Abstract
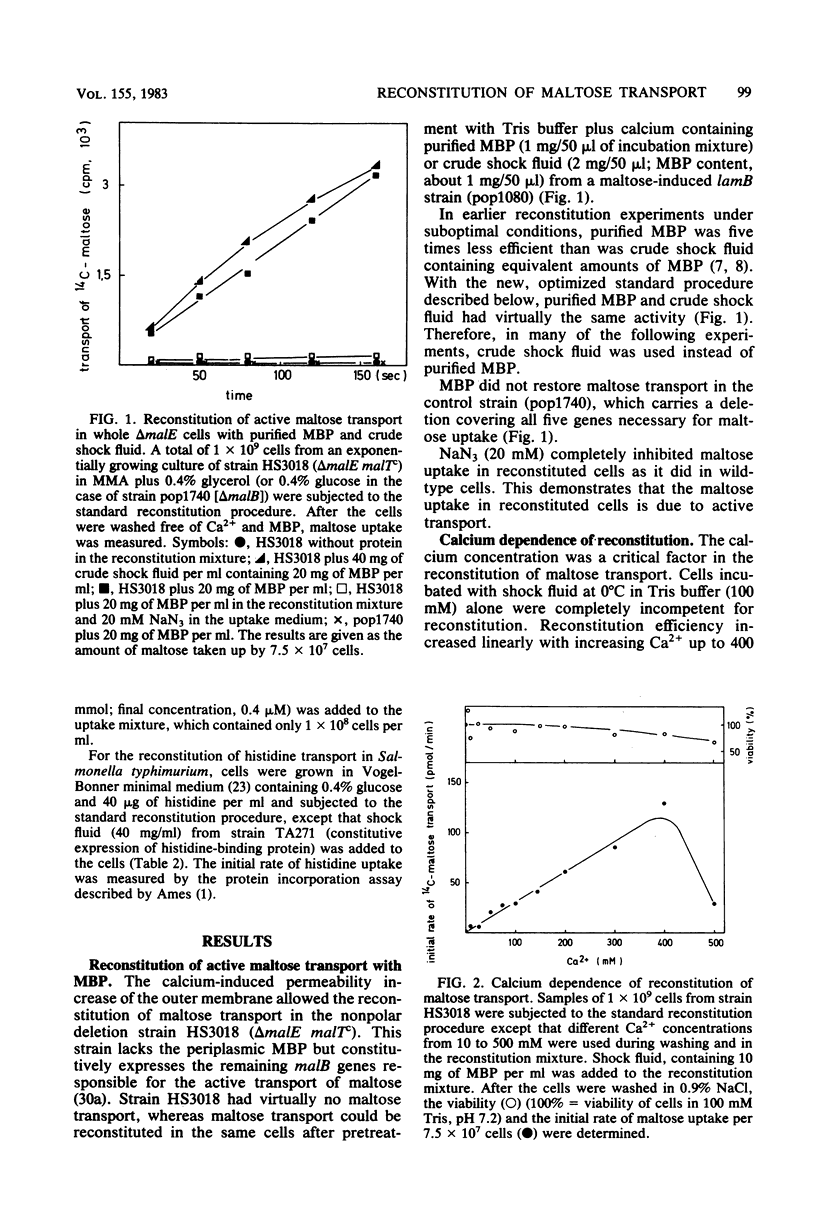
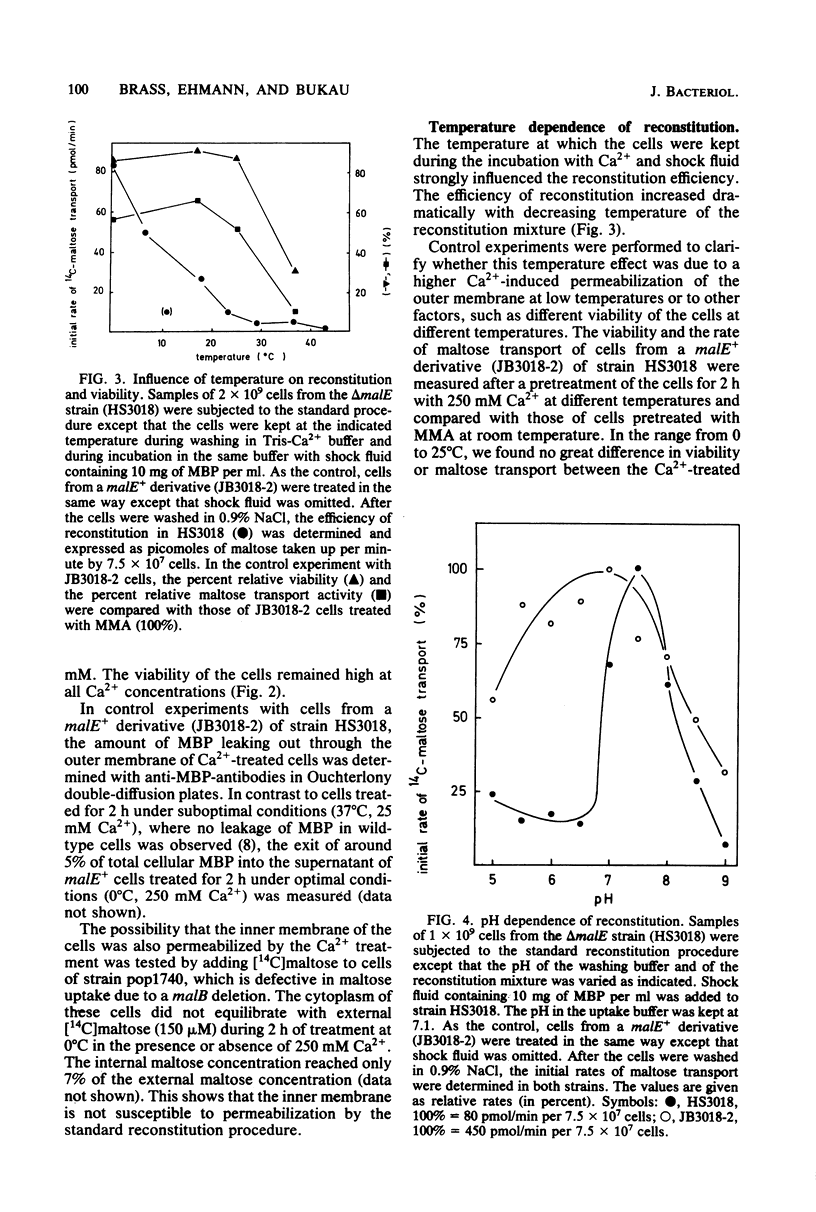
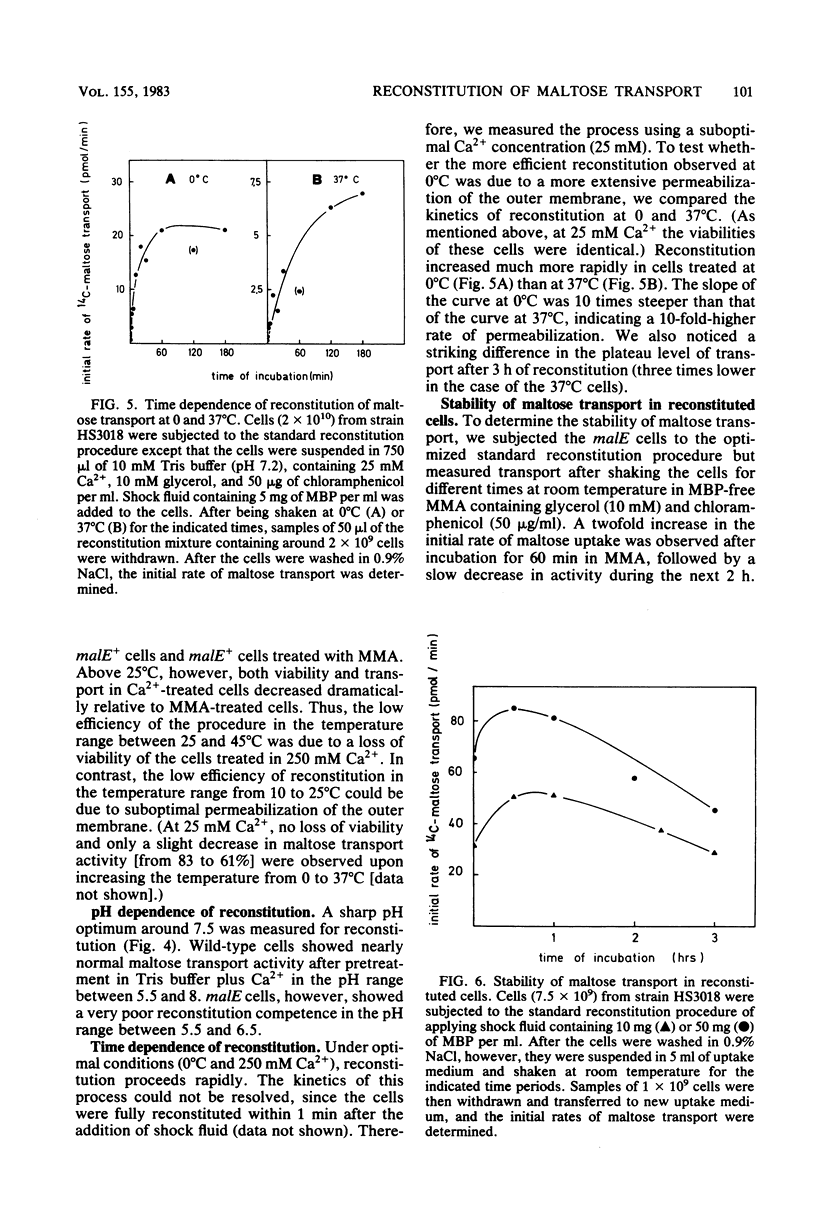
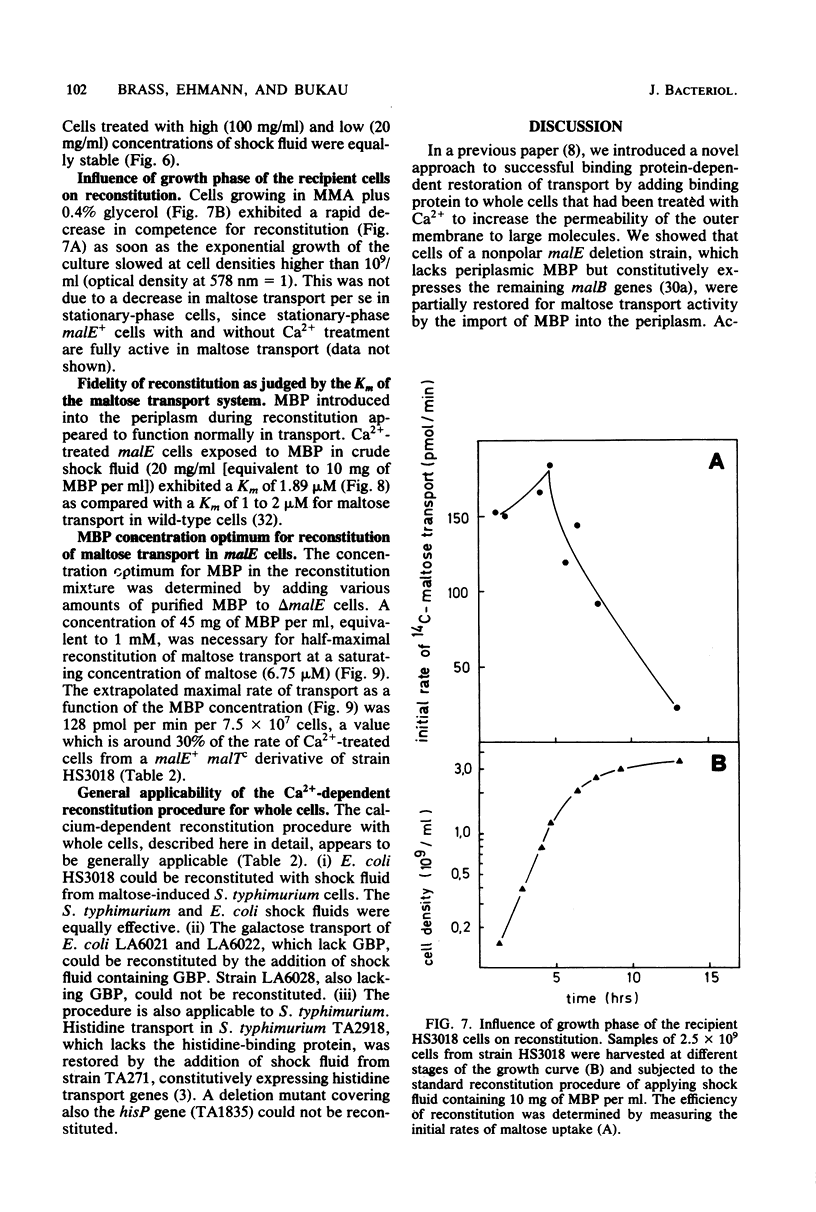
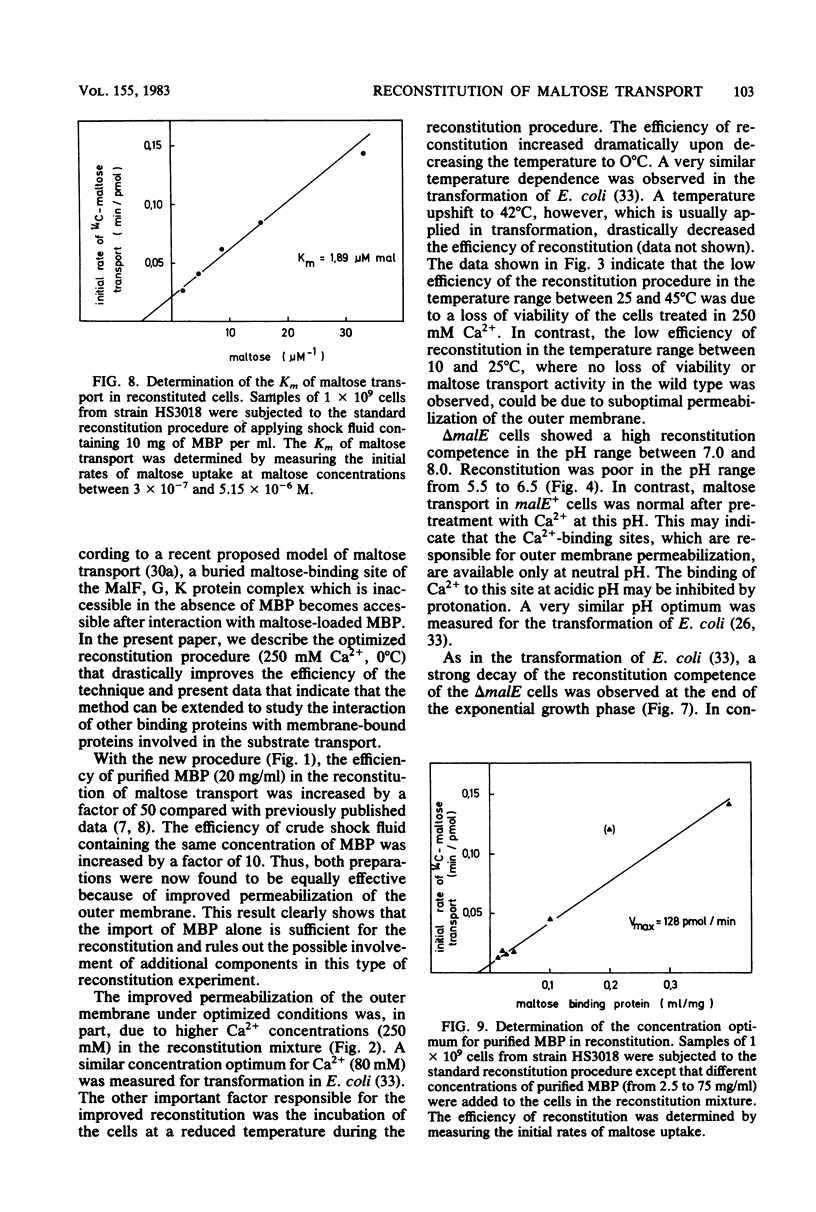
The reconstitution of active transport by the Ca2+ -induced import of exogenous binding protein was studied in detail in whole cells of a malE deletion mutant lacking the periplasmic maltose-binding protein. A linear increase in reconstitution efficiency was observed by increasing the Ca2+ - concentration in the reconstitution mixture up to 400 mM. A sharp pH optimum around pH 7.5 was measured for reconstitution. Reconstitution efficiency was highest at 0 degree C and decreased sharply with increasing temperature. The time necessary for optimal reconstitution at 0 degree C and 250 mM Ca2+ was about 1 min. The competence for reconstitution was highest in exponentially growing cultures with cell densities up to 1 X 10(9)/ml and declined when the cells entered the stationary-growth phase. The apparent Km for maltose uptake was the same as that of wild-type cells (1 to 2 microM). Vmax at saturating maltose-binding protein concentration was 125 pmol per min per 7.5 X 10(7) cells (30% of the wild-type activity). The concentration of maltose-binding protein required for half-maximal reconstitution was about 1 mM. The reconstitution procedure appears to be generally applicable. Thus, galactose transport in Escherichia coli could also be reconstituted by its respective binding protein. Maltose transport in E. coli was restored by maltose-binding protein isolated from Salmonella typhimurium. Finally, in S. typhimurium, histidine transport was reconstituted by the addition of shock fluid containing histidine-binding protein to a hisJ deletion mutant lacking histidine-binding protein. The method is fast and general enough to be used as a screening procedure to distinguish between transport mutants in which only the binding protein is affected and those in which additional transport components are affected.