Abstract
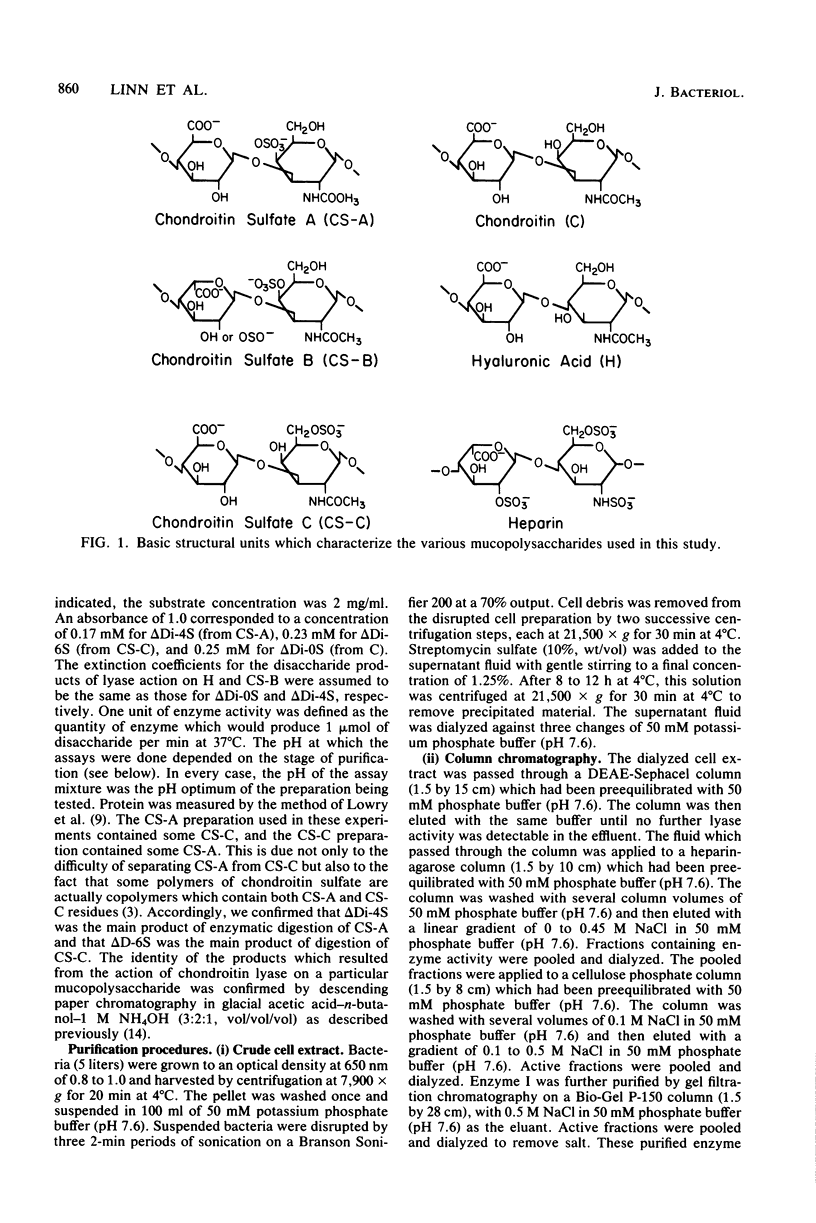
Two chondroitin lyases were isolated from the colon anaerobe Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. Both enzymes had similar molecular weights (104,000 and 108,000) and similar isoelectric points (8.0 and 7.9, respectively). Both enzymes were active against chondroitin sulfates A, B, and C and unsulfated polysaccharides, such as chondroitin and hyaluronic acid, although one of the enzymes was twice as active against chondroitin as the other enzyme. Both had similar Km values for chondroitin sulfates A and C (40 to 70 micrograms/ml) and for chondroitin (300 to 400 micrograms/ml). Neither enzyme could degrade the highly sulfated mucopolysaccharide heparin, but heparin was a potent inhibitor of the activity of both enzymes. Although enzymes I and II were similar in many respects, a comparison of peptides resulting from partial digestion with N-chlorosuccinimide or papain demonstrated that the two proteins are not related.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bickle T. A., Pirrotta V., Imber R. A simple, general procedure for purifying restriction endonucleases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2561–2572. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faltynek C. R., Silbert J. E. Copolymers of chondroitin 4-sulfate and chondroitin 6-sulfate in chick embryo epiphyses and other cartilage. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 10;253(21):7646–7649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuritza A. P., Salyers A. A. Digestion of proteoglycan by Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1180–1186. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1180-1186.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl U., Hök M. Glycosaminoglycans and their binding to biological macromolecules. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:385–417. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.002125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lischwe M. A., Ochs D. A new method for partial peptide mapping using N-chlorosuccinimide/urea and peptide silver staining in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Dec;127(2):453–457. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90203-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelacci Y. M., Dietrich C. P. Chondroitinase C from Flavobacterium heparinum. J Biol Chem. 1976 Feb 25;251(4):1154–1158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelacci Y. M., Dietrich C. P. Isolation and partial characterization of an induced chondroitinase B from Flavobacterium heparinum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Feb 27;56(4):973–980. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80284-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ototani N., Yosizawa Z. Purification of chondroitinase B and chondroitinase C using glycosaminoglycan-bound AH-Sepharose 4B. Carbohydr Res. 1979 May;70(2):295–306. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)87109-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salyers A. A., O'Brien M. Cellular location of enzymes involved in chondroitin sulfate breakdown by Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):772–780. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.772-780.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salyers A. A., Vercellotti J. R., West S. E., Wilkins T. D. Fermentation of mucin and plant polysaccharides by strains of Bacteroides from the human colon. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):319–322. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.319-322.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salyers A. A., West S. E., Vercellotti J. R., Wilkins T. D. Fermentation of mucins and plant polysaccharides by anaerobic bacteria from the human colon. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Nov;34(5):529–533. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.5.529-533.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva M. E., Dietrich C. P. Studies on the induction of heparin degrading enzymes in Flavobacterium heparinum. II. Structural requirements of the inducer. Biochimie. 1973;55(9):1101–1106. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(73)80449-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagata T., Saito H., Habuchi O., Suzuki S. Purification and properties of bacterial chondroitinases and chondrosulfatases. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 10;243(7):1523–1535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




