Abstract
1. NK1 and NK2 receptors have been characterized in guinea-pig lung membrane preparations by use of [125I-Tyr8]-substance P and [125I]-neurokinin A binding assays in conjunction with tachykinin-receptor selective agonists ([Sar9Met(O2)11]substance P for NK1 and [beta Ala8]neurokinin A (4-10) for NK2) and antagonists (CP-99,994 for NK1 and SR48968 for NK2). 2. The presence of high affinity, G-protein-coupled NK1 receptors in guinea-pig lung parenchymal membranes has been confirmed. The rank order of affinity for competing tachykinins was as predicted for an NK1 receptor: substance P = [Sar9Met(O2)11]substance P > substance P-methyl ester = physalaemin > neurokinin A = neurokinin B >> [beta Ala8]neurokinin A (4-10). The novel NK1 antagonist CP-99,994 has a Ki of 0.4 nM at this NK1 site. 3. In order to characterize [125I]-neurokinin A binding to guinea-pig lung, the number of [125I]-neurokinin A specific binding sites was increased 3-4 fold by purification of the parenchymal membranes over discontinuous sucrose gradients. The rank order of affinity determined for NK1- and NK2-receptor agonists and antagonists in competition for these sites showed that the majority (80%) of [125I]-neurokinin A specific binding was also to the NK1 receptor. 4. Under conditions where the guinea-pig lung parenchymal NK1 receptor was fully occupied by a saturating concentration of either [Sar9Met(O2)11]substance P (1 microM) or CP-99,994 (2.7 microM), residual [125I]-neurokinin A specific binding was inhibited in a concentration-dependent manner by both [beta Ala8]neurokinin A and SR48968. This result shows that the NK2 receptor is also present in these preparations.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

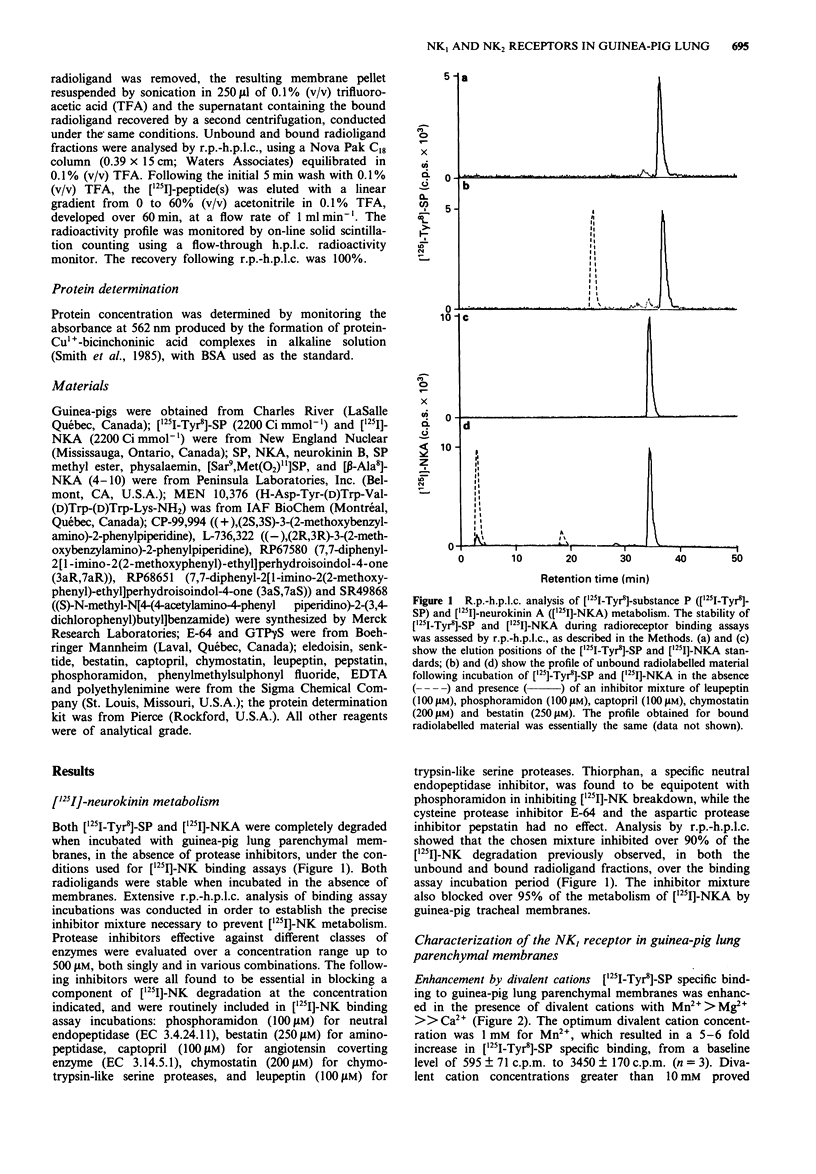
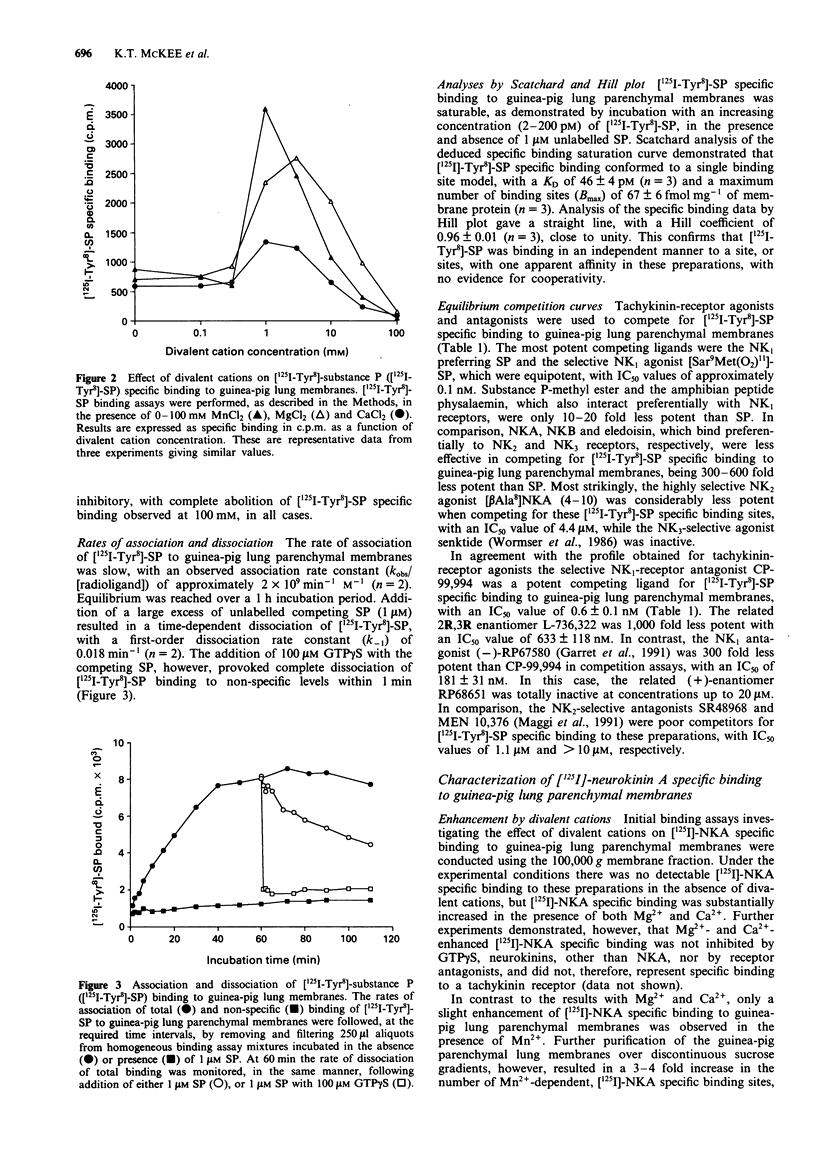
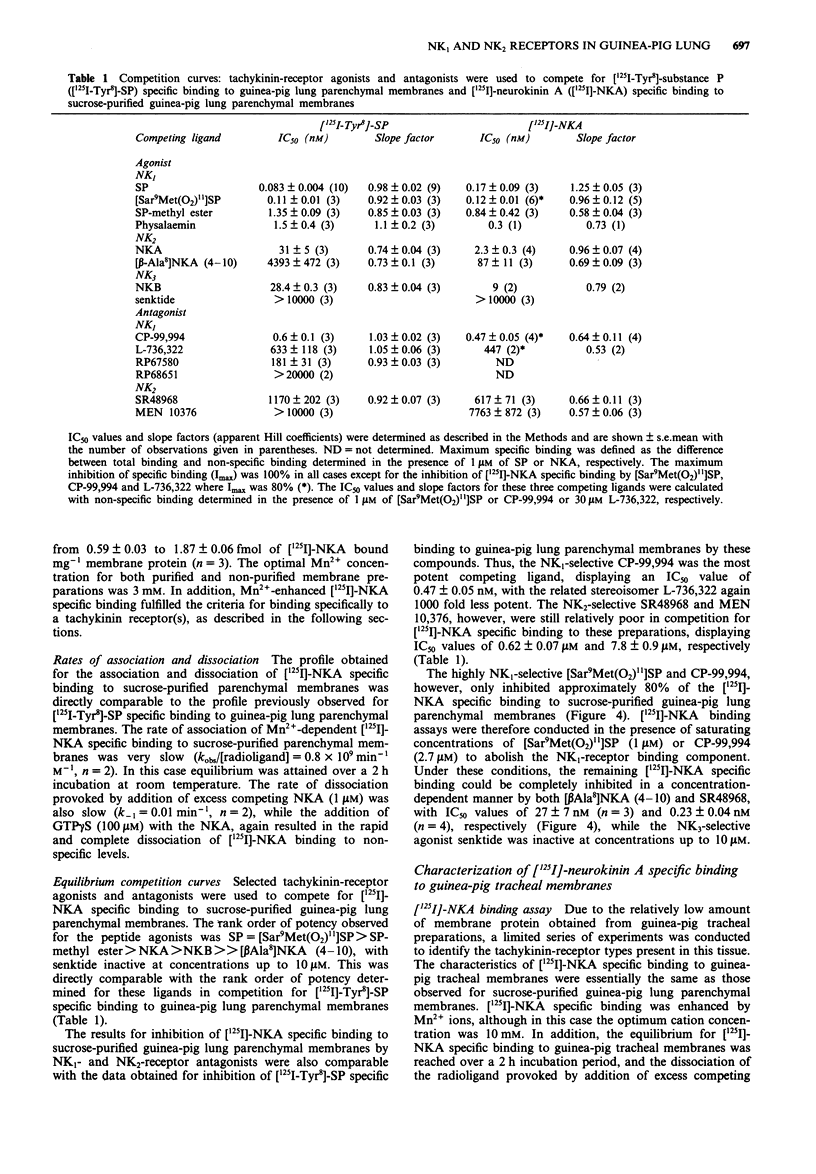
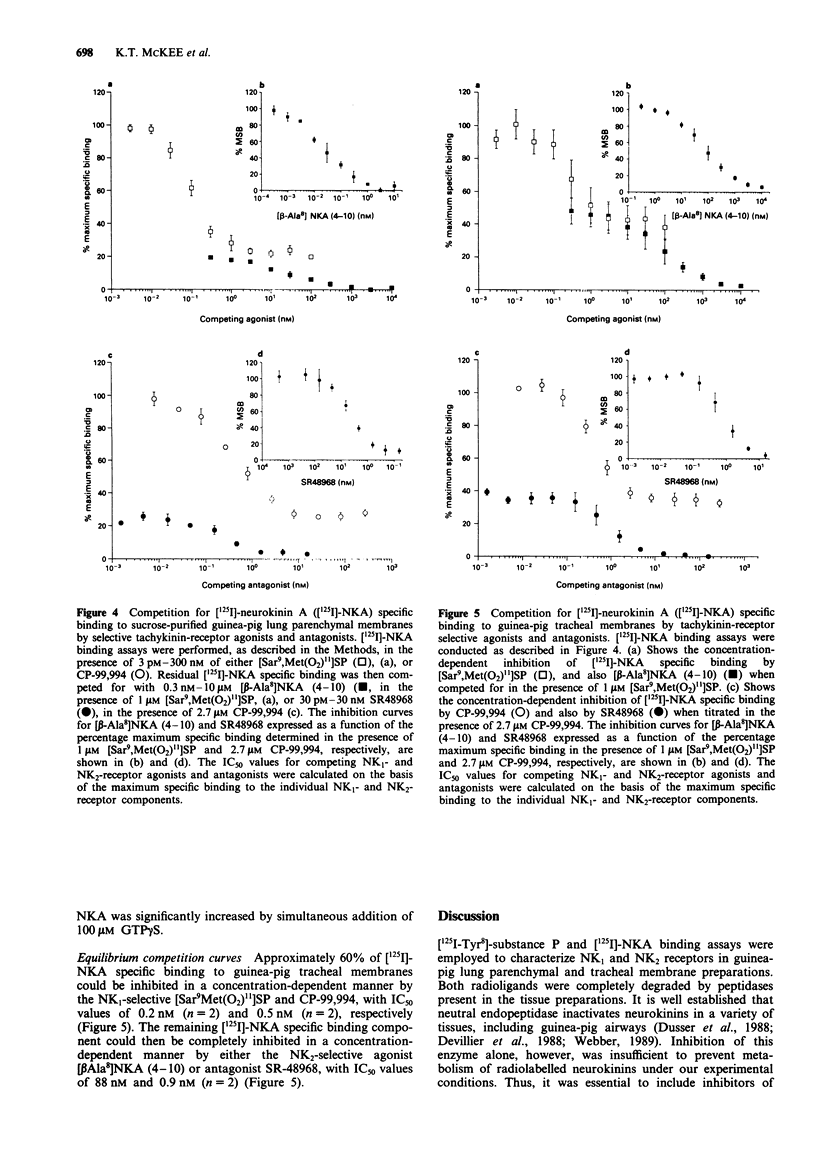


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aharony D., Catanese C. A., Woodhouse D. P. Binding of the novel ligand [4,5-3H-Leu10]substance P to high-affinity NK-1 receptors on guinea pig lung membranes: modulation by GTP analogs and sulfhydryl modifying agents. