Abstract
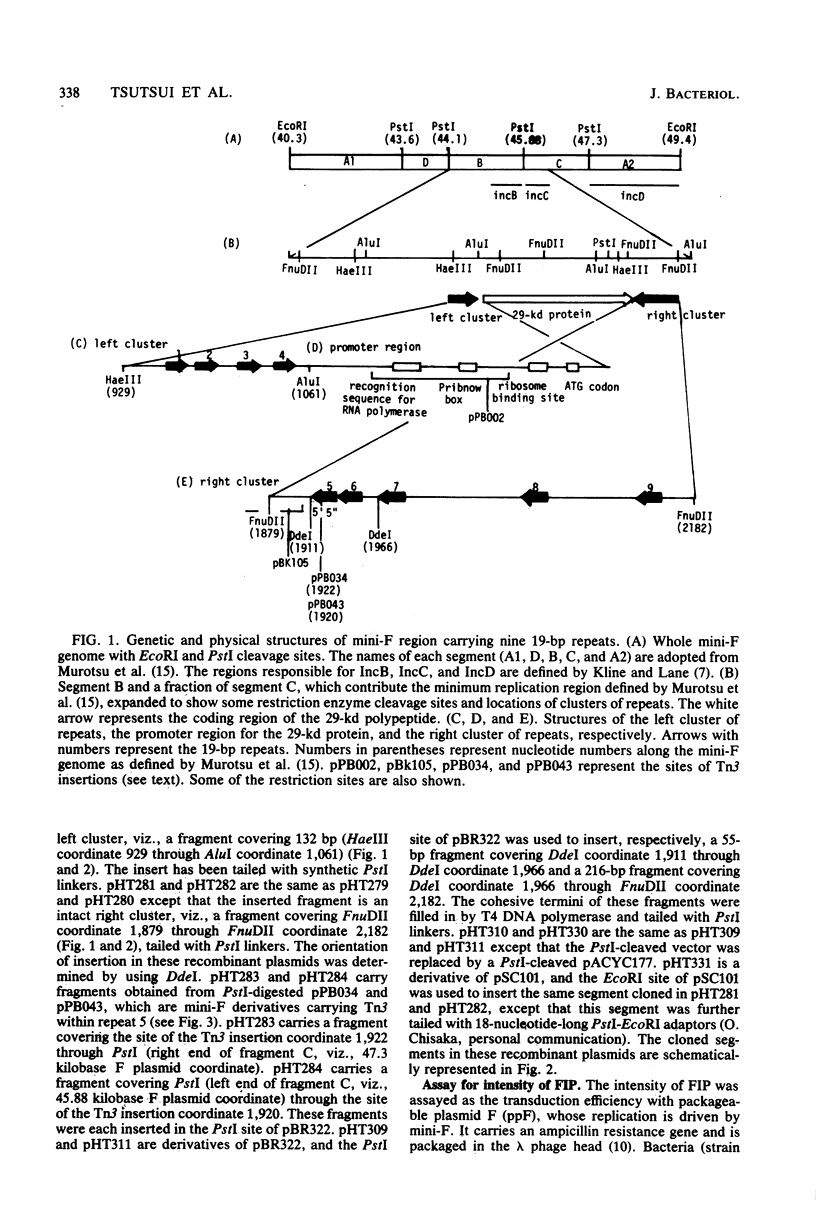
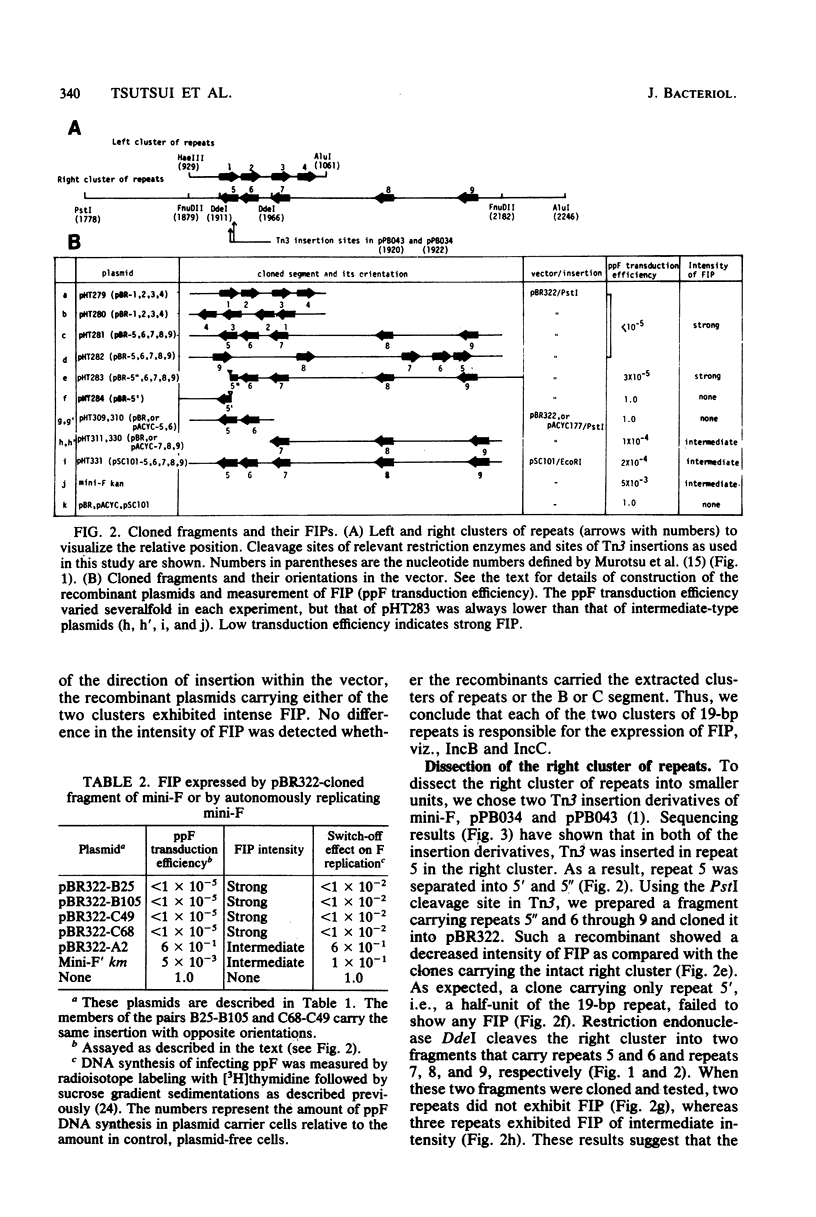
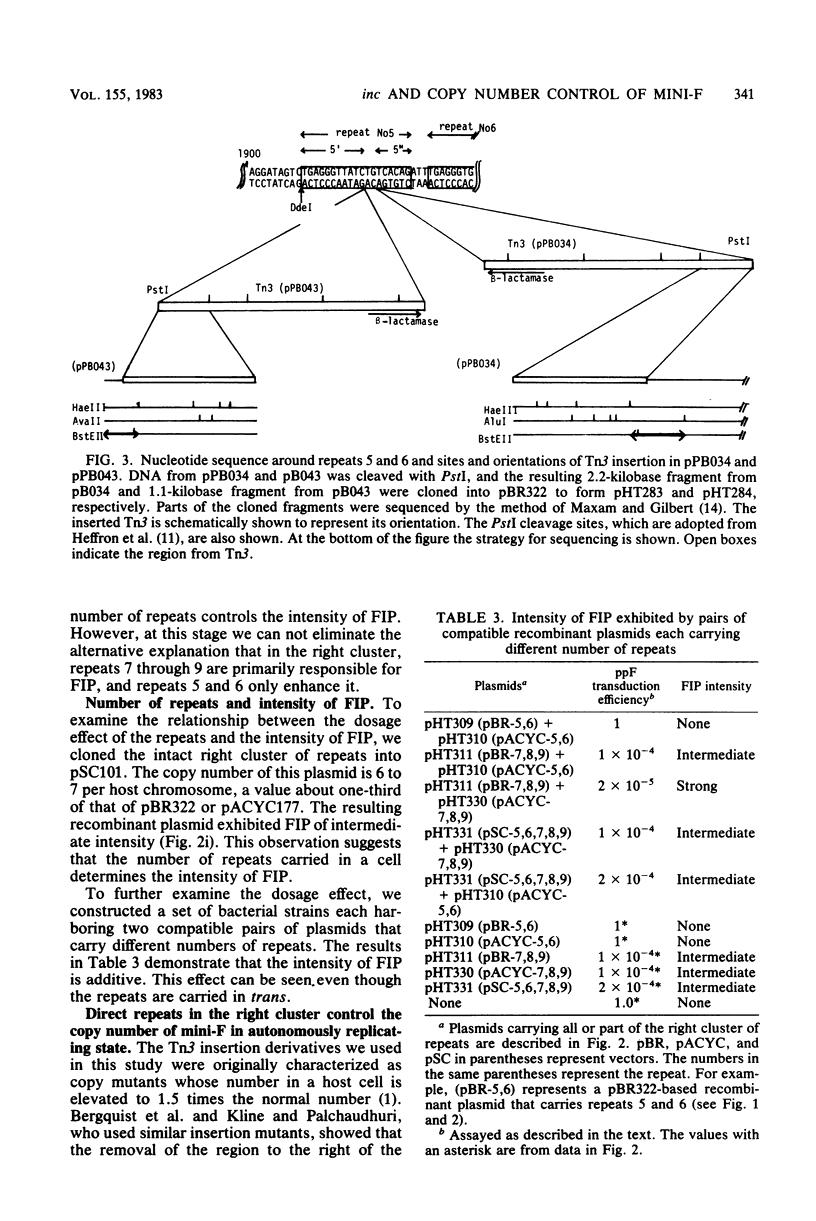
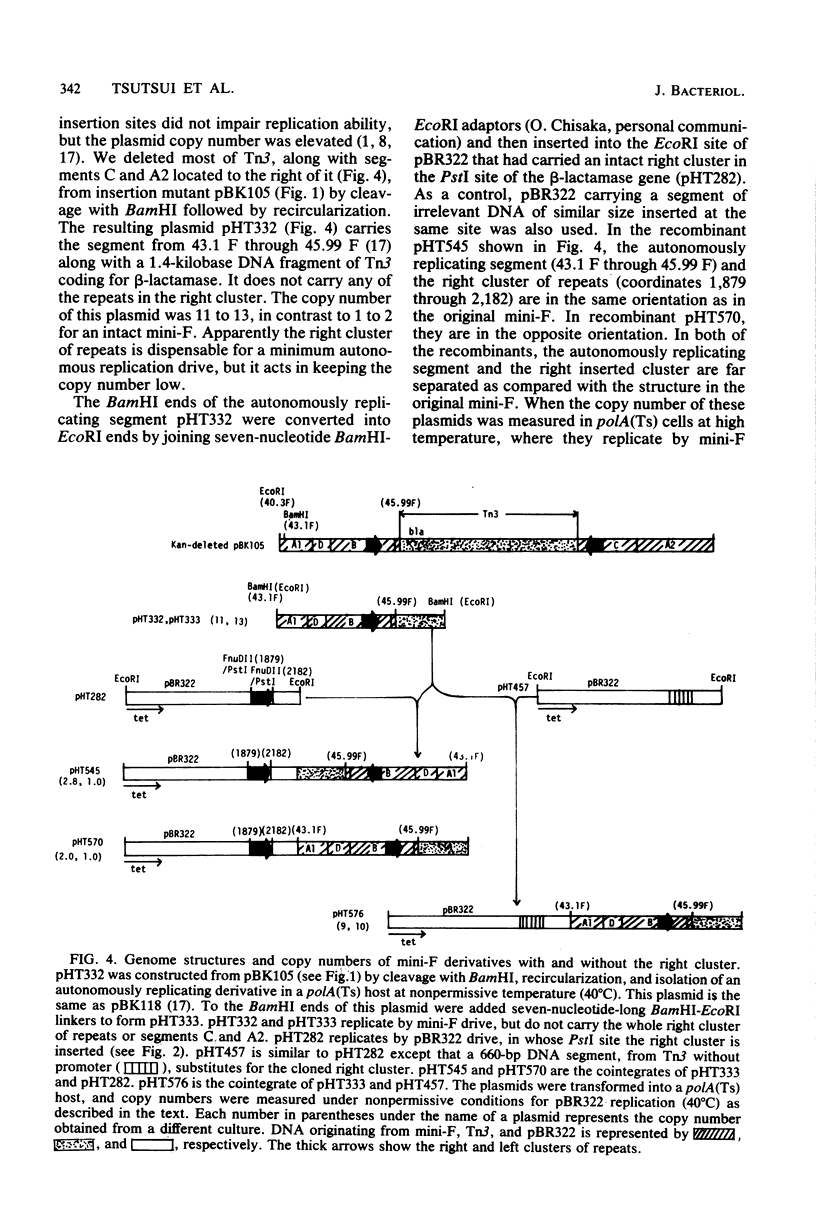
An autonomously replicating 2,248-base-pair DNA segment of the mini-F plasmid carries nine 19-base-pair repeating sequences. Five of the repeats are arranged in one direction and form the right cluster, whereas the remaining four repeats are arranged in the opposite direction and form the left cluster (Murotsu et al., Gene 15:257-271, 1981). Each cluster, cloned separately into the multicopy plasmid vector pBR322, exhibited a strong F-specific incompatibility phenotype (FIP). These clusters were thought to be responsible for the expression of IncB and IncC phenotypes, causing a switchoff function on mini-F replication. Mini-F DNA fragments containing two, three, or more than four repeats were inserted into pBR322. Cells carrying these recombinant plasmids exhibited, respectively, no, intermediate, and strong FIP intensity. Cloning of five repeats into pSC101, whose copy number is about 6 in contrast to 20 for pBR322, resulted in an FIP of intermediate intensity. Thus, the intensity of FIP reflects the dosage of repeats in a cell. The five repeats in the right cluster were eliminated from the mini-F derivative without impairing its autonomous-replicating ability (Bergquist et al., J. Bacteriol. 147:888-889, 1981; Kline and Palchavdhuri, Plasmid 4:281-289). Such deletion, however, caused a sixfold elevation of the copy number. When the eliminated cluster of repeats was reinserted in the derivative, the copy number was lowered to the original value, viz., 1 to 2. The position and orientation of this insertion was not important in the copy number control. Thus, the repeats are also related to copy number control. A model to account for the role of the repeating sequences in the control of copy number and FIP is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergquist P. L., Downard R. A., Caughey P. A., Gardner R. C., Lane H. E. Analysis of mini-F plasmid replication by transposition mutagenesis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):888–899. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.888-899.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C. Recircularization and autonomous replication of a sheared R-factor DNA segment in Escherichia coli transformants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1293–1297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa Y., Matsubara K. Construction and some properties of packageable plasmid F. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 16;169(1):107–112. doi: 10.1007/BF00267551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffron F., McCarthy B. J., Ohtsubo H., Ohtsubo E. DNA sequence analysis of the transposon Tn3: three genes and three sites involved in transposition of Tn3. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1153–1163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90228-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsbury D. T., Helinski D. R. Temperature-sensitive mutants for the replication of plasmids in Escherichia coli: requirement for deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase I in the replication of the plasmid ColE 1 . J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1116–1124. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1116-1124.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline B. C. Incompatibility between Flac, R386, and F:pSC101 recombinant plasmids: the specificity of F incompatibility genes. Plasmid. 1979 Jul;2(3):437–445. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90027-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline B. C., Lane D. A proposed system for nomenclature for incompatibility genes of the Escherichia coli sex factor, plasmid F. Plasmid. 1980 Sep;4(2):231–232. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(80)90013-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline B. C., Palchaudhuri S. Genetic studies of F plasmid maintenance genes. Plasmid. 1980 Nov;4(3):281–291. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(80)90067-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komai N., Nishizawa T., Hayakawa Y., Murotsu T., Matsubara K. Detection and mapping of six miniF-encoded proteins by cloning analysis of dissected miniF segments. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(2):193–203. doi: 10.1007/BF00331850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett M. A., Helinski D. R. Method for the isolation of the replication region of a bacterial replicon: construction of a mini-F'kn plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;127(2):982–987. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.2.982-987.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara K. Genetic structure and regulation of a replicon of plasmid lambdadv. J Mol Biol. 1976 Apr 15;102(3):427–439. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90325-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murotsu T., Matsubara K., Sugisaki H., Takanami M. Nine unique repeating sequences in a region essential for replication and incompatibility of the mini-F plasmid. Gene. 1981 Nov;15(2-3):257–271. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Jeffrey A., Johnson A. D., Maurer R., Meyer B. J., Pabo C. O., Roberts T. M., Sauer R. T. How the lambda repressor and cro work. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90383-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelke R. W., Kline B. C., Trawick J. D., Ritts G. D. Genetic studies of F plasmid maintenance genes involved in copy number control, incompatability, and partitioning. Plasmid. 1982 Mar;7(2):163–179. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90075-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skurray R. A., Guyer M. S., Timmis K., Cabello F., Cohen S. N., Davidson N., Clark A. J. Replication region fragments cloned from Flac+ are identical to EcoRI fragment f5 of F. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1571–1575. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1571-1575.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalker D. M., Kolter R., Helinski D. R. Nucleotide sequence of the region of an origin of replication of the antibiotic resistance plasmid R6K. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1150–1154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalker D. M., Thomas C. M., Helinski D. R. Nucleotide sequence of the region of the origin of replication of the broad host range plasmid RK2. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;181(1):8–12. doi: 10.1007/BF00338997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmis K., Cabello F., Cohen S. N. Cloning, isolation, and characterization of replication regions of complex plasmid genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2242–2246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolun A., Helinski D. R. Direct repeats of the F plasmid incC region express F incompatibility. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):687–694. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsutsui H., Matsubara K. Replication control and switch-off function as observed with a mini-F factor plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1981 Aug;147(2):509–516. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.2.509-516.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


