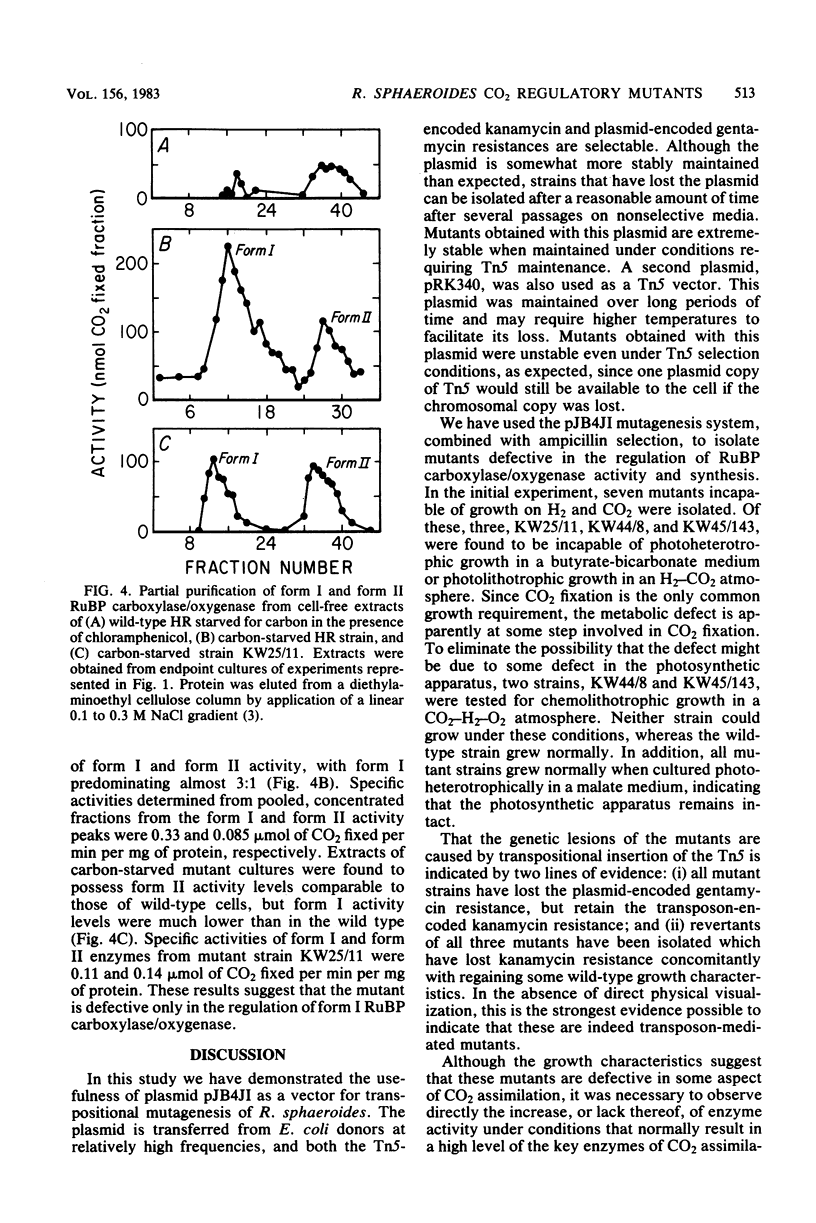
Abstract
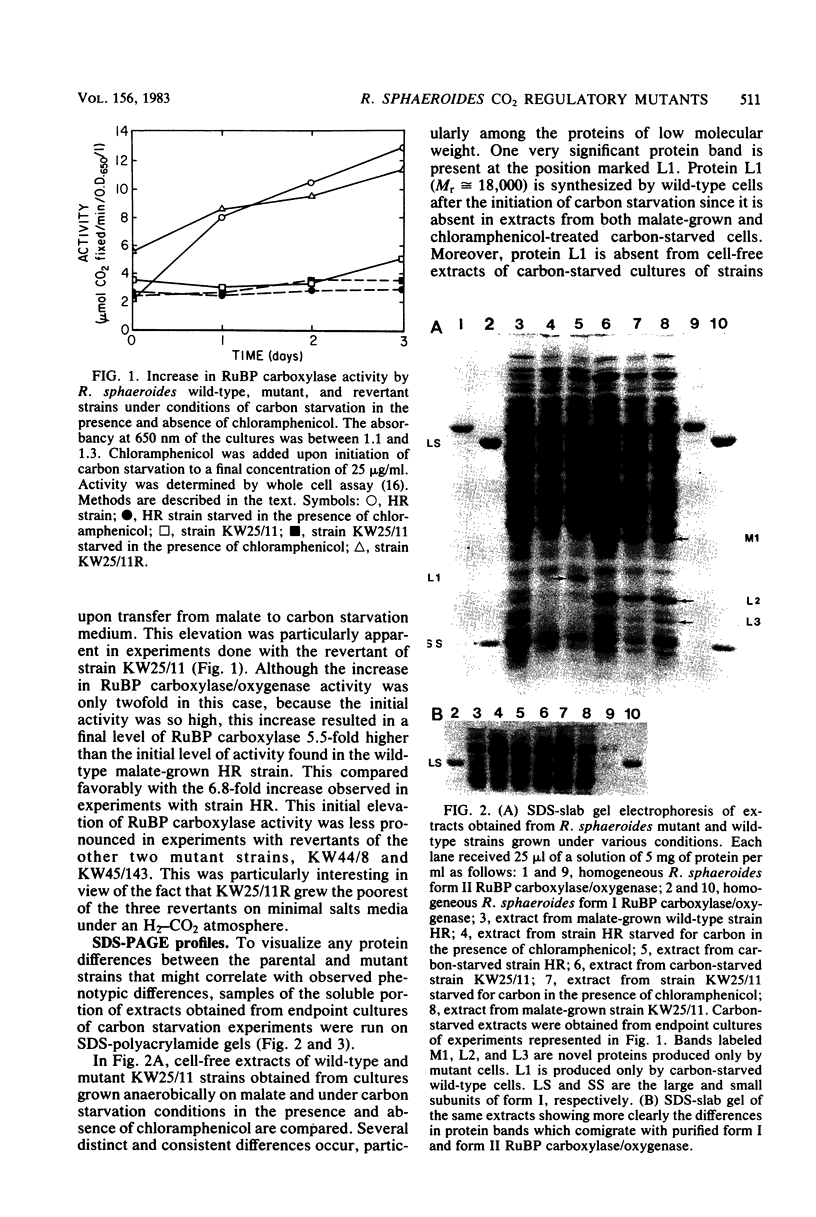
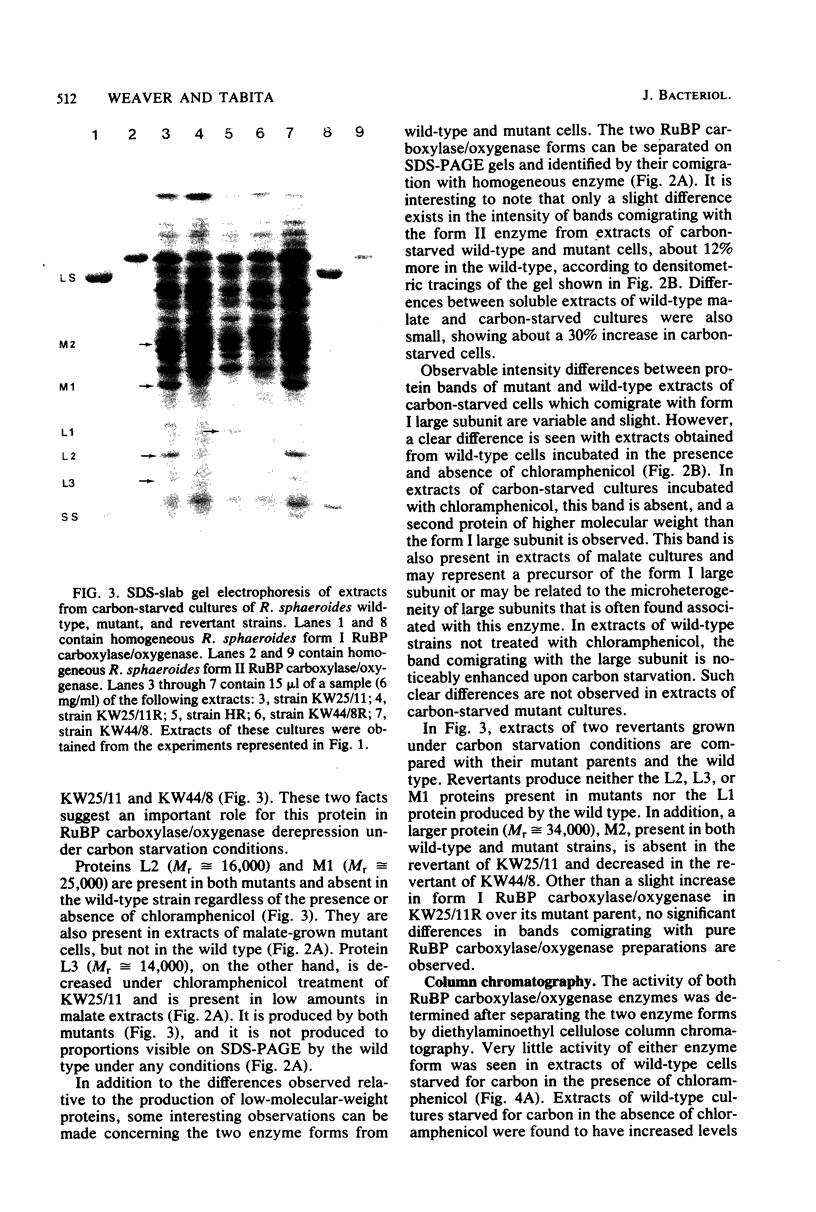
Several mutants of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides defective in the derepression of the enzyme ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase have been isolated by using the unstable Tn5 vectors pJB4JI and pRK340. Transpositional insertion mutants obtained with pJB4JI were demonstrated to be incapable of increasing ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase levels when grown on butyrate-bicarbonate medium or under conditions of carbon starvation, whereas the wild-type strain increased activity four- to eightfold. When the wild-type strain was starved for carbon in the presence of chloramphenicol, no derepression was observed. Crude extracts from mutant and wild-type strains had distinct and consistent differences in protein content as observed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Chromatographic evidence indicated that mutants were defective in the regulation of only one of the two forms of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase synthesized by R. sphaeroides.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson J. L., Tabita F. R. Activation of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides: probable role of the small subunit. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):1023–1027. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.1023-1027.