Abstract
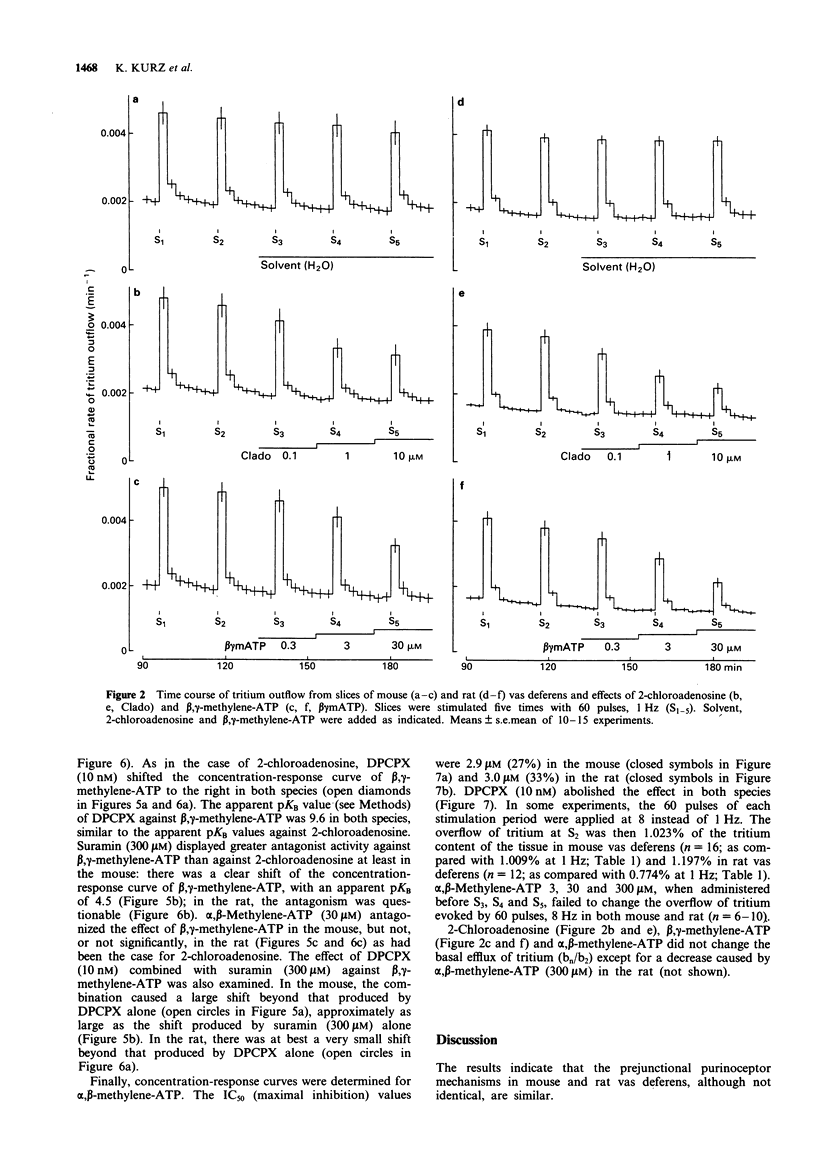
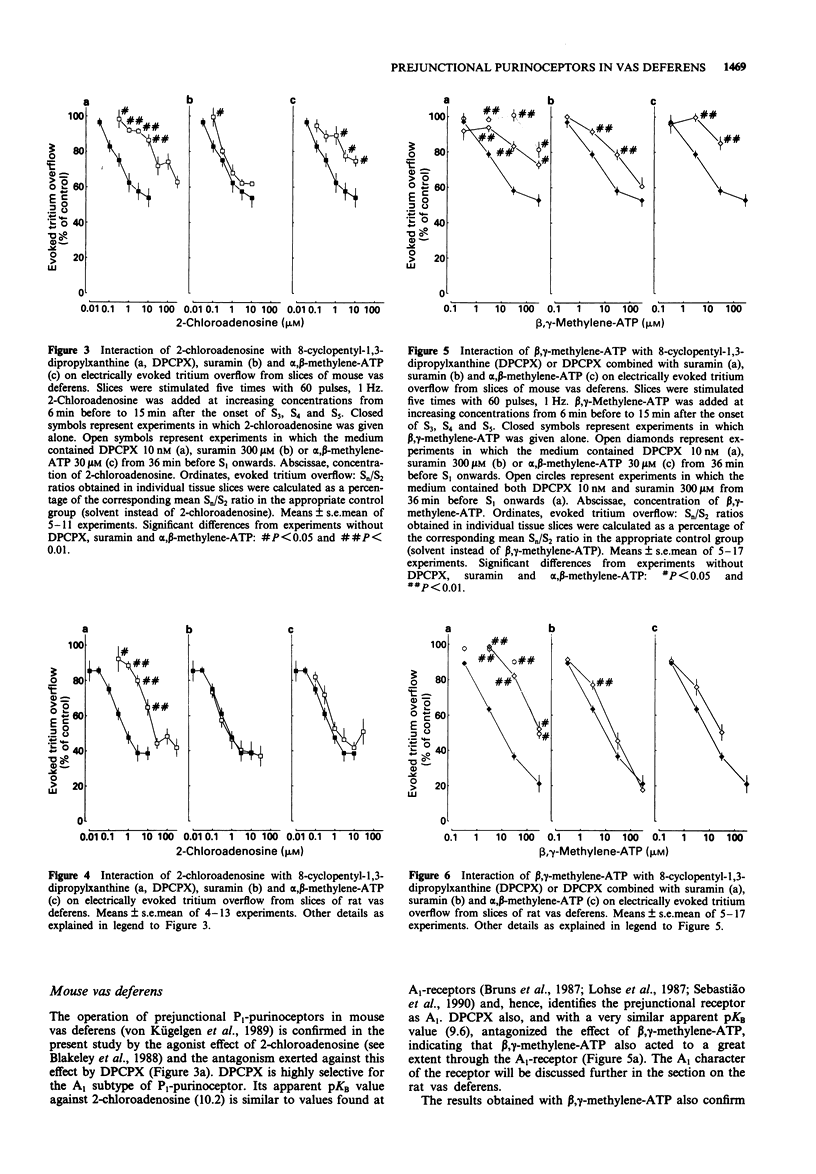
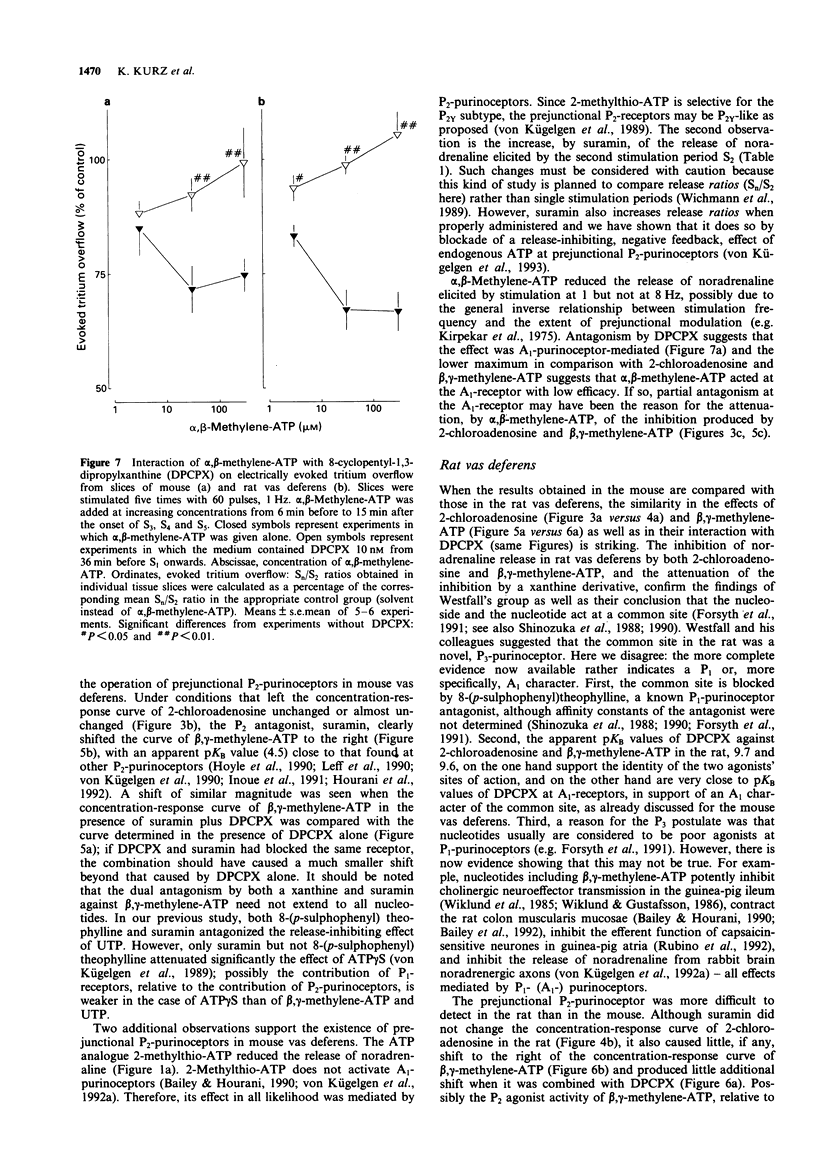
1. Prejunctional purinoceptors modulating the release of noradrenaline were compared in mouse and rat vas deferens. Tissue slices were preincubated with [3H]-noradrenaline and then superfused and stimulated electrically, in most experiments by trains of 60 pulses, 1 Hz. 2. In mouse vas deferens, 2-chloroadenosine (IC50 0.24 microM), beta,gamma-methylene-ATP (IC50 3.8 microM), alpha,beta-methylene-ATP (IC50 2.9 microM) and 2-methylthio-ATP (only 30 microM tested) reduced the evoked overflow of tritium. 8-Cyclopentyl-1,3-dipropylxanthine (DPCPX), 10 nM, antagonized the effect of 2-chloro-adenosine (apparent pKB 10.2) as well as of beta,gamma-methylene-ATP (apparent pKB 9.6) and alpha,beta-methylene-ATP. Suramin, 300 microM, attenuated the effect of 2-chloroadenosine at best very slightly, antagonized the effect of beta,gamma-methylene-ATP (apparent pKB 4.5) and, when combined with DPCPX 10 nM, caused a further marked shift to the right of the concentration-response curve of beta,gamma-methylene-ATP beyond the shift produced by DPCPX alone. 3. In rat vas deferens, 2-chloroadenosine (IC50 0.20 microM), beta,gamma-methylene-ATP (IC50 4.8 microM), alpha,beta-methylene-ATP (IC50 3.0 microM) and 2-methylthio-ATP (only 30 microM tested) also reduced the evoked overflow of tritium. DPCPX, 10 nM, antagonized the effect of 2-chloroadenosine (apparent pKB 9.7) as well as of beta,gamma-methylene-ATP (apparent pKB 9.6) and alpha,beta-methylene-ATP.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey S. J., Hickman D., Hourani S. M. Characterization of the P1-purinoceptors mediating contraction of the rat colon muscularis mucosae. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Feb;105(2):400–404. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14265.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey S. J., Hourani S. M. A study of the purinoceptors mediating contraction in the rat colon. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;100(4):753–756. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14087.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakeley A. G., Dunn P. M., Petersen S. A. A study of the actions of P1-purinoceptor agonists and antagonists in the mouse vas deferens in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 May;94(1):37–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11497.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. F., Fergus J. H., Badger E. W., Bristol J. A., Santay L. A., Hartman J. D., Hays S. J., Huang C. C. Binding of the A1-selective adenosine antagonist 8-cyclopentyl-1,3-dipropylxanthine to rat brain membranes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1987 Jan;335(1):59–63. doi: 10.1007/BF00165037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Kennedy C. Is there a basis for distinguishing two types of P2-purinoceptor? Gen Pharmacol. 