Abstract
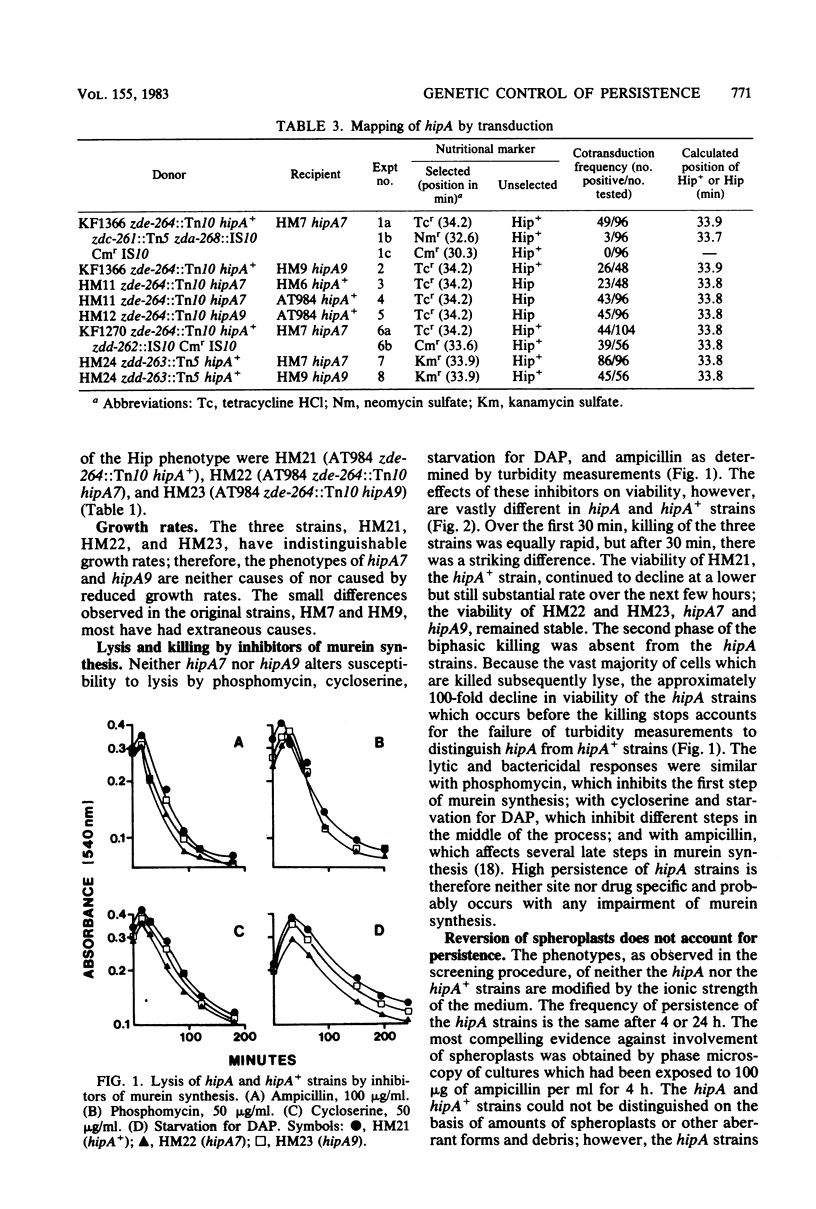
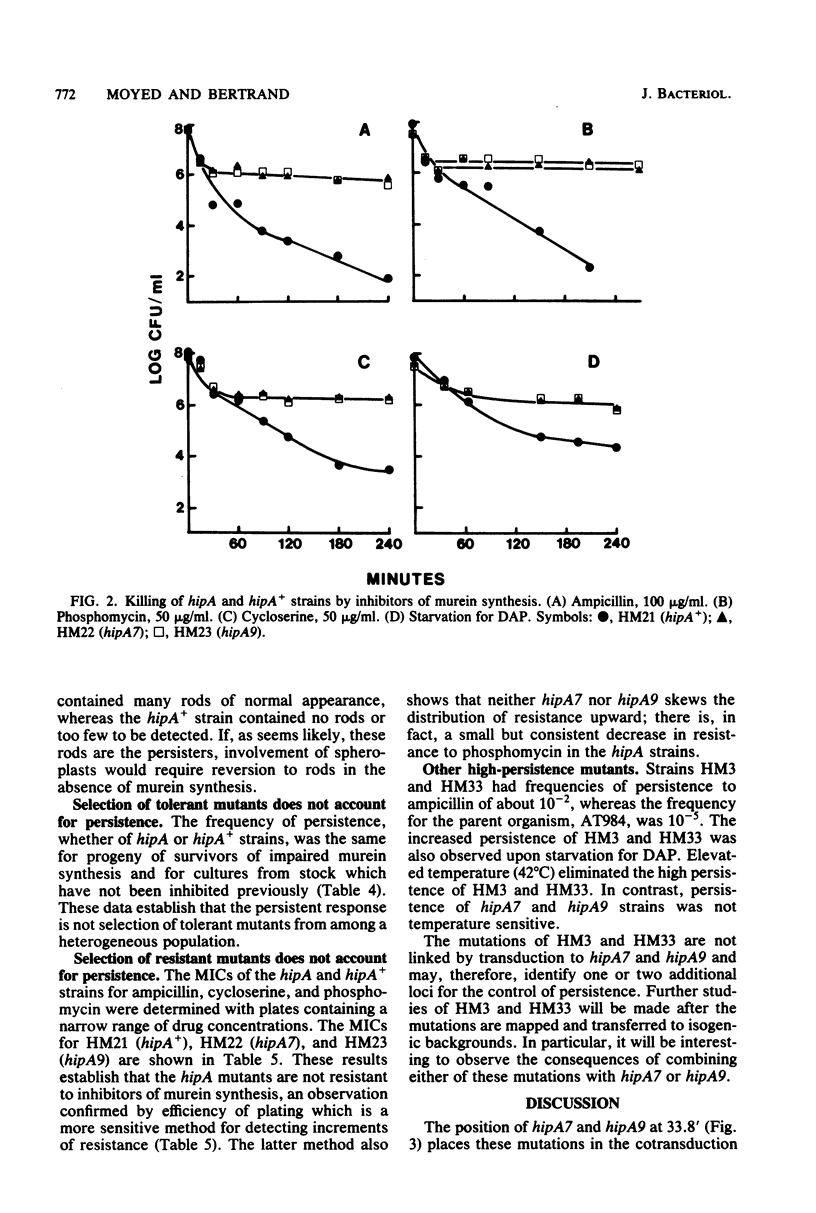
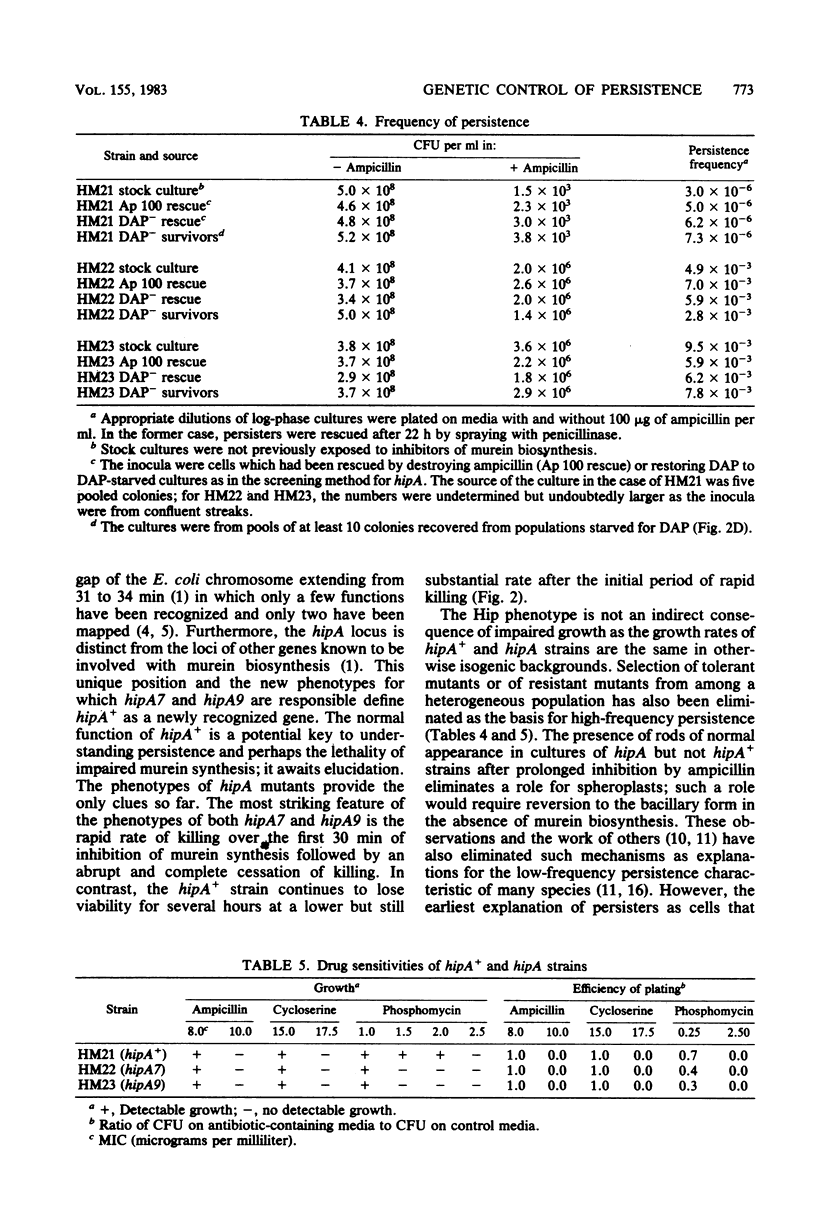
Except for a small fraction of persisters, 10(-6) to 10(-5), Escherichia coli K-12 is killed by prolonged inhibition of murein synthesis. The progeny of persisters are neither more resistant to inhibition of murein synthesis nor more likely to persist than normal cells. Mutants have been isolated in which a larger fraction, 10(-2), persists. The persistent response of the mutants, Hip (high persistence), is to inhibition of murein synthesis at early or late steps by antibiotics (phosphomycin, cycloserine, and ampicillin) or by metabolic block (starvation for diaminopimelic acid). Killing of the parent strain by each of the four inhibitors has two phases: The first is rapid and lasts about 30 min; the second is slower, but still substantial, and lasts 3 to 4 h. The first phase also occurs in the Hip mutants, but then viability of the mutants remains constant after about 30 min. Neither tolerance, resistance, impaired growth, nor reversion of spheroplasts accounts for high-frequency persistence. Two of the mutations map at 33.8 min in a region containing few other recognized functions. This position and the phenotypes define hipA as a newly recognized gene. Transposons Tn5 and Tn10 have been inserted close to hipA making it possible to explore the molecular genetics of persistence, a long recognized but poorly understood phenomenon.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J., Low K. B. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 6. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Mar;44(1):1–56. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.1.1-56.