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES G. F. UPTAKE OF AMINO ACIDS BY SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Jan;104:1–18. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(64)80028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F., Lever J. Components of histidine transport: histidine-binding proteins and hisP protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Aug;66(4):1096–1103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.4.1096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F., Noel K. D., Taber H., Spudich E. N., Nikaido K., Afong J. Fine-structure map of the histidine transport genes in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1289–1297. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1289-1297.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barash H., Halpern Y. S. Glutamate-binding protein and its relation to glutamate transport in Escherichia coli K-12. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Nov 5;45(3):681–688. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90470-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bavoil P., Nikaido H. Physical interaction between the phage lambda receptor protein and the carrier-immobilized maltose-binding protein of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11385–11388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergmans H. E., van Die I. M., Hoekstra W. P. Transformation in Escherichia coli: stages in the process. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):564–570. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.564-570.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass J. M., Boos W., Hengge R. Reconstitution of maltose transport in malB mutants of Escherichia coli through calcium-induced disruptions of the outer membrane. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):10–17. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.10-17.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass J. M. Reconstitution of maltose transport in malB and malA mutants of Escherichia coli. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1982 Jan;133A(1):171–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Rehn K. Chemical characterization, spatial distribution and function of a lipoprotein (murein-lipoprotein) of the E. coli cell wall. The specific effect of trypsin on the membrane structure. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Oct;10(3):426–438. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00707.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzel I., Kolb V., Boos W. Pole cap formation in Escherichia coli following induction of the maltose-binding protein. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Aug 1;118(2):207–218. doi: 10.1007/BF00415731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferenci T., Boos W. The role of the Escherichia coli lambda receptor in the transport of maltose and maltodextrins. J Supramol Struct. 1980;13(1):101–116. doi: 10.1002/jss.400130110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferenci T., Klotz U. Affinity chromatographic isolation of the periplasmic maltose binding protein of Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1978 Oct 15;94(2):213–217. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80940-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway D. R., Furlong C. E. Reconstitution of binding protein-dependent ribose transport in spheroplasts of Escherichia coli K-12. