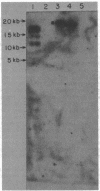
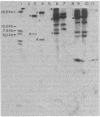
Abstract
The inactivation of a genetic determinant critical for streptolysin S production was accomplished by transfer and insertion of the transposon Tn916 into the DNA of a group A streptococcal strain. The group D strain CG110 was able to efficiently transfer Tn916 into the group A strain CS91 when donor and recipient cells were concentrated and incubated together on membrane filters. Among tetracycline-resistant transconjugants, nonhemolytic mutants that no longer produced streptolysin S and retained the capacity to produce streptolysin O were discovered. Hemolytic revertants from these mutants regained tetracycline sensitivity; other revertants still retained a tetracycline resistance phenotype. Hybridization studies employing Tn916 DNA located Tn916 sequences in EcoRI and HindIII fragments of DNA from mutants devoid of streptolysin S; one carried a single copy of Tn916, and the other two carried multiple copies of the transposon.
Full text
PDF


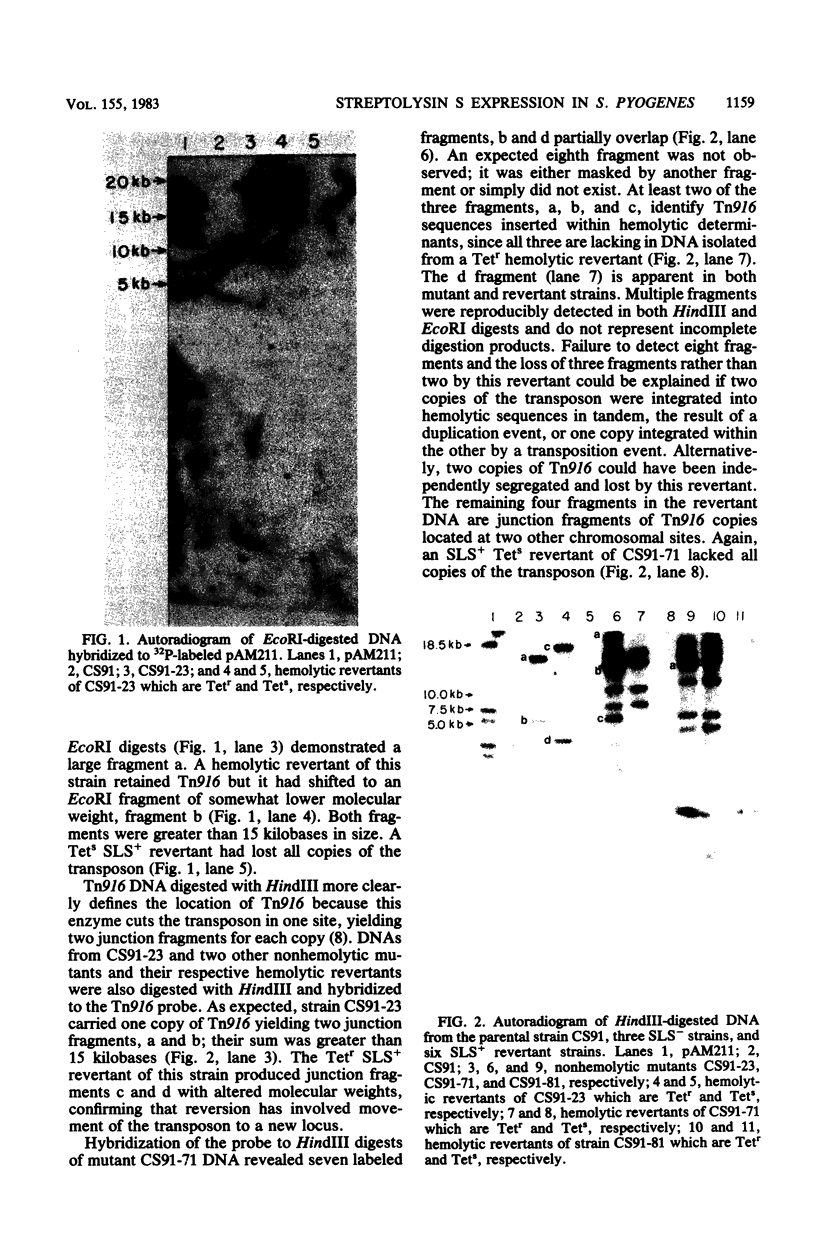


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alouf J. E., Raynaud M. Un Milieu simple pour la production de streptolysine O de titre élevé. Croissance et toxinogénèse sur ce milieu. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1965 Jun;108(6):759–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chassy B. M. A gentle method for the lysis of oral streptococci. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jan 26;68(2):603–608. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91188-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B. Plasmids, drug resistance, and gene transfer in the genus Streptococcus. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Sep;45(3):409–436. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.3.409-436.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke A. E., Clewell D. B. Evidence for a chromosome-borne resistance transposon (Tn916) in Streptococcus faecalis that is capable of "conjugal" transfer in the absence of a conjugative plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):494–502. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.494-502.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawron-Burke C., Clewell D. B. A transposon in Streptococcus faecalis with fertility properties. Nature. 1982 Nov 18;300(5889):281–284. doi: 10.1038/300281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James L., McFarland R. B. An epidemic of pharyngitis due to a nonhemolytic group A streptococcus at lowry air force base. N Engl J Med. 1971 Apr 8;284(14):750–752. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197104082841403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marker S. C., Gray E. D. Simple method for the preparation of streptococcal nucleases. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Feb;23(2):368–371. doi: 10.1128/am.23.2.368-371.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens W., Henley F., Barridge B. D. Hemolytic mutants of group A Streptococcus pyogenes. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Feb;7(2):153–157. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.2.153-157.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skjold S. A., Maxted W. R., Wannamaker L. W. Transduction of the genetic determinant for streptolysin S in group A streptococci. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):183–188. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.183-188.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannamaker L. W., Almquist S., Skjold S. Intergroup phage reactions and transduction between group C and group A streptococci. J Exp Med. 1973 Jun 1;137(6):1338–1353. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.6.1338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]