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck B. D., Park J. T. Activity of three murein hydrolases during the cell division cycle of Escherichia coli K-12 as measured in toluene-treated cells. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1250–1260. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1250-1260.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitner R. M., Kuempel P. L. P1 transduction mapping of the trg locus in rac+ and rac strains of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):529–533. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.529-533.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouché J. P., Gélugne J. P., Louarn J., Louarn J. M., Kaiser K. Relationships between the physical and genetic maps of a 470 x 10(3) base-pair region around the terminus of Escherichia coli K12 DNA replication. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jan 5;154(1):21–32. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90414-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukhari A. I., Taylor A. L. Genetic analysis of diaminopimelic acid- and lysine-requiring mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):844–854. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.844-854.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdett I. D., Murray R. G. Electron microscope study of septum formation in Escherichia coli strains B and B-r during synchronous growth. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):1039–1056. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.1039-1056.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott T. S., Greenwood D., Rodgers F. G., O'Grady F. The response of Staphylococcus aureus to benzylpenicillin. Br J Exp Pathol. 1979 Feb;60(1):14–23. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood D. Mucopeptide hydrolases and bacterial "persisters". Lancet. 1972 Sep 2;2(7775):465–466. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91858-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood D., O'Grady F. Trimodal response of Escherichia coli and Proteus mirabilis to penicillins. Nature. 1970 Oct 31;228(5270):457–458. doi: 10.1038/228457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakenbeck R., Messer W. Activity of murein hydrolases in synchronized cultures of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1239–1244. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1239-1244.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann B., Messer W., Schwarz U. Regulation of polar cap formation in the life cycle of Escherichia coli. J Supramol Struct. 1972;1(1):29–37. doi: 10.1002/jss.400010105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederberg J. BACTERIAL PROTOPLASTS INDUCED BY PENICILLIN. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1956 Sep;42(9):574–577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.42.9.574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leduc M., Kasra R., van Heijenoort J. Induction and control of the autolytic system of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):26–34. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.26-34.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A., Albino A., Zanati E. Multiple antibiotic resistance in a bacterium with suppressed autolytic system. Nature. 1970 Jul 11;227(5254):138–140. doi: 10.1038/227138a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