1985;16(5):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(85)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clanachan A. S., Johns A., Paton D. M. Presynaptic inhibitory actions of adenine nucleotides and adenosine on neurotransmission in the rat vas deferens. Neuroscience. 1977;2(4):597–602. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(77)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn P. M., Blakeley A. G. Suramin: a reversible P2-purinoceptor antagonist in the mouse vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Feb;93(2):243–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11427.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enero M. A., Saidman B. Q. Possible feed-back inhibition of noradrenaline release by purine compounds. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1977 Mar;297(1):39–46. doi: 10.1007/BF00508808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsyth K. M., Bjur R. A., Westfall D. P. Nucleotide modulation of norepinephrine release from sympathetic nerves in the rat vas deferens. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Mar;256(3):821–826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredholm B. B., Hedqvist P. Modulation of neurotransmission by purine nucleotides and nucleosides. Biochem Pharmacol. 1980 Jun 15;29(12):1635–1643. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(80)90117-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredholm B. B. Vascular and metabolic effects of theophylline, dibuturyl cyclic AMP and dibuturyl cyclic GMP in canine subcutaneous adipose tissue in situ. Acta Physiol Scand. 1974 Jan;90(1):226–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1974.tb05581.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuder H., Brink A., Meincke M., Tauber U. Purinoceptor-mediated modulation by endogenous and exogenous agonists of stimulation-evoked [3H]noradrenaline release on rat iris. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1992 Apr;345(4):417–423. doi: 10.1007/BF00176619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedqvist P., Fredholm B. B. Effects of adenosine on adrenergic neurotransmission; prejunctional inhibition and postjunctional enhancement. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1976 Jun;293(3):217–223. doi: 10.1007/BF00507344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hourani S. M., Hall D. A., Nieman C. J. Effects of the P2-purinoceptor antagonist, suramin, on human platelet aggregation induced by adenosine 5'-diphosphate. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Feb;105(2):453–457. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14274.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyle C. H., Knight G. E., Burnstock G. Suramin antagonizes responses to P2-purinoceptor agonists and purinergic nerve stimulation in the guinea-pig urinary bladder and taenia coli. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Mar;99(3):617–621. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12979.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue K., Nakazawa K., Ohara-Imaizumi M., Obama T., Fujimori K., Takanaka A. Selective and competitive antagonism by suramin of ATP-stimulated catecholamine-secretion from PC12 phaeochromocytoma cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;102(3):581–584. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12216.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa S. Actions of ATP and alpha, beta-methylene ATP on neuromuscular transmission and smooth muscle membrane of the rabbit and guinea-pig mesenteric arteries. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Dec;86(4):777–787. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb11099.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirpekar S. M., Prat J. C., Wakade A. R. Effect of calcium on the relationship between frequency of stimulation and release of noradrenaline from the perfused spleen of the cat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1975;287(2):205–212. doi: 10.1007/BF00510451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff P., Wood B. E., O'Connor S. E. Suramin is a slowly-equilibrating but competitive antagonist at P2x-receptors in the rabbit isolated ear artery. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):645–649. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14134.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limberger N., Trendelenburg A. U., Starke K. Pharmacological characterization of presynaptic alpha 2-autoreceptors in rat submaxillary gland and heart atrium. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Sep;107(1):246–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14494.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse M. J., Klotz K. N., Lindenborn-Fotinos J., Reddington M., Schwabe U., Olsson R. A. 8-Cyclopentyl-1,3-dipropylxanthine (DPCPX)--a selective high affinity antagonist radioligand for A1 adenosine receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1987 Aug;336(2):204–210. doi: 10.1007/BF00165806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukacsko P., Blumberg A. Modulation of the vasoconstrictor response to adrenergic stimulation by nucleosides and nucleotides. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Aug;222(2):344–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyahara H., Suzuki H. Pre- and post-junctional effects of adenosine triphosphate on noradrenergic transmission in the rabbit ear artery. J Physiol. 1987 Aug;389:423–440. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson R. A., Pearson J. D. Cardiovascular purinoceptors. Physiol Rev. 1990 Jul;70(3):761–845. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.3.761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubino A., Amerini S., Ledda F., Mantelli L. ATP modulates the efferent function of capsaicin-sensitive neurones in guinea-pig isolated atria. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;105(3):516–520. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb09011.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebastião A. M., Stone T. W., Ribeiro J. A. The inhibitory adenosine receptor at the neuromuscular junction and hippocampus of the rat: antagonism by 1,3,8-substituted xanthines. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Oct;101(2):453–459. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12729.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozuka K., Bjur R. A., Westfall D. P. Characterization of prejunctional purinoceptors on adrenergic nerves of the rat caudal artery. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 Sep;338(3):221–227. doi: 10.1007/BF00173391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozuka K., Bjur R. A., Westfall D. P. Effects of alpha,beta-methylene ATP on the prejunctional purinoceptors of the sympathetic nerves of the rat caudal artery. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Sep;254(3):900–904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperlagh B., Vizi E. S. Effect of presynaptic P2 receptor stimulation on transmitter release. J Neurochem. 1991 May;56(5):1466–1470. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb02039.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stjärne L., Astrand P. Relative pre- and postjunctional roles of noradrenaline and adenosine 5'-triphosphate as neurotransmitters of the sympathetic nerves of guinea-pig and mouse vas deferens. Neuroscience. 1985 Mar;14(3):929–946. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90155-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W. Physiological roles for adenosine and adenosine 5'-triphosphate in the nervous system. Neuroscience. 1981;6(4):523–555. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90145-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W. The activity of phosphorothioate analogues of ATP in various smooth muscle systems. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Jan;84(1):165–173. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. A., Wiese S., Faison E. P., Yarbrough G. G. Pharmacological characterization of purinergic receptors in the rat vas deferens. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Jan;224(1):40–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wichmann T., Limberger N., Starke K. Release and modulation of release of serotonin in rabbit superior colliculus. Neuroscience. 1989;32(1):141–151. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90114-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiklund N. P., Gustafsson L. E., Lundin J. Pre- and postjunctional modulation of cholinergic neuroeffector transmission by adenine nucleotides. Experiments with agonist and antagonist. Acta Physiol Scand. 1985 Dec;125(4):681–691. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1985.tb07771.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiklund N. P., Gustafsson L. E. Neuromodulation by adenine nucleotides, as indicated by experiments with inhibitors of nucleotide inactivation. Acta Physiol Scand. 1986 Feb;126(2):217–223. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1986.tb07808.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Kügelgen I., Bültmann R., Starke K. Interaction of adenine nucleotides, UTP and suramin in mouse vas deferens: suramin-sensitive and suramin-insensitive components in the contractile effect of ATP. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;342(2):198–205. doi: 10.1007/BF00166965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Kügelgen I., Kurz K., Starke K. Axon terminal P2-purinoceptors in feedback control of sympathetic transmitter release. Neuroscience. 1993 Sep;56(2):263–267. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90330-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Kügelgen I., Schöffel E., Starke K. Inhibition by nucleotides acting at presynaptic P2-receptors of sympathetic neuro-effector transmission in the mouse isolated vas deferens. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;340(5):522–532. doi: 10.1007/BF00260607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Kügelgen I., Späth L., Starke K. Adenosine but not an adenine nucleotide mediates tonic purinergic inhibition, as well as inhibition by glutamate, of noradrenaline release in rabbit brain cortex slices. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1992 Dec;346(6):677–684. doi: 10.1007/BF00168742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Kügelgen I., Späth L., Starke K. Stable adenine nucleotides inhibit [3H]-noradrenaline release in rabbit brain cortex slices by direct action at presynaptic adenosine A1-receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1992 Aug;346(2):187–196. doi: 10.1007/BF00165300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


