Abstract
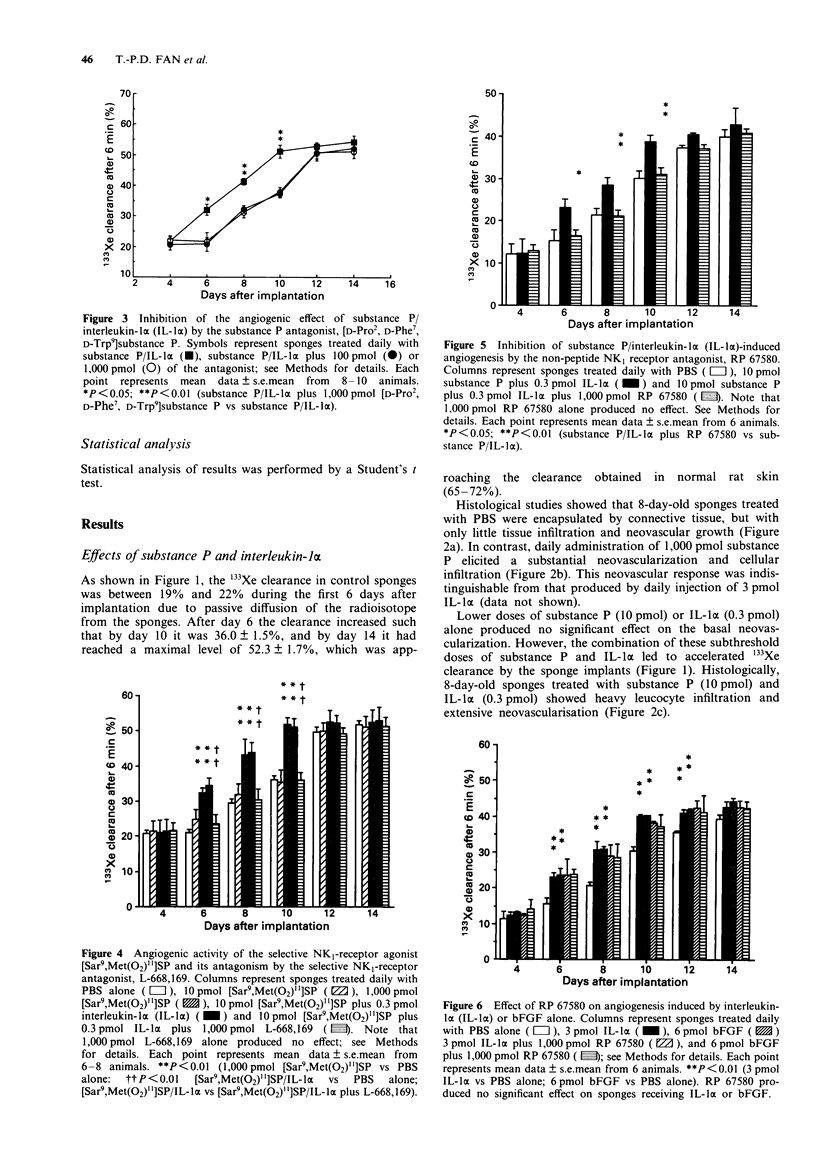
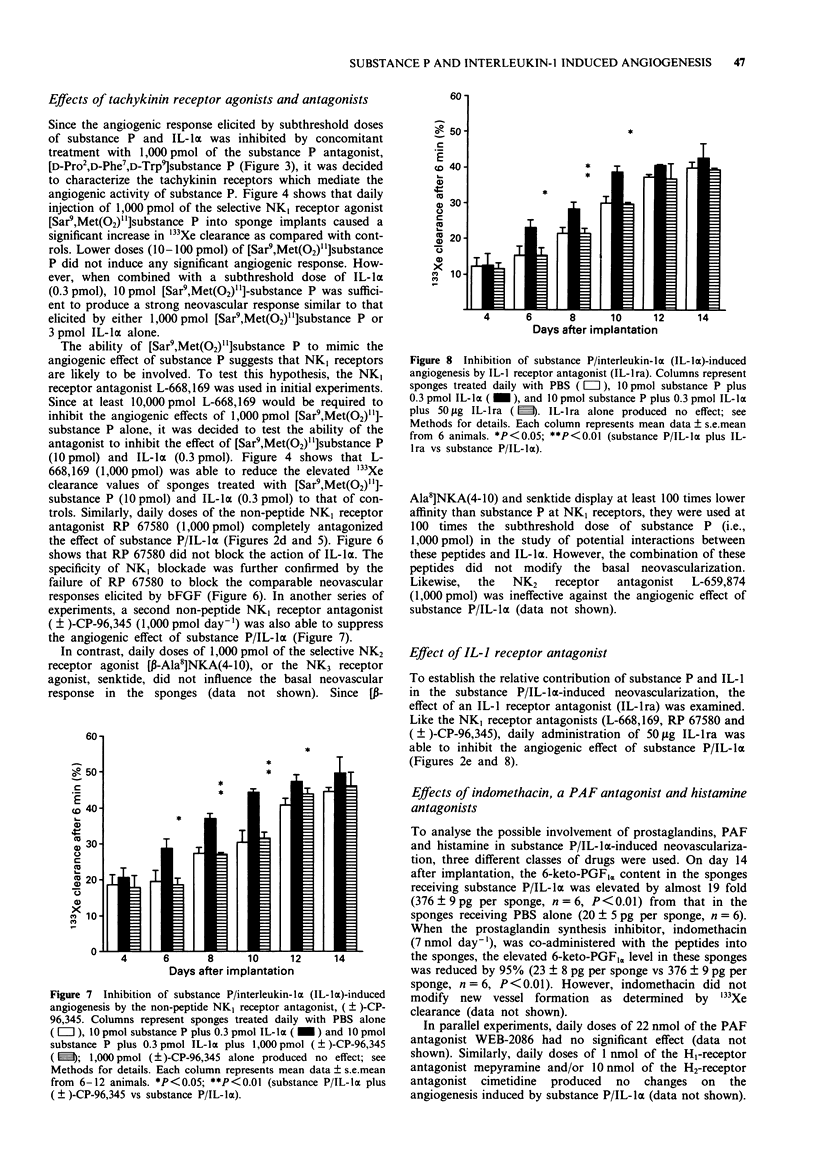
1. Daily administration of 1 nmol substance P or 3 pmol recombinant human interleukin-1 alpha (IL-1 alpha) caused intense neovascularization in a rat sponge model of angiogenesis. Lower doses of substance P (10 pmol) or IL-1 alpha (0.3 pmol) were ineffective when given alone. When combined at these low doses, substances P and IL-1 alpha interacted to produce an enhanced neovascular response. 2. By use of selective tachykinin NK1, NK2 and NK3 receptor agonists, ([Sar9,Met(O2)11]substance P, [beta-Ala8]neurokinin A(4-10), Succ-[Asp6,MePhe8]substance P(6-11) (senktide), respectively), it was established that the activation of NK1 receptors is most likely to mediate the angiogenic response to substance P in this model. 3. The angiogenic activity of substance P and IL-1 alpha (10 pmol and 0.3 pmol day-1, respectively) was abolished by co-administration of (i) the selective peptide NK1 receptor antagonist, L-668,169 (1 nmol day-1), (ii) the selective non-peptide NK1 receptor antagonists, RP 67580 and (+/-)-CP-96,345 (both at 1 nmol day-1) or (iii) the IL-1 receptor antagonist, IL-1ra, (50 micrograms day-1). In contrast, the selective NK2 receptor antagonist, L-659,874 (1 nmol day-1) was ineffective. 4. The angiogenic action of substance P and IL-1 alpha was resistant to modification by mepyramine (1 nmol day-1) and/or cimetidine (10 nmol day-1), indomethacin (7 nmol day-1) or the platelet-activating factor (PAF) antagonist, WEB-2086 (22 nmol day-1), indicating that histamine, prostaglandins and PAF are not likely to be involved in this neovascular response.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrade S. P., Fan T. P., Lewis G. P. Quantitative in-vivo studies on angiogenesis in a rat sponge model. Br J Exp Pathol. 1987 Dec;68(6):755–766. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai K. I., Lee F., Miyajima A., Miyatake S., Arai N., Yokota T. Cytokines: coordinators of immune and inflammatory responses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:783–836. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.004031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brain S. D., Williams T. J. Interactions between the tachykinins and calcitonin gene-related peptide lead to the modulation of oedema formation and blood flow in rat skin. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 May;97(1):77–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11926.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunelleschi S., Ceni E., Giotti A., Fantozzi R. Tachykinins stimulate lyso-PAF:acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase activity in neutrophils. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Sep 21;186(2-3):367–368. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90463-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley T. L., Brain S. D., Collins P. D., Williams T. J. Inflammatory edema induced by interactions between IL-1 and the neuropeptide calcitonin gene-related peptide. J Immunol. 1991 May 15;146(10):3424–3430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussolino F., Breviario F., Tetta C., Aglietta M., Mantovani A., Dejana E. Interleukin 1 stimulates platelet-activating factor production in cultured human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):2027–2033. doi: 10.1172/JCI112532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casals-Stenzel J., Muacevic G., Weber K. H. Pharmacological actions of WEB 2086, a new specific antagonist of platelet activating factor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Jun;241(3):974–981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozzolino F., Torcia M., Aldinucci D., Ziche M., Almerigogna F., Bani D., Stern D. M. Interleukin 1 is an autocrine regulator of human endothelial cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6487–6491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detmar M., Tenorio S., Hettmannsperger U., Ruszczak Z., Orfanos C. E. Cytokine regulation of proliferation and ICAM-1 expression of human dermal microvascular endothelial cells in vitro. J Invest Dermatol. 