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Oct;259(1):146–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appell K. C., Fragale B. J., Loscig J., Singh S., Tomczuk B. E. Antagonists that demonstrate species differences in neurokinin-1 receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Apr;41(4):772–778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. J., Belvisi M. G., Rogers D. F. Modulation of neurogenic inflammation: novel approaches to inflammatory disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 May;11(5):185–189. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90112-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carruette A., Moussaoui S. M., Champion A., Cottez D., Goniot P., Garret C. Comparison in different tissue preparations of the in vitro pharmacological profile of RP 67580, a new non-peptide substance P antagonist. Neuropeptides. 1992 Dec;23(4):245–250. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(92)90131-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casale T. B. Neuropeptides and the lung. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1991 Jul;88(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(91)90292-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coats S. R., Gerard N. P. Characterization of the substance P receptor in guinea pig lung tissues. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1989 Oct;1(4):269–275. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/1.4.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devillier P., Advenier C., Drapeau G., Marsac J., Regoli D. Comparison of the effects of epithelium removal and of an enkephalinase inhibitor on the neurokinin-induced contractions of guinea-pig isolated trachea. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jul;94(3):675–684. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11575.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dusser D. J., Umeno E., Graf P. D., Djokic T., Borson D. B., Nadel J. A. Airway neutral endopeptidase-like enzyme modulates tachykinin-induced bronchoconstriction in vivo. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 Dec;65(6):2585–2591. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.65.6.2585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emonds-Alt X., Vilain P., Goulaouic P., Proietto V., Van Broeck D., Advenier C., Naline E., Neliat G., Le Fur G., Brelière J. C. A potent and selective non-peptide antagonist of the neurokinin A (NK2) receptor. Life Sci. 1992;50(15):PL101–PL106. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90352-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garret C., Carruette A., Fardin V., Moussaoui S., Peyronel J. F., Blanchard J. C., Laduron P. M. Pharmacological properties of a potent and selective nonpeptide substance P antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10208–10212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geraghty D. P., Mussap C. J., Burcher E. Radioiodinated substance P, neurokinin A, and eledoisin bind predominantly in NK1 receptors in guinea pig lung. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Jan;41(1):147–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham A., Hopkins B., Powell S. J., Danks P., Briggs I. Isolation and characterisation of the human lung NK-2 receptor gene using rapid amplification of cDNA ends. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 May 31;177(1):8–16. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91940-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey A. D., Krause J. E. Molecular characterization of a functional cDNA encoding the rat substance P receptor. Science. 1990 Feb 23;247(4945):958–962. doi: 10.1126/science.2154852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins B., Powell S. J., Danks P., Briggs I., Graham A. Isolation and characterisation of the human lung NK-1 receptor cDNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Oct 31;180(2):1110–1117. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81181-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ireland S. J., Bailey F., Cook A., Hagan R. M., Jordan C. C., Stephens-Smith M. L. Receptors mediating tachykinin-induced contractile responses in guinea-pig trachea. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jun;103(2):1463–1469. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb09812.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause J. E., Takeda Y., Hershey A. D. Structure, functions, and mechanisms of substance P receptor action. J Invest Dermatol. 1992 Jun;98(6 Suppl):2S–7S. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12462082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Giuliani S., Ballati L., Lecci A., Manzini S., Patacchini R., Renzetti A. R., Rovero P., Quartara L., Giachetti A. In vivo evidence for tachykininergic transmission using a new NK-2 receptor-selective antagonist, MEN 10,376. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Jun;257(3):1172–1178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Patacchini R., Rovero P., Giachetti A. Tachykinin receptors and tachykinin receptor antagonists. J Auton Pharmacol. 