Abstract
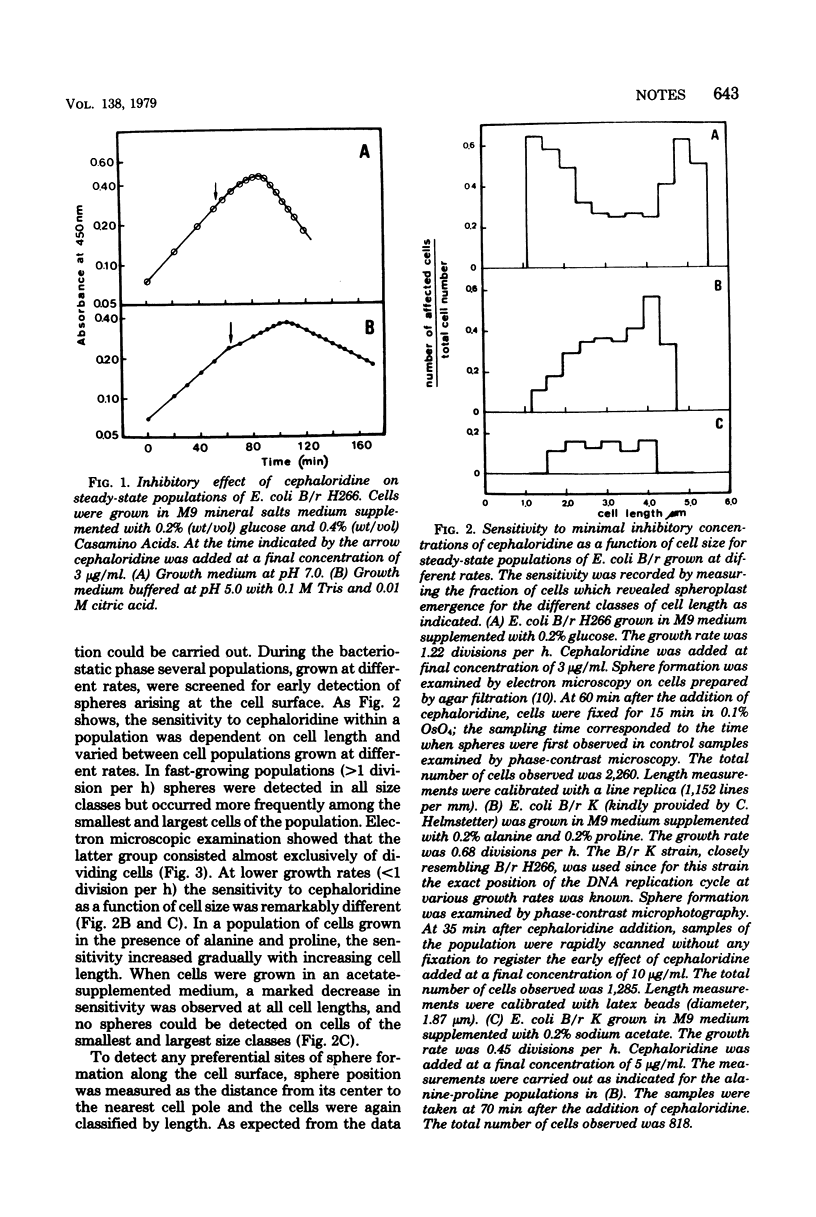
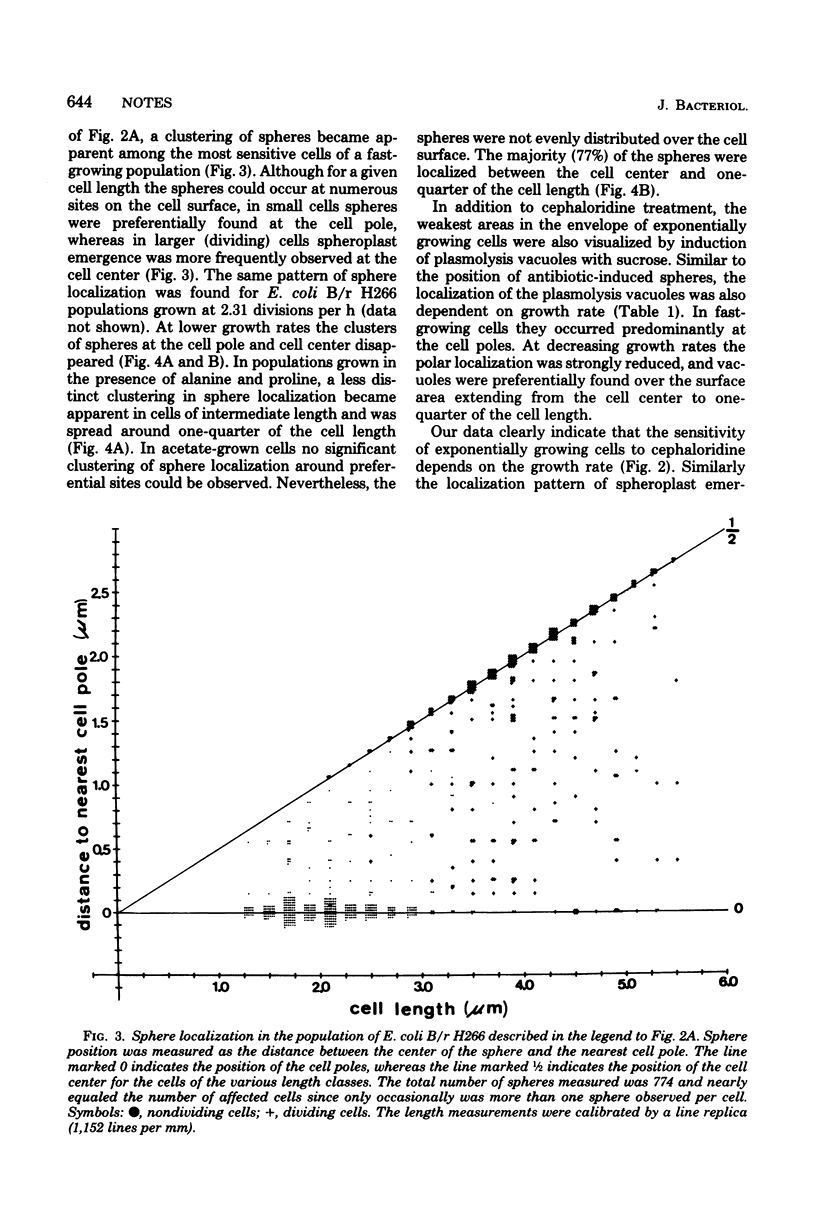
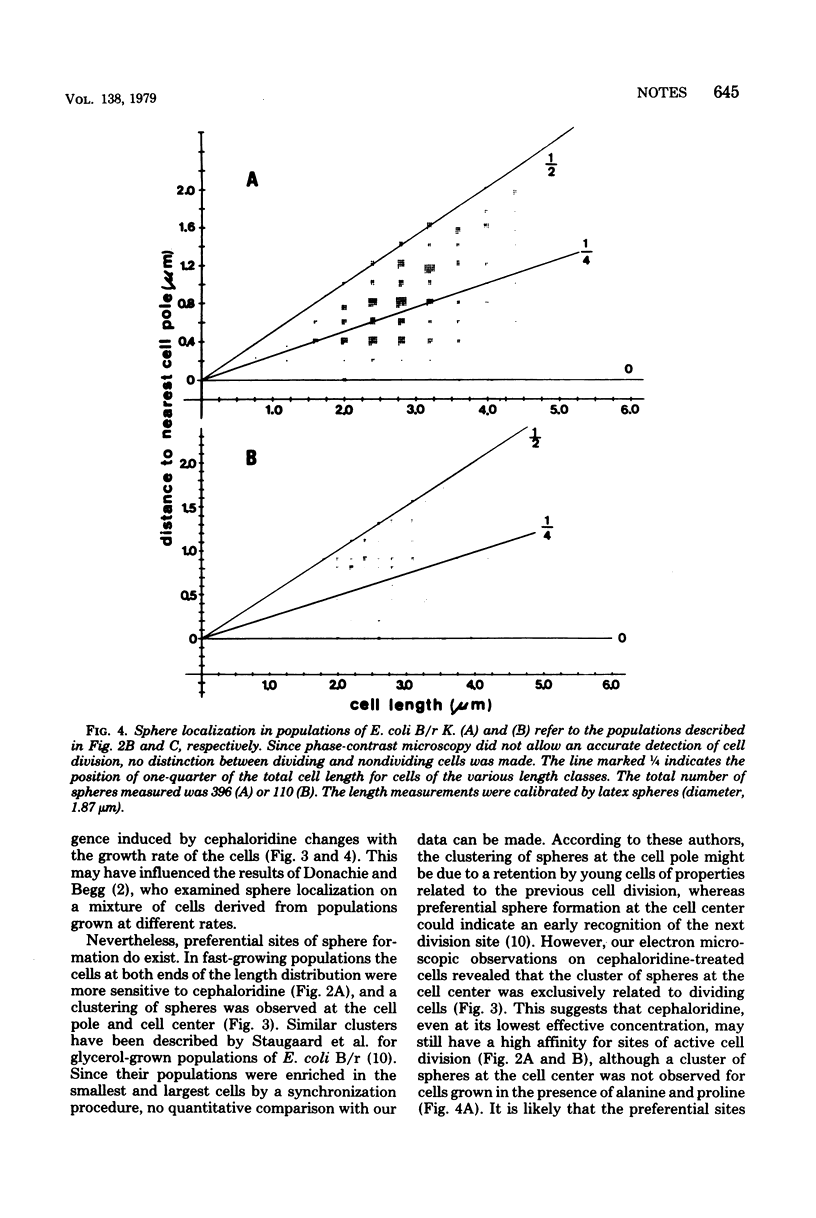
Steady-state populations of Escherichia coli B/r were treated with cephaloridine at minimal inhibitory concentrations. The antibiotic sensitivity of the cells and the localization of spheroplast emergence along the cell surface were examined as a function of cell length and growth rate. In fast-growing populations (greater than 1 division per h) the sites of cephaloridine interaction occurred preferentially at the cell pole in the smaller cells and at the cell center in dividing cells. At decreasing growth rates the cells became more resistant to cephaloridine, and a gradual shift from the cell pole toward the cell center was observed for the sphere position. A similar growth rate-dependent change in localization was found for sucrose-induced plasmolysis vacuoles.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Begg K. J., Doanachie W. D. Growth of the Escherichia coli cell surface. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1524–1536. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1524-1536.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donachie W. D., Begg K. J. Growth of the bacterial cell. Nature. 