1992 Feb;98(2):147–153. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12555746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapeau G., D'Orléans-Juste P., Dion S., Rhaleb N. E., Rouissi N. E., Regoli D. Selective agonists for substance P and neurokinin receptors. Neuropeptides. 1987 Jul;10(1):43–54. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(87)90088-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Klagsbrun M. Angiogenic factors. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):442–447. doi: 10.1126/science.2432664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foreman J., Jordan C. Histamine release and vascular changes induced by neuropeptides. Agents Actions. 1983 Apr;13(2-3):105–116. doi: 10.1007/BF01967311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freidin M., Kessler J. A. Cytokine regulation of substance P expression in sympathetic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3200–3203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garret C., Carruette A., Fardin V., Moussaoui S., Peyronel J. F., Blanchard J. C., Laduron P. M. Pharmacological properties of a potent and selective nonpeptide substance P antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10208–10212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haegerstrand A., Dalsgaard C. J., Jonzon B., Larsson O., Nilsson J. Calcitonin gene-related peptide stimulates proliferation of human endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3299–3303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannum C. H., Wilcox C. J., Arend W. P., Joslin F. G., Dripps D. J., Heimdal P. L., Armes L. G., Sommer A., Eisenberg S. P., Thompson R. C. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist activity of a human interleukin-1 inhibitor. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):336–340. doi: 10.1038/343336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart R. P., Shadiack A. M., Jonakait G. M. Substance P gene expression is regulated by interleukin-1 in cultured sympathetic ganglia. J Neurosci Res. 1991 Jul;29(3):282–291. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490290303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermanson A., Dalsgaard C. J., Björklund H., Lindblom U. Sensory reinnervation and sensibility after superficial skin wounds in human patients. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Mar 9;74(3):377–382. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90327-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu D. E., Fan T. P. [Leu8]des-Arg9-bradykinin inhibits the angiogenic effect of bradykinin and interleukin-1 in rats. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 May;109(1):14–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13525.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimball E. S., Fisher M. C. Potentiation of IL-1-induced BALB/3T3 fibroblast proliferation by substance P. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;540:681–683. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb27211.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M., D'Amore P. A. Regulators of angiogenesis. Annu Rev Physiol. 1991;53:217–239. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.53.030191.001245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J. D., Clark R., Devor M., Helms C., Moskowitz M. A., Basbaum A. I. Intraneuronal substance P contributes to the severity of experimental arthritis. Science. 