1993 Feb;13(1):23–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1993.tb00396.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggio J. E. Tachykinins. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1988;11:13–28. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.11.030188.000305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masu Y., Nakayama K., Tamaki H., Harada Y., Kuno M., Nakanishi S. cDNA cloning of bovine substance-K receptor through oocyte expression system. 1987 Oct 29-Nov 4Nature. 329(6142):836–838. doi: 10.1038/329836a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murai M., Morimoto H., Maeda Y., Fujii T. Effects of the tripeptide substance P antagonist, FR113680, on airway constriction and airway edema induced by neurokinins in guinea-pigs. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jun 24;217(1):23–29. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90506-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Drapeau G., Dion S., Couture R. New selective agonists for neurokinin receptors: pharmacological tools for receptor characterization. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Aug;9(8):290–295. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Drapeau G., Dion S., D'Orléans-Juste P. Pharmacological receptors for substance P and neurokinins. Life Sci. 1987 Jan 12;40(2):109–117. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90349-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal H. E. A graphic method for the determination and presentation of binding parameters in a complex system. Anal Biochem. 1967 Sep;20(3):525–532. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90297-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovero P., Pestellini V., Patacchini R., Giuliani S., Santicioli P., Maggi C. A., Meli A., Giachetti A. A potent and selective agonist for NK-2 tachykinin receptor. Peptides. 1989 May-Jun;10(3):593–595. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(89)90148-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shigemoto R., Yokota Y., Tsuchida K., Nakanishi S. Cloning and expression of a rat neuromedin K receptor cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):623–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider R. M., Constantine J. W., Lowe J. A., 3rd, Longo K. P., Lebel W. S., Woody H. A., Drozda S. E., Desai M. C., Vinick F. J., Spencer R. W. A potent nonpeptide antagonist of the substance P (NK1) receptor. Science. 