1970 Sep 19;227(5264):1220–1224. doi: 10.1038/2271220a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodell E. W., Lopez R., Tomasz A. Suppression of lytic effect of beta lactams on Escherichia coli and other bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3293–3297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D., Yashouv-Gan Y., Nuchamovitz Y., Rozenhak S., Ron E. Z. Murein biosynthesis during a synchromous cell cycle of Escherichia coli B. J Bacteriol. 1978 May;134(2):458–461. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.2.458-461.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryter A., Hirota Y., Schwarz U. Process of cellular division in Escherichia coli growth pattern of E. coli murein. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jun 25;78(1):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90437-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz U., Asmus A., Frank H. Autolytic enzymes and cell division of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):419–429. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90285-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz U., Ryter A., Rambach A., Hellio R., Hirota Y. Process of cellular division in Escherichia coli: differention of growth zones in the Sacculus. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 15;98(4):749–759. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80008-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Distinct penicillin binding proteins involved in the division, elongation, and shape of Escherichia coli K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2999–3003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Properties of the penicillin-binding proteins of Escherichia coli K12,. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jan;72(2):341–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staugaard P., van den Berg F. M., Woldringh C. L., Nanninga N. Localization of ampicillin-sensitive sites in Escherichia coli by electron microscopy. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1376–1381. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1376-1381.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Nishimura Y., Hirota Y. On the process of cellular division in Escherichia coli: a series of mutants of E. coli altered in the penicillin-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):664–668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woldringh C. L. Morphological analysis of nuclear separation and cell division during the life cycle of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jan;125(1):248–257. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.1.248-257.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