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Oct 1;197(1):158–162. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90231-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes R. G., Strickland K. P., Rosenberg H. Restoration of phosphate transport by the phosphate-binding protein in spheroplasts of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 Aug;131(2):512–518. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.2.512-518.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirota Y., Suzuki H., Nishimura Y., Yasuda S. On the process of cellular division in Escherichia coli: a mutant of E. coli lacking a murein-lipoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1417–1420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofnung M., Hatfield D., Schwartz M. malB region in Escherichia coli K-12: characterization of new mutations. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):40–47. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.40-47.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofnung M., Jezierska A., Braun-Breton C. lamB mutations in E. coli K12: growth of lambda host range mutants and effect of nonsense suppressors. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 May 7;145(2):207–213. doi: 10.1007/BF00269595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt A. G., Hong J. The reconstitution of binding protein-dependent active transport of glutamine in isolated membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):11988–11991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEIVE L. A NONSPECIFIC INCREASE IN PERMEABILITY IN ESCHERICHIA COLI PRODUCED BY EDTA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Apr;53:745–750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.4.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller N., Heine H. G., Boos W. Cloning of mglB, the structural gene for the galactose-binding protein of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;185(3):473–480. doi: 10.1007/BF00334143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Heppel L. A. The release of enzymes from Escherichia coli by osmotic shock and during the formation of spheroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3685–3692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgard M. V., Keem K., Monahan J. J. Factors affecting the transformation of Escherichia coli strain chi1776 by pBR322 plasmid DNA. Gene. 1978 Jul;3(4):279–292. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90038-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richarme G., Kepes A. Release of glucose from purified galactose-binding protein of Escherichia coli upon addition of galactose. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jun 1;45(1):127–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03537.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb F. T., Furlong C. E. Reconstitution of binding protein dependent ribose transport in spheroplasts derived from a binding protein negative Escherichia coli K12 mutant and from Salmonella typhimurium. J Supramol Struct. 1980;13(2):183–190. doi: 10.1002/jss.400130206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbusch J. P. Characterization of the major envelope protein from Escherichia coli. Regular arrangement on the peptidoglycan and unusual dodecyl sulfate binding. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 25;249(24):8019–8029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabelnikov A. G., Domaradsky I. V. Effect of metabolic inhibitors on entry of exogenous deoxyribonucleic acid into Ca2+-treated Escherichia coli cells. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):435–443. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.435-443.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silhavy T. J., Boos W. Selection procedure for mutants defective in the beta-methylgalactoside transport system of Escherichia coli utilizing the compound 2R-glyceryl-beta-D-galactopyranoside. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):424–432. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.424-432.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szmelcman S., Schwartz M., Silhavy T. J., Boos W. Maltose transport in Escherichia coli K12. A comparison of transport kinetics in wild-type and lambda-resistant mutants as measured by fluorescence quenching. Eur J Biochem. 1976 May 17;65(1):13–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10383.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taketo A. Sensitivity of Escherichia coli to viral nucleic acid. 8. Idiosyncrasy of Ca2+-dependent competence for DNA. J Biochem. 1974 Apr;75(4):895–904. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilby M., Hindennach I., Henning U. Bypass of receptor-mediated resistance to colicin E3 in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1978 Dec;136(3):1189–1191. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.3.1189-1191.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wandersman C., Schwartz M., Ferenci T. Escherichia coli mutants impaired in maltodextrin transport. J Bacteriol. 1979 Oct;140(1):1–13. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.1.1-13.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Pedro M. A., Schwarz U. Heterogeneity of newly inserted and preexisting murein in the sacculus of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5856–5860. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