1991 Jan 25;251(4992):435–437. doi: 10.1126/science.1703323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solway J., Leff A. R. Sensory neuropeptides and airway function. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1991 Dec;71(6):2077–2087. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1991.71.6.2077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Chou K. B., Takeda J., Sachais B. S., Krause J. E. Molecular cloning, structural characterization and functional expression of the human substance P receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Sep 30;179(3):1232–1240. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91704-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tousignant C., Chan C. C., Guevremont D., Brideau C., Hale J. J., MacCoss M., Rodger I. W. NK2 receptors mediate plasma extravasation in guinea-pig lower airways. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Feb;108(2):383–386. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb12813.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watling K. J. Nonpeptide antagonists herald new era in tachykinin research. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Jul;13(7):266–269. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90082-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webber S. E. Receptors mediating the effects of substance P and neurokinin A on mucus secretion and smooth muscle tone of the ferret trachea: potentiation by an enkephalinase inhibitor. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;98(4):1197–1206. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12665.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wormser U., Laufer R., Hart Y., Chorev M., Gilon C., Selinger Z. Highly selective agonists for substance P receptor subtypes. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2805–2808. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04571.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota Y., Sasai Y., Tanaka K., Fujiwara T., Tsuchida K., Shigemoto R., Kakizuka A., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S. Molecular characterization of a functional cDNA for rat substance P receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17649–17652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


