meeker S. N., Burch R. M. Induction of vascular smooth muscle bradykinin B1 receptors in vivo during antigen arthritis. Agents Actions. 1991 Sep;34(1-2):191–193. doi: 10.1007/BF01993275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fock S., Mense S. Excitatory effects of 5-hydroxytryptamine, histamine and potassium ions on muscular group IV afferent units: a comparison with bradykinin. Brain Res. 1976 Apr 9;105(3):459–469. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90593-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griesbacher T., Lembeck F. Effect of bradykinin antagonists on bradykinin-induced plasma extravasation, venoconstriction, prostaglandin E2 release, nociceptor stimulation and contraction of the iris sphincter muscle in the rabbit. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Oct;92(2):333–340. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11328.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hock F. J., Wirth K., Albus U., Linz W., Gerhards H. J., Wiemer G., Henke S., Breipohl G., König W., Knolle J. Hoe 140 a new potent and long acting bradykinin-antagonist: in vitro studies. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;102(3):769–773. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12248.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang E., Novak A., Reeh P. W., Handwerker H. O. Chemosensitivity of fine afferents from rat skin in vitro. J Neurophysiol. 1990 Apr;63(4):887–901. doi: 10.1152/jn.1990.63.4.887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner U. H., Modéer T. Bradykinin B1 and B2 receptor agonists synergistically potentiate interleukin-1-induced prostaglandin biosynthesis in human gingival fibroblasts. Inflammation. 1991 Dec;15(6):427–436. doi: 10.1007/BF00923340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizumura K., Minagawa M., Tsujii Y., Kumazawa T. The effects of bradykinin agonists and antagonists on visceral polymodal receptor activities. Pain. 1990 Feb;40(2):221–227. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(90)90072-L. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins M. N., Campbell E., Dray A. Antinociceptive activity of the bradykinin B1 and B2 receptor antagonists, des-Arg9, [Leu8]-BK and HOE 140, in two models of persistent hyperalgesia in the rat. Pain. 1993 May;53(2):191–197. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(93)90080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P., Bevan S., Dray A. Chemical activation of nociceptive peripheral neurones. Br Med Bull. 1991 Jul;47(3):534–548. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Barabé J. Pharmacology of bradykinin and related kinins. Pharmacol Rev. 1980 Mar;32(1):1–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steranka L. R., Farmer S. G., Burch R. M. Antagonists of B2 bradykinin receptors. FASEB J. 1989 Jul;3(9):2019–2025. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.9.2545496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiffany C. W., Burch R. M. Bradykinin stimulates tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 release from macrophages. FEBS Lett. 1989 Apr 24;247(2):189–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81331-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda N., Bian K., Akiba T., Okamura T. Heterogeneity in mechanisms of bradykinin action in canine isolated blood vessels. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Mar 31;135(3):321–329. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90681-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalley E. T., Clegg S., Stewart J. M., Vavrek R. J. The effect of kinin agonists and antagonists on the pain response of the human blister base. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1987 Dec;336(6):652–655. doi: 10.1007/BF00165756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- deBlois D., Bouthillier J., Marceau F. Pharmacological modulation of the up-regulated responses to des-Arg9-bradykinin in vivo and in vitro. Immunopharmacology. 1989 May-Jun;17(3):187–198. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(89)90047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


