Abstract
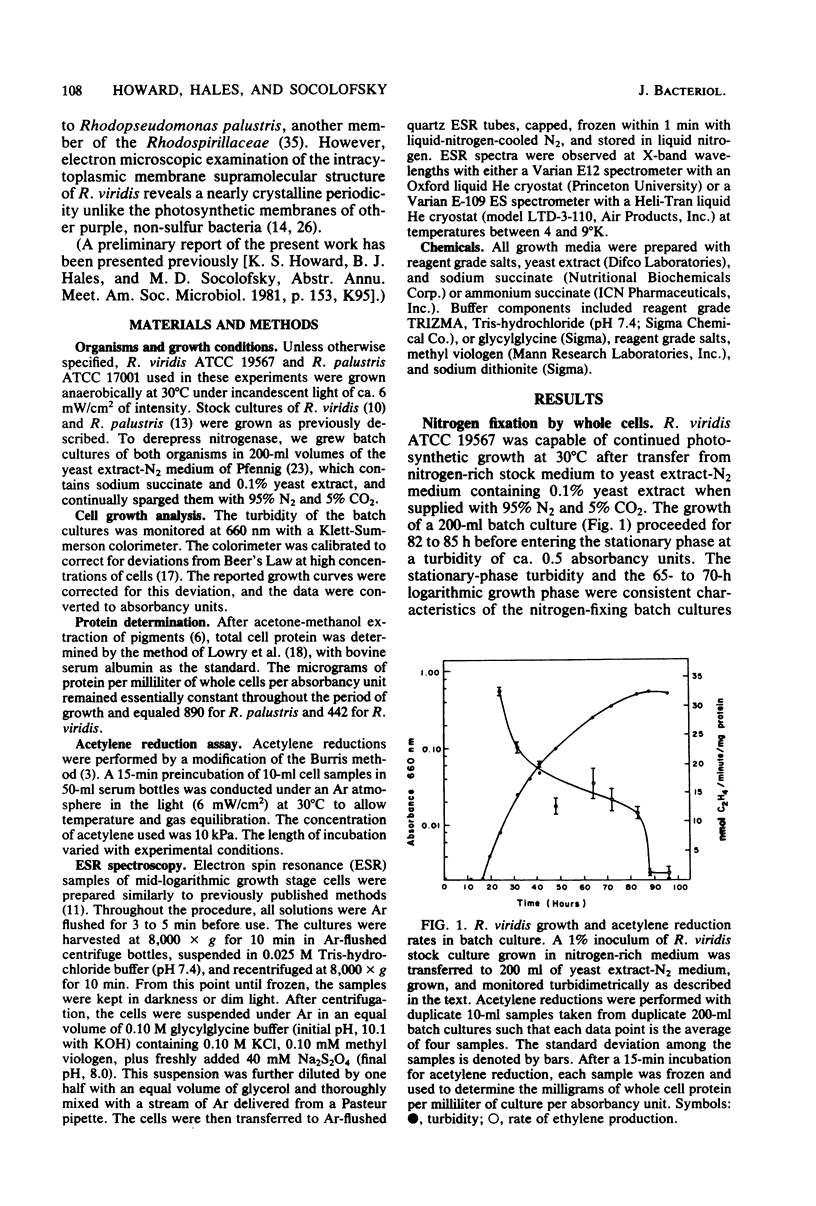
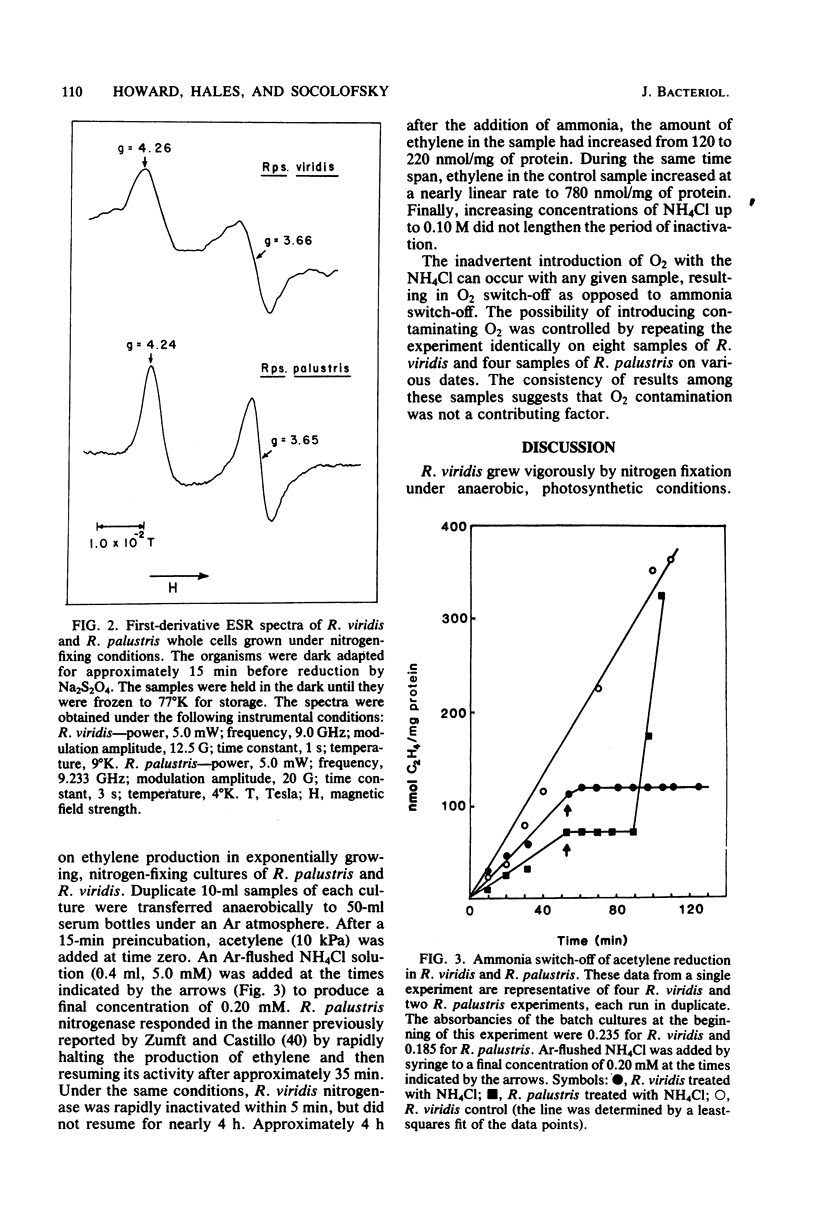
Rhodopseudomonas viridis ATCC 19567 grows by means of nitrogen fixation in yeast extract-N2 or nitrogen-free medium when sparged with 5% CO2 and 95% N2 in the light at 30 degrees C. Acetylene reduction assays for nitrogenase activity revealed an initially high level of activity during early-logarithmic growth phase, a lower plateau during mid- to late-logarithmic phase, and a dramatic reduction of activity at the beginning of the stationary phase. When viewed by electron microscopy, nitrogen-fixing R. viridis cells appeared to be morphologically and ultrastructurally similar to cells grown on nitrogen-rich media. Whole cells prepared under reducing conditions in the dark for electron spin resonance spectroscopy yielded g4.26 and g3.66 signals characteristic of the molybdenum-iron protein of nitrogenase. During growth on N2 in the absence of fixed-nitrogen sources, the nitrogenase activity of R. viridis measured by acetylene reduction stopped rapidly in response to the addition of NH4Cl as has been observed in other Rhodospirillaceae. However, unlike the nitrogenase of Rhodopseudomonas palustris or Rhodospirillum rubrum, which recover from this treatment within 40 min, the nitrogenase activity of R. viridis was not detectable for nearly 4 h.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burgess B. K., Stiefel E. I., Newton W. E. Oxidation-reduction properties and complexation reactions of the iron-molybdenum cofactor of nitrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):353–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burris R. H. Nitrogen fixation--assay methods and techniques. Methods Enzymol. 1972;24:415–431. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(72)24088-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAYTON R. K. TOWARD THE ISOLATION OF A PHOTOCHEMICAL REACTION CENTER IN RHODOPSEUDOMONAS SPHEROIDES. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Nov 29;75:312–323. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90618-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carithers R. P., Yoch D. C., Arnon D. I. Two forms of nitrogenase from the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodospirillum rubrum. J Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;137(2):779–789. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.2.779-789.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. C., Shah V. K., Brill W. J., Orme-Johnson W. H. Nitrogenase. II. Changes in the EPR signal of component I (iron-molybdenum protein) of Azotobacter vinelandii nitrogenase during repression and derepression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 28;256(2):512–523. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90079-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drews G., Giesbrecht P. Rhodopseudomonas viridis, nov. spec., ein neu isoliertes, obligat phototrophes Bakterium. Arch Mikrobiol. 1966 Mar 31;53(3):255–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank H. A., Friesner R., Nairn J. A., Dismukes G. C., Sauer K. The orientation of the primary donor in bacterial photosynthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Sep 11;547(3):484–501. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(79)90029-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotto J. W., Yoch D. C. Regulation of Rhodospirillum rubrum nitrogenase activity. Properties and interconversion of active and inactive Fe protein. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):2868–2873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochman A., Burris R. H. Effect of oxygen on acetylene reduction by photosynthetic bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1981 Aug;147(2):492–499. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.2.492-499.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludden P. W., Burris R. H. Activating factor for the iron protein of nitrogenase from Rhodospirillum rubrum. Science. 1976 Oct 22;194(4263):424–426. doi: 10.1126/science.824729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludden P. W., Burris R. H. Purification and properties of nitrogenase from Rhodospirillum rubrum, and evidence for phosphate, ribose and an adenine-like unit covalently bound to the iron protein. Biochem J. 1978 Oct 1;175(1):251–259. doi: 10.1042/bj1750251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludden P. W., Burris R. H. Removal of an adenine-like molecule during activation of dinitrogenase reductase from Rhodospirillum rubrum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6201–6205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilson A. H., Nordlund S. Regulation of nitrogenase synthesis in intact cells of Rhodospirillum rubrum: inactivation of nitrogen fixation by ammonia, L-glutamine and L-asparagine. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Nov;91(1):53–62. doi: 10.1099/00221287-91-1-53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordlund S., Eriksson U., Baltscheffsky H. Properties of the nitrogenase system from a photosynthetic bacterium, Rhodospirillum rubrum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 9;504(2):248–254. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(78)90173-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oelze J., Drews G. Membranes of photosynthetic bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Apr 18;265(2):209–239. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(72)90003-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt D. C., Frenkel A. W. Studies on Nitrogen Fixation and Photosynthesis of Rhodospirillum Rubrum. Plant Physiol. 1959 May;34(3):333–337. doi: 10.1104/pp.34.3.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince R. C., Leigh J. S., Jr, Dutton P. L. Thermodynamic properties of the reaction center of Rhodopseudomonas viridis. In vivo measurement of the reaction center bacteriochlorophyll-primary acceptor intermediary electron carrier. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 13;440(3):622–636. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(76)90047-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlings J., Shah V. K., Chisnell J. R., Brill W. J., Zimmermann R., Münck E., Orme-Johnson W. H. Novel metal cluster in the iron-molybdenum cofactor of nitrogenase. Spectroscopic evidence. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 25;253(4):1001–1004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schick H. J. Substrate and light dependent fixation of molecular nitrogen in Rhodospirillum rubrum. Arch Mikrobiol. 1971;75(2):89–101. doi: 10.1007/BF00407997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet W. J., Burris R. H. Inhibition of nitrogenase activity by NH+4 in Rhodospirillum rubrum. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):824–831. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.824-831.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittenbury R., McLee A. G. Rhodopseudomonas palustris and Rh. viridis--photosynthetic budding bacteria. Arch Mikrobiol. 1967;59(1):324–334. doi: 10.1007/BF00406346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoch D. C., Cantu M. Changes in the regulatory form of Rhodospirillum rubrum nitrogenase as influenced by nutritional and environmental factors. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jun;142(3):899–907. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.3.899-907.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoch D. C., Gotto J. W. Effect of light intensity and inhibitors of nitrogen assimilation on NH4+ inhibition of nitrogenase activity in Rhodospirillum rubrum and Anabaena sp. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):800–806. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.800-806.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zumft W. G., Castillo F. Regulatory properties of the nitrogenase from Rhodopseudomonas palustris. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Apr 27;117(1):53–60. doi: 10.1007/BF00689351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