1984 Nov 2;226(4674):547–549. doi: 10.1126/science.6208609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotz M., Carson D. A., Vaughan J. H. Substance P activation of rheumatoid synoviocytes: neural pathway in pathogenesis of arthritis. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):893–895. doi: 10.1126/science.2433770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotz M., Vaughan J. H., Carson D. A. Effect of neuropeptides on production of inflammatory cytokines by human monocytes. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1218–1221. doi: 10.1126/science.2457950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantyh C. R., Gates T. S., Zimmerman R. P., Welton M. L., Passaro E. P., Jr, Vigna S. R., Maggio J. E., Kruger L., Mantyh P. W. Receptor binding sites for substance P, but not substance K or neuromedin K, are expressed in high concentrations by arterioles, venules, and lymph nodules in surgical specimens obtained from patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3235–3239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses M. A., Langer R. Inhibitors of angiogenesis. Biotechnology (N Y) 1991 Jul;9(7):630–634. doi: 10.1038/nbt0791-630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson J., von Euler A. M., Dalsgaard C. J. Stimulation of connective tissue cell growth by substance P and substance K. Nature. 1985 May 2;315(6014):61–63. doi: 10.1038/315061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payan D. G. Neuropeptides and inflammation: the role of substance P. Annu Rev Med. 1989;40:341–352. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.40.020189.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovero P., Pestellini V., Rhaleb N. E., Dion S., Rouissi N., Tousignant C., Télémaque S., Drapeau G., Regoli D. Structure-activity studies of neurokinin A. Neuropeptides. 1989 May-Jun;13(4):263–270. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(89)90080-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smither R. L., Fan T. P. Effects of platelet-activating factor on endothelial cells and fibroblasts in vitro. EXS. 1992;61:230–234. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-7001-6_35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider R. M., Constantine J. W., Lowe J. A., 3rd, Longo K. P., Lebel W. S., Woody H. A., Drozda S. E., Desai M. C., Vinick F. J., Spencer R. W. A potent nonpeptide antagonist of the substance P (NK1) receptor. Science. 1991 Jan 25;251(4992):435–437. doi: 10.1126/science.1703323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tumer N., Houck W. T., Boehm C., Roberts J. Cardiac beta-adrenoceptor binding characteristics with age following adrenal demedullation. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jan;99(1):87–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14658.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh D. A., Mapp P. I., Wharton J., Rutherford R. A., Kidd B. L., Revell P. A., Blake D. R., Polak J. M. Localisation and characterisation of substance P binding to human synovial tissue in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992 Mar;51(3):313–317. doi: 10.1136/ard.51.3.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wormser U., Laufer R., Hart Y., Chorev M., Gilon C., Selinger Z. Highly selective agonists for substance P receptor subtypes. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2805–2808. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04571.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziche M., Morbidelli L., Pacini M., Geppetti P., Alessandri G., Maggi C. A. Substance P stimulates neovascularization in vivo and proliferation of cultured endothelial cells. Microvasc Res. 1990 Sep;40(2):264–278. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(90)90024-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