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson J. L., Tabita F. R. Characterization of antiserum directed against form II ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Bacteriol. 1977 Sep;131(3):1020–1022. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.3.1020-1022.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson J. L., Tabita F. R. Different molecular forms of D-ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):943–949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madigan M. T., Gest H. Growth of the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodopseudomonas capsulata chemoautotrophically in darkness with H2 as the energy source. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):524–530. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.524-530.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden B. A. Autotrophic CO2 assimilation and the evolution of ribulose diphosphate carboxylase. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Sep;37(3):289–319. doi: 10.1128/br.37.3.289-319.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden B. A., Tabita F. R. D-ribulose-1, 5-diphosphate carboxylase and the evolution of autotrophy. Biosystems. 1974 Oct;6(2):93–112. doi: 10.1016/0303-2647(74)90002-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton I. L., Welch M. H., Hartman F. C. Evidence for essential lysyl residues in ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase by use of the affinity label 3-bromo-1,4-dihydroxy-2-butanone 1,4-bisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 25;250(20):8062–8068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORMEROD J. G., ORMEROD K. S., GEST H. Light-dependent utilization of organic compounds and photoproduction of molecular hydrogen by photosynthetic bacteria; relationships with nitrogen metabolism. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Sep;94:449–463. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90073-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarles L. S., Tabita F. R. Derepression of the synthesis of D-ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase from Rhodospirillum rubrum. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):458–464. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.458-464.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., Caruso P., Whitman W. Facile assay of enzymes unique to the Calvin cycle in intact cells, with special reference to ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. Anal Biochem. 1978 Feb;84(2):462–472. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., McFadden B. A. D-ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase from Rhodospirillum rubrum. I. Levels, purification, and effects of metallic ions. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3453–3458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., McFadden B. A. D-ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase from Rhodospirillum rubrum. II. Quaternary structure, composition, catalytic, and immunological properties. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3459–3464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]